Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
In the heat, bbc bitesize cardiovascular system, blood vessels close to the surface of the skin enlarge. This process is called vasodilation close vasodilation The increase in diameter of the skin arterioles to increase blood flow and increase heat loss by radiation. This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface.
An explanation of how the cardiovascular system works during exercise. In the heat, blood vessels close to the surface of the skin enlarge. This process is called vasodilation close vasodilation The increase in diameter of the skin arterioles to increase blood flow and increase heat loss by radiation. This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. When a person takes part in exercise their face can become pink due to vasodilation of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface. In the cold, blood vessels at the skin's surface close. This process is called vasoconstriction close vasoconstriction The narrowing of the skin arterioles to reduce blood flow and reduce heat loss by radiation.
Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
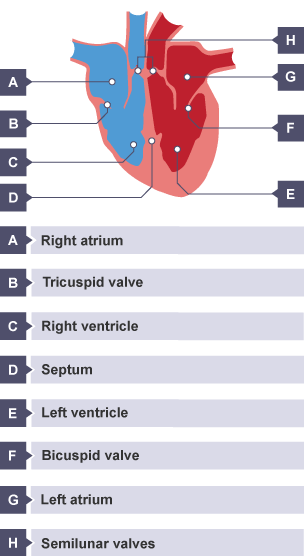
The right side pumps deoxygenated close deoxygenated Blood that is low in oxygen as cells have used it and high in carbon dioxide as cells have produced it. The left side pumps oxygenated close oxygenated Blood that is high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide. This unidirectional flow of blood through the heart shows that mammals have a double circulatory system. Ventricular walls are thicker than atrial walls because the ventricles have to pump blood further. The left ventricle wall is thicker than the right because it pumps blood around the body while the right pumps blood to the lungs, located close to the heart. The coronary arteries provide the heart muscle with the glucose and oxygen it needs for respiration close respiration The chemical change that takes place inside living cells, which uses glucose and oxygen to release the energy that organisms need to live. Carbon dioxide is a by-product of respiration. These are small blood vessels that branch off the aorta and can be seen on the external surface of the heart. In this guide. Components The blood vessels The heart The effects of exercise. The heart. The heart is a unidirectional pump. Valves are present to prevent the backflow of blood. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the vena cava. Blood moves into right ventricle.
In the cold, blood vessels at the skin's surface close. The heart's function is to pump the blood and circulate it round the body.
Arteries close arteries An elastic, muscular-walled vessel taking blood away from the heart. This means it is under high pressure close high pressure Gases and liquids are under high pressure when their volume has been reduced and so they exert a force against the structure surrounding them. The walls of arteries are made of thick muscle to withstand this pressure. This muscle is also elastic to allow a pulse of blood to travel along when your heart beats. Veins close veins A somewhat elastic, muscular-walled vessel taking blood towards the heart. This blood is under lower pressure close low pressure Gases and liquids are under low pressure when their volume has increased and so they exert less force against the structure surrounding them. The walls of veins are made of thinner muscle and are less elastic than arteries.
The first number is the systolic value and the second number is the diastolic value. Blood pressure is determined by Q cardiac output and the resistance to the blood flow R. Resistance to blood flow is caused both by the diameter of the blood vessels and by the thickness of the blood. Furthermore, if a person has a condition called atherosclerosis plaque in the arteries , their resistance to blood flow will increase and so will blood pressure. This can have serious health implications such as causing chronic high blood pressure, angina or even heart attack or stroke.
Bbc bitesize cardiovascular system
The heart is working hard to pump blood around the body. Well, the blood has to be kept moving around all the time because it's the body's delivery system. Every possible part of the body has to be supplied with oxygen and food and water, and the veins and arteries are like roads going all the way through your body with the blood cells like delivery vans. So it's a good job we've got the circulatory system to transport nutrients, water and oxygen to the entire body. Your heart is a very strong muscle which contracts gets smaller and relaxes to pump blood around your body. A heart beat varies from person to person - for an average person it beats times a minute. You feel this when you feel your pulse. Check out the muscular heart and its extraordinary pumps.
Bird chest tattoo
Photosynthesis and respiration in plants. Personalise your Bitesize! This allows more heat to be lost from the blood. This muscle is also elastic to allow a pulse of blood to travel along when your heart beats. Left-hand side. Next page. If you clench your hand into a fist, this is approximately the same size as your heart. The heart is working hard to pump blood around the body. Hepatic artery Carries oxygenated blood to the liver. Ventricular walls are thicker than atrial walls because the ventricles have to pump blood further. The circulatory system is the heart and all the blood vessels in the body which carry cells and substances to all its parts. A rteries carry oxygenated blood a way from the heart except for the pulmonary artery which carries deoxygenated blood away from the right ventricle to the lungs. Heart rate HR is the number of times the heart beats or the ventricles pump blood out in one minute. Blood vessel Hepatic portal vein Function Carries digested food from the small intestine to the liver. Next page.
If you clench your hand into a fist, this is approximately the same size as your heart.
In this guide. The pathway of blood through the heart. Personalise your Bitesize! Heart rate HR is the number of times the heart beats or the ventricles pump blood out in one minute. We assess the heart's performance by measuring how much blood it pumps out each minute. Heart rate. If you clench your hand into a fist, this is approximately the same size as your heart. Functions of the cardiovascular system. During exercise, tidal volume increases as the depth and rate of breathing both become greater. Thick muscular walls to withstand blood flowing at high pressure as it leaves the heart; the largest artery is the aorta. It has four chambers. Muscular system - Edexcel Skeletal system - Edexcel Respiratory system - Edexcel Aerobic and anaerobic exercise - Edexcel Long and short term effects of exercise - Edexcel Movement analysis in sport - Edexcel.

Your inquiry I answer - not a problem.
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.