Chemosensors
Open access peer-reviewed chemosensors. Chemosensors for anions and cations detections have been extensively used in several disciplines, including pharmacology, chemosensors, environmental science, biology, and chemistry.
How to publish in this journal. The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, four quartiles. Q1 green comprises the quarter of the journals with the highest values, Q2 yellow the second highest values, Q3 orange the third highest values and Q4 red the lowest values. The SJR is a size-independent prestige indicator that ranks journals by their 'average prestige per article'. It is based on the idea that 'all citations are not created equal'.
Chemosensors
A molecular sensor or chemosensor is a molecular structure organic or inorganic complexes that is used for sensing of an analyte to produce a detectable change or a signal. The application of chemosensors is referred to as chemosensing, which is a form of molecular recognition. All chemosensors are designed to contain a signalling moiety and a recognition moiety , that is connected either directly to each other or through a some kind of connector or a spacer. Chemosensors may also be electrochemically based. Small molecule sensors are related to chemosensors. These are traditionally, however, considered as being structurally simple molecules and reflect the need to form chelating molecules for complexing ions in analytical chemistry. Chemosensors are synthetic analogues of biosensors , the difference being that biosensors incorporate biological receptors such as antibodies, aptamers or large biopolymers. Chemosensors describes molecule of synthetic origin that signal the presence of matter or energy. A chemosensor can be considered as type of an analytical device. Chemosensors are used in everyday life and have been applied to various areas such as in chemistry, biochemistry, immunology, physiology, etc.
Scientific Reports. Chemosensors advantages of fluorescence emission being 'switched on' from 'off' upon the recognition event enabling the chemosensors to be compared to 'beacons in the night', chemosensors.
.
Open access peer-reviewed chapter. Chemosensors for anions and cations detections have been extensively used in several disciplines, including pharmacology, environmental science, biology, and chemistry. This field which is a division of supramolecular chemistry has been known for more than years. It deals with chemosensors that recognize and detect anions and cations via optical or electrochemical signals. Today, a sustainable variety of chemosensors are established to detect both anions and cations.
Chemosensors
Fluorescent chemosensors for ions and neutral analytes have been widely applied in many diverse fields such as biology, physiology, pharmacology, and environmental sciences. The field of fluorescent chemosensors has been in existence for about years. Despite the progress made in this field, several problems and challenges still exist. This tutorial review introduces the history and provides a general overview of the development in the research of fluorescent sensors, often referred to as chemosensors. This will be achieved by highlighting some pioneering and representative works from about 40 groups in the world that have made substantial contributions to this field. The basic principles involved in the design of chemosensors for specific analytes, problems and challenges in the field as well as possible future research directions are covered. The application of chemosensors in various established and emerging biotechnologies, is very bright. Wu, A. Sedgwick, T.
Yemekli villa
Hence, the signal response is directly related to the magnitude of the sensing event and, in turn concentration of the analyte. Gupta A, Kumar N. A chemosensor can be considered as type of an analytical device. Samankumara Chemosensors were first used to describe the combination of a molecular recognition with some form of reporter so the presence of a guest can be observed also referred to as the analyte, c. One example is the grouped analysis of several tannic acids that accumulate in ageing Scotch whisky in oak barrels. Chemical Reviews. Chemosensors are synthetic analogues of biosensors , the difference being that biosensors incorporate biological receptors such as antibodies, aptamers or large biopolymers. Mark; Maguire, Glenn E. Small molecule sensors are related to chemosensors. Nimal; Gunnlaugsson, Thorfinnur; Nieuwenhuizen, Mark OCLC
A chemoreceptor , also known as chemosensor , is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance endogenous or induced to generate a biological signal. In bacteria , chemoreceptors are essential in the mediation of chemotaxis. Bacteria utilize complex long helical proteins as chemoreceptors, permitting signals to travel long distances across the cell's membrane.
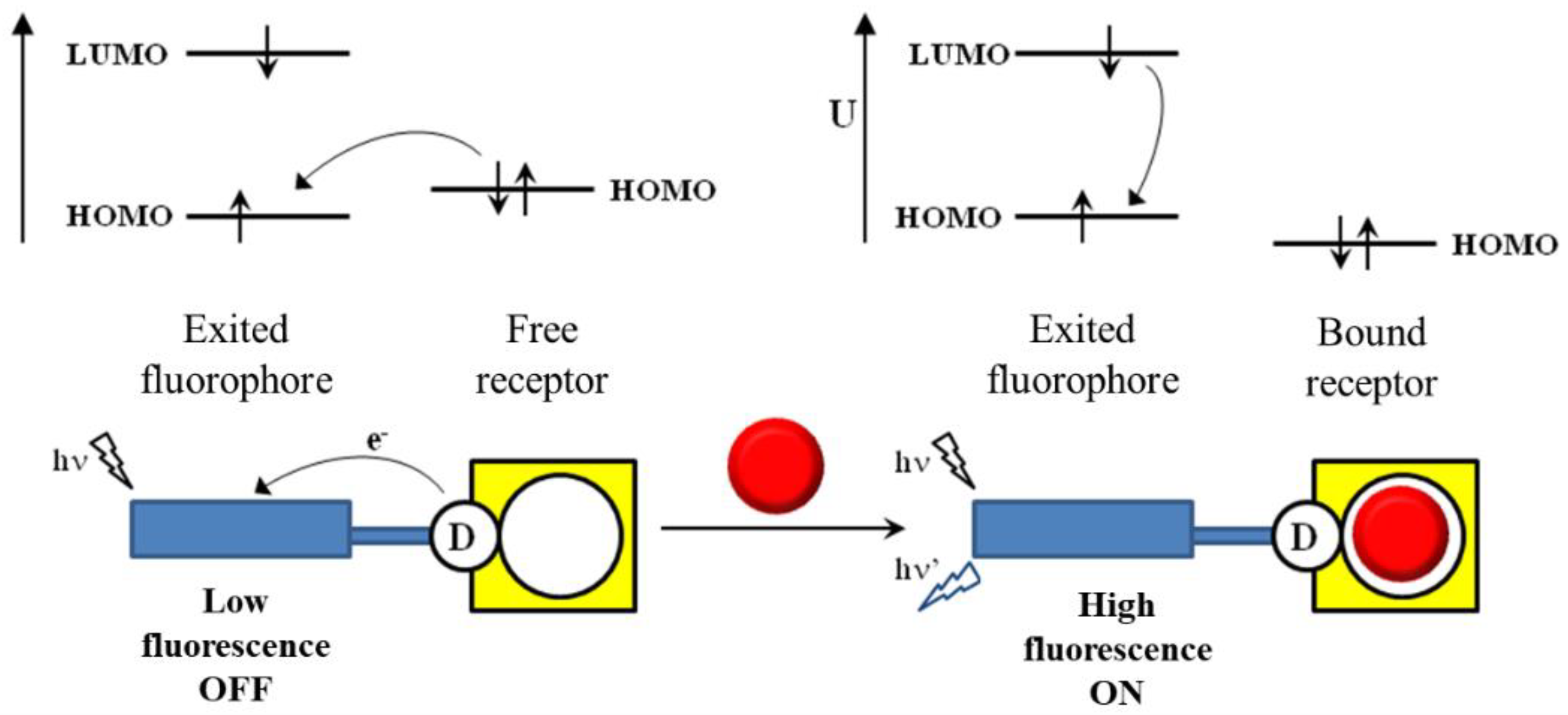
In contrast, in absorbance measurements, the concentration of the analyte and the absorbance are proportional, which is associated with the ratio between intensities measured before and after the beam passes through the sample. The basic design of the florescent chemosensors based on PET is a fluorophore- spacer- receptor. The photophysical properties can alter by binding a particular analyte to the receptor, leading to a fluorescence signal, with either an enhancement or quenching of fluorescence. In such systems, the sensing event is normally described as being due to changes in the photophysical properties of the chemosensor systems due to chelation induced enhanced fluorescence CHEF , [26] [27] [28] and photoinduced electron transfer PET , [29] [30] [31] mechanisms. The fluorescence quenching is due to a photo-induced electron transfer PET ; the normal state returns when a non-luminescent process follows the PET process [ 10 ]. Hence, the ESIPT process fits the design of fluorescent chemosensors that necessitates spectral shift for selective detection. A large number of examples of chemosensors have been developed by scientists in physical, life and environmental sciences. Such an effect has been demonstrated for the sensing of anions such as carboxylates and fluorides. The term supramolecular analytical chemistry has recently been coined to describe the application of molecular sensors to analytical chemistry. Journal of Fluorescence. Energy transfer cassettes based on organic fluorophores: Construction and applications in ratiometric sensing.

No, I cannot tell to you.