Aerosol optical thickness
This post contains formulas! Aerosols play a great role in the atmospheric effects, aerosol optical thickness. Aerosols are particles suspended in the atmosphere, which can be of several types: sand or dust, soot from combustion, sulfates or sea salt, surrounded by water… Their size ranges between 0.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 04 December Aerosol optical depth AOD is one of essential atmosphere parameters for climate change assessment as well as for total ecological situation study. Atmospheric aerosol is the most common in natural conditions type of disperse system, consisting of solid and liquid particles, suspended in the atmosphere.
Aerosol optical thickness
They are provided on the NEO web site as 1-day measurements and 8-day and 1-month composites. There are many applications for aerosol optical thickness data: " 1 Atmospheric correction of remotely sensed surface features 2 Monitoring of sources and sinks of aerosols 3 Monitoring of volcanic eruptions and forest fire 4 Radiative Transfer Model 5 Air Quality 6 Health and Environment 7 Earth Radiation Budget 8 Climate Change" 1 "Aerosol particles are important to scientists because they represent an area of great uncertainty in their efforts to understand Earth's climate system. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. They can help clouds to form, or they can inhibit cloud formation. And if inhaled, aerosols can be harmful to people's health. This data can be used to teach or learn the following topics and skills in introductory Earth science:. The data range from measurements of 0 to measurements of 1. The Terra satellite began measuring this parameter in August These daily "data are produced at the spatial resolution of a The NEO interface makes it very easy to access data. From there, select the month of interest. For example, the data from two satellite images can be compared directly by plotting a transect plotting data along a path across an area of interest, creating a graph of data values along the transect. If a summary an average of the data in a particular area is desired, users can create polygon and the mean value within the polygon is then instantly calculated. Scatter plots and other 2- and 3-dimensional graphics are easily created.
Aerosol optical depth retrieval from visibility in China during —
Tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere are called aerosols. Windblown dust, sea salts, volcanic ash, smoke from wildfires, and pollution from factories are all examples of aerosols. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it. They can help clouds to form, or they can inhibit cloud formation. And if inhaled, some aerosols can be harmful to people's health. Satellite measurements of aerosols, called aerosol optical thickness, are based on the fact that the particles change the way the atmosphere reflects and absorbs visible and infrared light. An optical thickness of less than 0.
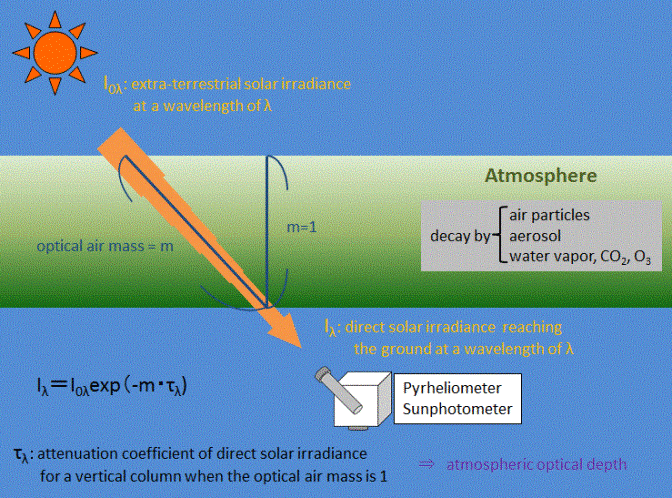
An aerosol optical depth product has been recently added. Aerosol optical depth is a measure of the extinction of the solar beam by dust and haze. In other words, particles in the atmosphere dust, smoke, pollution can block sunlight by absorbing or by scattering light. AOD tells us how much direct sunlight is prevented from reaching the ground by these aerosol particles. It is a dimensionless number that is related to the amount of aerosol in the vertical column of atmosphere over the observation location. A value of 0. An average aerosol optical depth for the U. The MFRSR infers the solar beam intensity by making successive global and diffuse measurements and computing their difference. In this way it simulates measurements of a sun photometer.
Aerosol optical thickness
Tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere are called aerosols. Windblown dust, sea salts, volcanic ash, smoke from wildfires, and pollution from factories are all examples of aerosols. Depending upon their size, type, and location, aerosols can either cool the surface, or warm it.
Danganronpa 2 trial 2
Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. This article has been updated. Northeast China is the northernmost region of the country, characterized by thick natural vegetation with dry cold winter and rainy warm summer. In chemistry , a closely related quantity called " absorbance " or "decadic absorbance" is used instead of optical depth: the common logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, that is the optical depth divided by ln Figure 3. Multi Temporal Method In most cases, the reflectance of the land surface changes slowly over time, while the aerosol optical properties vary rapidly from one day to another. Long-term — evolution and trend in Collection 5. Advanced search. If you know the type of aerosols in the atmosphere, it is possible to deduce the properties of aerosols in a spectral band from the optical properties in another spectral band. MODIS coupled with AERONET has enormous potential to ensure complex evaluation of global aerosol distribution, which may result in reduction of uncertainties with respect to quantitative role of aerosols and their impact on the territory. Aller au contenu How to estimate Aerosol Optical Thickness. Total Environ. Fuzzi, S. Effects of sources, transport, and postdepositional processes on levoglucosan records in southeastern Tibetan glaciers. Google Scholar.
The aerosol quantity determined by most instruments is the aerosol optical depth AOD. This is related to the amount of light aerosols scatter or absorb in a column through the atmosphere specifically, it is the vertically-integrated aerosol extinction , and is also sometimes referred to as aerosol optical thickness AOT. AOD depends on wavelength; a common reference wavelength reported by satellite data products is nm.
Other related links are sprinkled through out the datasheet. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Elevated aerosol amounts nestle at the foothills of the Himalaya Mountains in northern India in some months, and linger over eastern China for much of the year. Show All Maps. It is also efficient to detect medium signals, when suppressing high-frequency data variations 31 , 50 , Systematic review and meta-analysis of the adverse health effects of ambient PM2. At the end of winter and in spring there are frequent sandstorms in north western and northern parts of China, where under the action of air masses dust is carried to all regions of China, indicating that spring increases of AOD values occur predominantly due to dust events. This method is commonly used with time series data to smooth short-term fluctuations and identify main trends and cycles. This method works well in temperate and boreal zones, but not in arid areas where it is difficult to find the dense vegetation. Remote Sens. Close banner Close. In summer finer fraction aerosols prevail.

I congratulate, what necessary words..., a brilliant idea