At what depth below the surface of earth
Subterranean erosion in the Bieszczady Mountains is greater than expected say geomorphologists, soil scientists and geophysicists. It bothered me that these large forms had not been examined in detail by anyone.
Link to the lesson. You will discuss the interior structure of the Earth based on a scheme;. Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki. As a result of geological research, it was found that our planet consists of the following layers counting from the surface :. Mohorovičić ;. Earth's core — below the lower boundary of the mantle, i.
At what depth below the surface of earth
By University of Cambridge July 27, Credit: NASA. Their findings, published in Nature Communications , suggest that only about a third of the carbon recycled beneath volcanic chains returns to the surface via recycling, in contrast to previous theories that what goes down mostly comes back up. Scientists had thought that much of this carbon was then returned to the atmosphere as CO 2 via emissions from volcanoes. The work supports growing evidence that carbonate rocks, which have the same chemical makeup as chalk, become less calcium-rich and more magnesium-rich when channeled deeper into the mantle. Instead, the majority of the carbonate sinks deeper into the mantle where it may eventually become diamond. The findings are also important for understanding the role of carbonate formation in our climate system more generally. The team have been looking into the use of similar methods for carbon capture, which moves atmospheric CO 2 into storage in rocks and the oceans. Rosa, Remo N. Redfern, 14 July , Nature Communications. DOI: The evidence is very clear.. All geological features were formed in the One event, and have stayed that way ever since. A better way to put it is that your comment is void of science — we can see subduction zones and plate tectonics which has long since replaced the older hypothesis of continental drift — and it seems that is because you prefer to impress your suoerstitious neliefs on nature. The concept was independently and more fully developed by Alfred Wegener in , but his hypothesis was rejected by many for lack of any motive mechanism.
More on SciTechDaily. Date modified:
Identifies the local surface form of a polygon component. Descriptions define classes of local physical surface forms assemblage of slopes or recurring patterns of forms which occur at the earth's surface. When applied to consolidated materials, form refers to the product of their modification by geological processes. A very complex sequence of slopes extending from somewhat rounded concavities or swales of various sizes to irregular conical knolls or knobs and short discontinuous ridges; there is a general lack of concordance between knolls and swales. Examples are hummocky moraines and hummocky fluvioglacial landforms. A sloping, unidirectional surface with a generally constant slope unbroken by marked irregularity or gullies; a weakly developed dissected pattern provides external drainage for the local area. Examples are morainal plains and hill lands.
Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration gained by an object due to gravitational force. Acceleration due to gravity is represented by g. The standard value of g on the surface of the earth at sea level is 9. Gravity is the force with which the earth attracts a body towards its centre. Let us consider two bodies of masses, m a and m b.
At what depth below the surface of earth
Skip Content. How Deep is the Earth and What is at its Centre? The Earths diameter was estimated, with reasonable accuracy, as early as BC by a Greek named Eratosthenes. He based his calculation on the Suns shadows at two different places.
Best florist near me
Home Earth. The globalists are gas lighting you! The core is subdivided into an upper liquid layer down to a depth of about km and a central solid inner core with a radius of about km. Rosa, Remo N. First used in SLC 1. Set them in the correct order starting with the surface. Such a spontaneous reversal is impossible according to the laws of physics conservation of angular momentum. Z lewej strony jest podziałka z głębokością w kilometrach od zera na górze wykresu do sześciu tysięcy trzystu siedemdziesięciu na dole wykresu. A fen with a gently sloping, featureless surface. The surface is relatively flat, scored by a polygonal pattern of trenches that developed over ice wedges. S01 Stream swamp A swamp occurring along the banks of permanent or semipermanent streams. B13 Basin bog A bog situated in a basin with essentially closed drainage which receives water from precipitation and runoff from the immediate surroundings. Peat thickness is usually B20 Lowland polygon bog A bog with flat-topped or convex peat surfaces often referred to as 'high-centre polygons' separated by trenches over ice wedges that form a polygonal pattern when viewed from above. When applied to consolidated materials, form refers to the product of their modification by geological processes. Kartik July 28, at am Reply.
Magma is a molten and semi-molten rock mixture found under the surface of Earth.
It is a kind of underground erosion that involves washing soil particles by the water seeping below the surface. Changes in pressure and temperature along with increasing depth in the interior of the earth. The resulting subsidence changes water flow on the slope. A marsh occupying the contact zone between high and low water marks bordering semipermanent or permanent lakes. Mr Sharma said there was a sense among participants that the lived experience of climate change was bringing home to people the urgency of the situation. But substantial obstacles to achieving this goal remain, of which the rapid phasing out of coal is key. A swamp developed in a topographically defined basin where water derived locally may be augmented by drainage from other parts of the watershed. RoszY8amesU5h Nagranie słówka: core of the Earth. Suffosion is most often discussed in the context of loess areas or areas in semi-arid climates, while Bieszczady Mountains have brown soils that have not been considered susceptible to this process. The person whom the data concern has a right to access the data, correct and remove them, as well as limit their processing. Their findings, published in Nature Communications , suggest that only about a third of the carbon recycled beneath volcanic chains returns to the surface via recycling, in contrast to previous theories that what goes down mostly comes back up. Gradual collapse of the pipes leads to the formation of new valleys or extends existing ones. Slopes are generally M Rolling A very regular sequence of moderate slopes extending from rounded and, in some places, confined concave depressions to broad, rounded convexities producing a wavelike pattern of moderate relief.

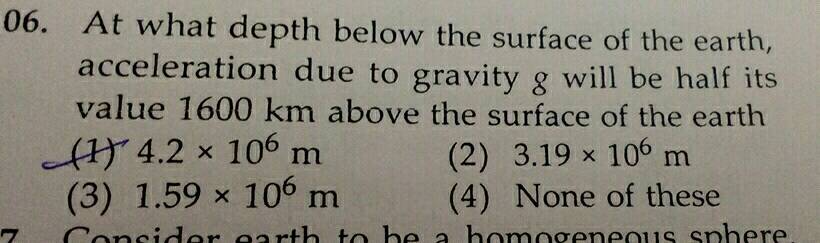
0 thoughts on “At what depth below the surface of earth”