B lewis structure
A Lewis Structure is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule, b lewis structure. It is used to show how the electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule.
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:. Lewis symbols can also be used to illustrate the formation of cations from atoms, as shown here for sodium and calcium:.
B lewis structure
Together the three resonance structures suggest partial double-bond character in the Be-X bond, which results in an intermediate bond length between a single and double bond. There are issues with each of these resonance structures. The structure in the middle is a mix of these problems. None of these situations is ideal according to Lewis theory. In contrast to BeF 2 , solid BeCl 2 is a 1-dimensional polymer consisting of edge-shared tetrahedral. In the gas phase, BeCl 2 exists as a dimer with two chlorine atoms bridging two Be atoms. In the dimer, the Be atoms are 3-coordinate. Bridging Cl atoms are two-coordinate, while terminal Cl atoms are one-coordinate. At higher temperatures in the vapor phase, the linear monomer also exists. The structure with only single bonds is the most common representation for this molecule because the charge separation shown in the other structures is considered to be unfavorable. The highly polarized B-F bond has a dipole moment that lies opposite to the indicated formal charges shown in the resonance structures with double bonds between boron and fluorine. The case is similar to structures of other boron trihalides as well. Boron trihalides are electron deficient at the boron center and react readily with Lewis bases.
Exceptions to the Octet Rule Many covalent molecules have central atoms that do not have eight electrons in their Lewis structures. Distribute the remaining electrons as lone b lewis structure on the terminal atoms except hydrogencompleting an octet around each atom.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot symbol or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used.
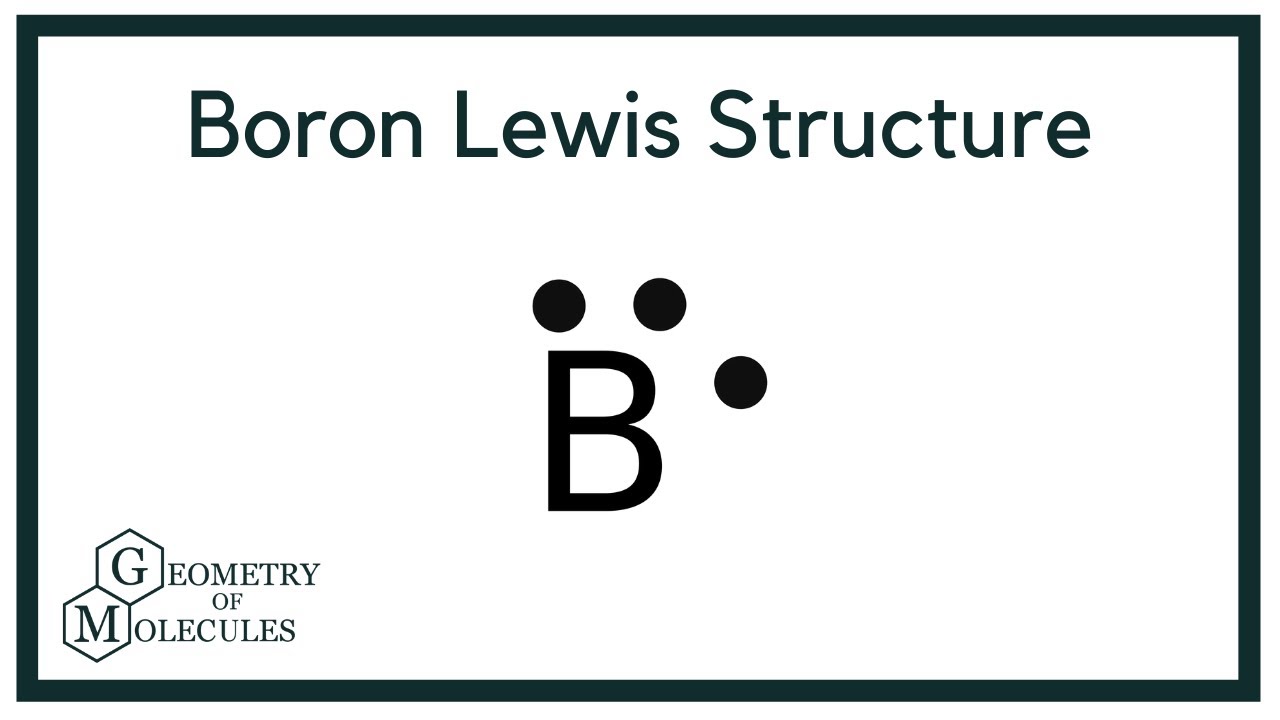
A Lewis structure is a way to show how atoms share electrons when they form a molecule. Lewis structures show all of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule. The valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell. For representative elements, the number of valence electrons equals the group number on the periodic table. To draw the Lewis structure of an atom, write the symbol of the atom and draw dots around it to represent the valence electrons.
B lewis structure
In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. In this section, we will explore the typical method for depicting valence shell electrons and chemical bonds, namely Lewis symbols and Lewis structures. We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. A Lewis symbol consists of an elemental symbol surrounded by one dot for each of its valence electrons:.
Fucium ore
A solid line indicating a bond between the two atoms connects the atoms to the central atom. Lewis Symbols We use Lewis symbols to describe valence electron configurations of atoms and monatomic ions. For anions, add one electron for each negative charge. Check Your Learning What is the Lewis electron dot symbol for each element? Where needed, distribute electrons to the terminal atoms:. Two of the valence electrons in the HCl molecule are shared, and the other six are located on the Cl atom as lone pairs of electrons. N 5 O x 3 18 charge 1 24 Draw a skeletal structure for the molecule which connects all atoms using only single bonds. The Lewis structure was named after Gilbert N. Write the Lewis structure for the diatomic molecule P 2 , an unstable form of phosphorus found in high-temperature phosphorus vapor. The resonance structure should not be interpreted to indicate that the molecule switches between forms, but that the molecule acts as the average of multiple forms. This can be achieved by sharing electrons to form covalent bonds or by transferring electrons to form ionic bonds. This allows each halogen atom to have a noble gas electron configuration. What are the Lewis structures of these two molecules? Remember that H is never a central atom:. Electrons in covalent bonds are split equally between the atoms involved in the bond.
We know that the formation of covalent bonds is achieved by an overlap of orbitals between two atoms that share a pair of valence electrons. The bonds are most often shown with either two dots or a line, and these representations are called Lewis symbols or Lewis structures. So the bonds can be represented either with a line or a pair of electrons two dots and therefore, we can say that Lewis structures are electron-dot representations for molecules.
For example, each atom of a group 14 element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. In general, the less electronegative elements are more likely to be central atoms. For more complicated molecules and molecular ions, it is helpful to follow the step-by-step procedure outlined here:. For anions, add one electron for each negative charge. Glossary double bond covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms free radical molecule that contains an odd number of electrons hypervalent molecule molecule containing at least one main group element that has more than eight electrons in its valence shell Lewis structure diagram showing lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons in a molecule or an ion Lewis symbol symbol for an element or monatomic ion that uses a dot to represent each valence electron in the element or ion lone pair two a pair of valence electrons that are not used to form a covalent bond octet rule guideline that states main group atoms will form structures in which eight valence electrons interact with each nucleus, counting bonding electrons as interacting with both atoms connected by the bond single bond bond in which a single pair of electrons is shared between two atoms triple bond bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. In the dimer, the Be atoms are 3-coordinate. To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH 3 ammonia. Is it necessary for the first dot around an atomic symbol to go on a particular side of the atomic symbol? In condensed structural formulas, many or even all of the covalent bonds may be left out, with subscripts indicating the number of identical groups attached to a particular atom. The valence electron configuration for selenium is 4 s 2 4 p 4. Methanol, H 3 COH, is used as the fuel in some race cars.

Logically
I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion.
It agree, very useful message