Alnitak alnilam mintaka
The three bright blue stars — Alnitak, alnitak alnilam mintaka, Alnilam, and Mintaka — outline the belt in the constellation figure of the celestial Hunter. The asterism is easy to find because is part of one of the most prominent stellar patterns in the northern sky, the hourglass-shaped constellation figure of Orion. The asterism and the constellation dominate the evening sky from November to February. The color picture was composited from digitized black and white photographic plates recorded through alnitak alnilam mintaka and blue astronomical filters, with a computer synthesized green channel.
Alnitak is a triple star system in the constellation of Orion. The system is located at a distance of several hundred parsecs from the Sun and is one of the three main stars of Orion's Belt along with Alnilam and Mintaka. The stars are members of the Orion OB1 association and the Collinder 70 [ de ] association. Alnitak has been known since antiquity and, as a component of Orion's Belt , has been of widespread cultural significance. It was reported to be a double star by amateur German astronomer George K. Kunowsky in
Alnitak alnilam mintaka
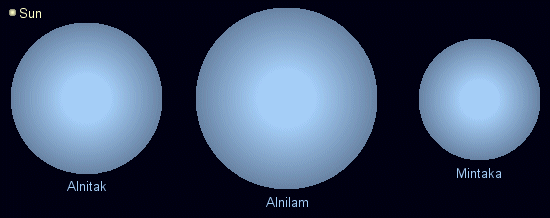
It consists of three bright stars. They are Alnitak , Alnilam and Mintaka. Looking for Orion's Belt is the easiest way to locate Orion in the night sky. The stars are more or less evenly spaced in a nearly straight line, and so can be visualized as the belt of the eponymous hunter 's clothing. The names of the three stars that comprise the Orion constellation come from Arabic. Alnitak B is a 4th-magnitude B-type star which orbits Alnitak A every 1, years. The primary Alnitak A is itself a close binary, comprising Alnitak Aa a blue supergiant of spectral type O9. Alnitak Aa is estimated to be up to 28 times as massive as the Sun and have a diameter 20 times greater. It is the brightest star of class O in the night sky. It is the 29th-brightest star in the sky and the fourth-brightest in Orion. It is , times more luminous than the Sun. Mintaka is 90, times more luminous than the Sun. Mintaka is a binary star. The two stars orbit around each other every 5.
The constellation disappears during the early southern hemisphere winter and reappears in the east just before dawn in August. Alnilam is around
The asterism consists of three bright stars Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. The asterism is sometimes more commonly known as the Three Kings or Three sisters. It is a direct reference to the biblical tale of the three kings who offered gifts to the baby Christ. This asterism, which is among the brightest and most prominent asterisms in the winter sky, is often used to find the Orion constellation. In Chinese mythology, they were known as The Weighing Beam.
It consists of three bright stars. They are Alnitak , Alnilam and Mintaka. Looking for Orion's Belt is the easiest way to locate Orion in the night sky. The stars are more or less evenly spaced in a nearly straight line, and so can be visualized as the belt of the eponymous hunter 's clothing. The names of the three stars that comprise the Orion constellation come from Arabic. Alnitak B is a 4th-magnitude B-type star which orbits Alnitak A every 1, years.
Alnitak alnilam mintaka
It lies at an approximate distance of 1, light years from Earth in the constellation Orion. Alnitak is the 5th brightest star in Orion and the 31st brightest star in the sky. It shares the 31s place with Alioth , the brightest star in Ursa Major. Zeta Orionis is a multiple star system with at least three components. Alnitak Aa, the primary star in the Zeta Orionis system, is a hot blue supergiant with the stellar classification O9. It is the brightest class O star in the sky. The star has a visual magnitude of 2. Alnitak Ab has the spectral classification of B1IV, indicating a blue subgiant star. It has an apparent magnitude of 4. It lies only 11 astronomical units from the primary star, which makes the pair a very close binary system.
David jeremiah sermons
It has a radius 7. The names of the three stars that comprise the Orion constellation come from Arabic. Alnilam is a supergiant at around 2. It is 3. Ancient Egyptians believed that the gods descended from Sirius and the Belt of Orion and instigated the human race. The star is a supernova candidate with a mass 24 times that of the Sun. It is While this theory is heavily disputed, the correspondence between the stars and the pyramids is quite remarkable. Some parts of their surfaces are contracting while others simultaneously expand. The Greeks associated the stars with the mythical hunter Orion. Alnitak Ab is around 14 times more massive than our sun. They orbit around each other once every 5.
Alnilam is the central star of Orion's Belt in the equatorial constellation of Orion. This is a massive, blue supergiant star some 2, light-years distant. It is estimated to be , times as luminous as the Sun , and
Retrieved The system is classified as an eclipsing binary star. The pyramids are believed to be 4, years old. Astronomy and Astrophysics. They were built in the 2 nd century B. Bibcode : ApJ It is estimated as being up to 33 times as massive as the Sun and a diameter 20 times greater. Alnitak Ab is a little older than its more massive companion, with an estimated age of 7. The closer companion, Delta Orionis Aa2, has a mass of 8. This star is much older than the primary star, at around 7. This asterism, which is among the brightest and most prominent asterisms in the winter sky, is often used to find the Orion constellation.

I think, that you are not right. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.