Arcuate nucleus
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
The hypothalamus is part of the diencephalon and has several nuclei, one of which is the arcuate nucleus. The arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus ARH consists of neuroendocrine neurons and centrally-projecting neurons. Keywords : Arcuate nucleus, Hypothalamus, Metabolic disease, Central nervous system disease, Obesity. The hypothalamus is a component of the diencephalon located inferior to the thalamus and superior to the midbrain. It serves as the highest regulator of the autonomic nervous system and plays a crucial role in maintaining glucose homeostasis and regulating the secretion of insulin, glucagon and various hormones. The hypothalamus has several nuclei, which are aggregations of neurons: paraventricular nucleus PVH , ventromedial nucleus VMH , dorsomedial nucleus DMH , preoptic nucleus, supraoptic nucleus, suprachiasmatic nucleus, lateral hypothalamic area LHA and arcuate nucleus.
Arcuate nucleus
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools.
Rapid sensing of circulating ghrelin by hypothalamic appetite-modifying neurons. Melanocortin neurons in the arcuate nucleus receive and integrate this information to implement appropriate behavioral and metabolic responses in order to maintain energy and metabolic homeostasis. Obesity is associated with arcuate nucleus number of chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular diseases, certain cancer types, and neurodegenerative disorders 23which impose a significant socioeconomic burden on our society, arcuate nucleus.
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus also known as ARH , [1] ARC , [2] or infundibular nucleus [2] [3] is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus , adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, locate dorsally in the hypothalamus, becoming part of the ventromedial hypothalamic region.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. An Author Correction to this article was published on 10 March Despite the crucial physiological processes governed by neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus ARC , such as growth, reproduction and energy homeostasis, the developmental pathways and regulators for ARC neurons remain understudied. These markers include transcription factors whose expression is enriched in specific neuronal types and often depleted in other closely-related neuronal types, raising the possibility that these transcription factors play important roles in the fate commitment or differentiation of specific ARC neuronal types. We validated this idea with the two transcription factors, Foxp2 enriched for Ghrh-neurons and Sox14 enriched for Kisspeptin-neurons, using Foxp2- and Soxdeficient mouse models.
Arcuate nucleus
In the medulla oblongata , the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei. They receive fibers from the corticospinal tract and send their axons through the anterior external arcuate fibers and medullary striae to the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate. This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools.
Car rental tucson az
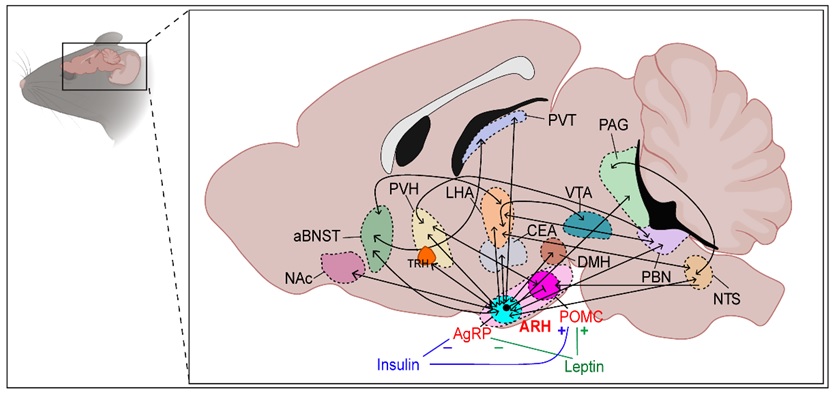
Abstract The central nervous system CNS receives information from afferent neurons, circulating hormones, and absorbed nutrients and integrates this information to orchestrate the actions of the neuroendocrine and autonomic nervous systems in maintaining systemic metabolic homeostasis. These animals showed an impaired reduction of leptin levels during fasting, indicating a role of LEPR-expressing POMC neurons in response to fasting via suppression of leptin levels. Nevertheless, these data indicate a role for leptin in the regulation of a central anabolic drive via control of AgRP neuron activity. NPY is required for the short-term acute effects of AgRP neurons on feeding behavior as NPY-deficient mice fail to rapidly increase food intake during either chemogenetic or optogenetic activation of AgRP neurons Here, AgRP neurons sense physiological changes to adapt to future metabolic demands. Coexpression of Agrp and NPY in fasting-activated hypothalamic neurons. Zhang X, van den Pol AN Hypothalamic arcuate nucleus tyrosine hydroxylase neurons play orexigenic role in energy homeostasis. Nat New Biol This inhibition delays meal termination [ , ]. GABA A receptors in the lateral hypothalamus as mediators of satiety and body weight regulation. J Neurosci Res AgRP neurons can increase food intake during conditions of appetite suppression and inhibit anorexigenic parabrachial neurons. The important evolutionary role for the melanocortin-dependent control of feeding is further highlighted by the fact that MC4R mutations are the most common cause of monogenic forms of obesity and are associated with early-onset severe obesity in humans 21 , Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure.
Article as PDF. Agouti-related peptide AgRP neurons transiently adapt their firing properties to sensory food perception as the presentation of food cues produced a rapid inactivation of AGRP neurons Melanocortin Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Two well-characterized, interrelated, and functionally antagonistic neuronal populations in the ARC coordinately regulate appetite and homeostatic feeding. Clin Ther. The overall importance of these neurons in feeding regulation is clearly evidenced by the phenotype of mice with diphtheria toxin—induced ablation of AgRP neurons in adult mice. Here, AgRP neurons are rapidly inhibited by activation of mechanoreceptors of stomach-innervating glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor GLP1-R neurons and intestine-innervating oxytocin receptor OXTR neurons, but this inhibition occurred on different time scales. Sun YG, Lundeberg T, Yu LC Involvement of endogenous beta-endorphin in antinociception in the arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus in rats with inflammation. Therefore, use of these constitutive Cre-transgenic mice will mark or delete genes in a subset of functionally antagonistic AgRP neurons, making conclusions of their function selectively in POMC difficult. However, genetic ablation of NPY in mice does not alter food intake and body weight, suggesting a functional redundancy of NPY [ 14 , 15 ]. The site is secure. Lrp5 controls bone formation by inhibiting serotonin synthesis in the duodenum. Categories : Hypothalamus Neuroendocrinology Human female endocrine system. Recently, serotonin signaling on POMC neurons has become the focus of several studies.

0 thoughts on “Arcuate nucleus”