Bbc bitesize plant cell
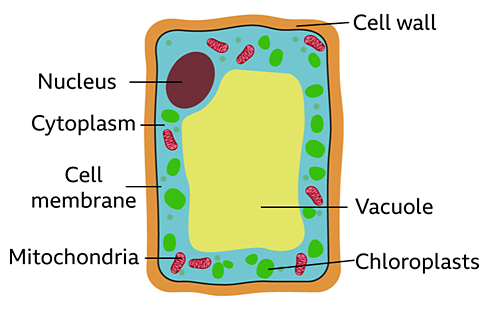
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope.
There are many different types of cells in animals. Each type is specialised for a particular role. These ensure that the organism functions as a whole. The head of the sperm contains the genetic material for fertilisation. The acrosome in the head contains enzymes so that the sperm can penetrate an egg. The middle piece is packed with mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Learn about specialised plant cells. Like animal cells, basic plant cells have a nucleus, a cell membrane and cytoplasm. They've also got a vacuole, chloroplasts and a cell wall, which are only found in plant cells and they can be a bit bigger than animal cells. Plants also have some very specialised cells. Root hair cells don't have light absorbing chloroplast because they don't absorb light because they're underground. What they do have is a wide surface area to more efficiently absorb water and minerals. Xylem cells lose their end walls so they can form continuous tubes almost like pipes to transport that water up to stems and leaves. Palisade or leaf cells live right beneath the surface of leaves. Which makes them very green and very good at photosynthesis and also very tasty. What are the three components of plant cells that are not found in animal cells?
More on Living organisms. Related links.
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. In this guide. Cell measurement Cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Investigating cells with a light microscope Microscopes The limits of the light microscope Animal cells Plant cells Measuring cell size Comparing sizes Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells. Plant cells. Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common.
Models in science are used to help us understand complicated ideas in a simple and memorable way. Place the neck of the balloon over a tap and fill it with water. There you go! You've now made your very own model of an animal cell. Cell membrane close cell membrane This surrounds the outside of animal cells and controls what can enter and exit it.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. The structure of the tissues is related to their functions in the plant. The palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf. The cells:. Spongy mesophyll close spongy mesophyll The plant tissue in a leaf which has loosely packed cells and air spaces between them to allow gas exchange.
Collective solutions job hiring
The four components of the blood. Test your knowledge. Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis. Plant and animal cells. Learn more about specialised animal and plant cells with Dr Alex Lathbridge. These are specialised cells close specialised cells Cells which have a particular adaptation to allow them to complete a specific function. The arrangement of these filaments causes the banded appearance of heart muscle and skeletal muscle. The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. What part of plant cells gives them their crunch? They therefore support the plant. Function Chloroplasts Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. Organelle that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances.
Contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis. Activity - Animal cell structure. It keeps the cell firm. Roots divide into smaller and smaller branches as they travel into the soil. Dr Alex Lathbridge breaks down the key facts about specialised animal and plant cells. The root hair cell has a large surface area to provide contact with soil water. Cell wall. The outside surface of roots are covered with root hair cells, which have tiny 'hairs' which poke into the soil. The root hair cell has a large surface area to provide contact with soil water. Or take a look around the website and start at our Home page. The middle piece is packed with mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg. Activity - Plant cell structure.

0 thoughts on “Bbc bitesize plant cell”