Davinci fhir
This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2.
The DaVinci Sandbox environment provides a fully automated continuous Deployment Pipeline for nearly any type of service to be deployed. As a developer:. Once we go through our checklist, below, the CD pipeline will automatically build and, when successful, deploy all changes pushed to your master branch. This is configurable. Once we're in contact, we have a number of manual configuration steps to setting up your project's CD pipeline. HL7 DaVinci.
Davinci fhir
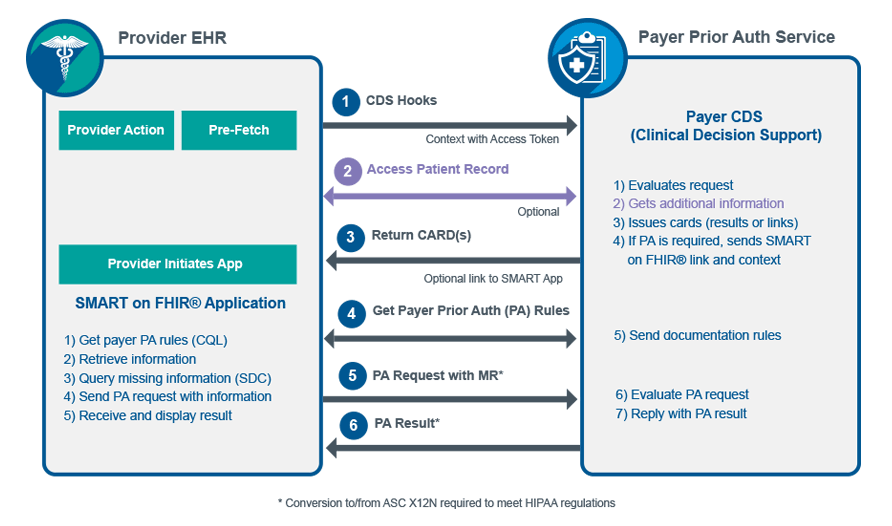
For example, the core specification describes the most common attributes of a patient resource type name, gender, date of birth and so forth. However, most real-world use cases need more than a single resource type. Generally, multiple profiles will be described together in an Implementation Guide — which will also include other material like the descriptive text, supported and required searches, security requirements, ValueSets and additional information. Da Vinci is a US project that brings together payers, providers and healthcare technology vendors, along with HL7 International. Such a move significantly increases the need for high quality and timely exchange of data between participants that do not typically share data easily. Selecting FHIR as the standard demonstrates the belief in those communities that FHIR has the maturity, acceptance and staying power that is needed to support this exchange. There are a number of use cases and Implementation Guides that are part of the overall Da Vinci project. Initially, 12 were identified — of which two were chosen to start with, and three more are in the active phases of development. As described above, value-based care is all about improving quality, and this requires concrete measures to be used. The first example shares information about a medication reconciliation which is performed for a patient by a healthcare provider after discharge from the hospital, and this needs to be completed within 30 days, so the attestation that this activity was performed is time sensitive. CRD refers to the need to understand what is needed by a payer to authorise payment for particular procedures — whether investigations or treatments. Because of this complexity, the CDS Hooks standard Implementation Guide streamlines the process to provide real-time advice. In summary:. All this occurs in real-time, so the clinician and patient can decide whether to proceed with the procedure or to look at alternatives. The next 3 Use Cases are new and related to the following diagram.
Page standards status: Informative.
This blog provides background on the project and previews the use cases that will be covered in the session. The Da Vinci Project is an HL7 FHIR accelerator of payers, providers and software vendors, implemented on the HL7 platform with the goal of advancing interoperability around value-based care and payment models—with a strong focus on payers. As of June , DaVinci had 18 use cases in development in the following areas:. Linda and Yan will focus on quality improvement use cases1. Data Exchange for Quality Measurement DEQM , which defines standard methods of exchanging data necessary to close gaps in care and reporting of quality measures2. Gaps-in-Care and Information, which defines standard implementations for communicating gaps in care.
This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2. See the Directory of published versions. Risk adjusted premium calculations are important to government managed care. The first Standard for Trial Use STU version of this implementation guide focused on the standard exchange format of risk adjustment coding gaps from payers to providers, it offers potential for reducing the administrative burden experienced by providers by standardizing the reporting they receive from all payers. This version of the implementation guide focuses on the communication from providers back to payers. It adds functionalities to support the workflow that allows providers and certified risk adjustment coders to review and remediate the risk adjustment coding gap reports provided by the payer. Providers and risk adjustment coders may close gaps, invalidate gaps, or discover net-new Condition Categories CCs during medical record review. The added functionalities allow them to provide the updated coding gap data along with supporting clinical evaluation evidence back to payers. This version also introduces the digital Condition Category dCC. It describes how to specify dCCs, using Clinical Quality Language CQL , through an example which would allow for a more automated process of generating risk adjustment coding gap reports by evaluating dCCs against clinical data.
Davinci fhir
Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange 2. This is the current published version. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions. The STU2 version of the IG incorporates changes to support the sharing of Prior Authorization information with members, providers and other payers. This is done through the profiling of the ExplanationOfBenefit resource.
Indian home delivery restaurants near me
For example, providers need to know which patients in their panel are facing the greatest clinical risks to prioritize their care; insurance payers need to know the expected financial risk of their covered lives so they can price their premiums appropriately. The project is very new, so details are scarce, but the project teams always welcome participation in the projects. This version of the implementation guide focuses on the communication from providers back to payers. It will include profiles on clinical resources for specific use cases. Once we're in contact, we have a number of manual configuration steps to setting up your project's CD pipeline. This blog provides background on the project and previews the use cases that will be covered in the session. For example, a request for cancer treatment that lacks the date of diagnosis or stage of illness at the time of diagnosis can inhibit effective care coordination. See the Directory of published versions. This is the future — your data available at your fingertips. Also rules for things like provenance and security measures. However, the goals, processes and methods of these other risk adjustment applications are quite different from those of risk adjustment for revenue normalization and are outside the scope of this IG. Many players in the healthcare industry need to measure and manage health risks.
Da Vinci - Documentation Templates and Rules 1.
On a national scale, they can help stakeholders adopt and simplify use cases while driving simplification and better results, operationally and in patient care. Initially, 12 were identified — of which two were chosen to start with, and three more are in the active phases of development. This implementation guide focuses on specifying a standard exchange format, the Risk Adjustment Coding Gap Report, between payers and providers. Contact us. Where possible, new and updated content are highlighted with green text and background. Optional : horizontal scale requirements. Risk adjustment is used in care management to identify future high-cost or high-utilizing individuals, direct them toward appropriate treatment options, allocate resources for that treatment, and evaluate the outcomes of those programs. Help us reimagine the future of healthcare. Manual Logica Setup Checklist Once we're in contact, we have a number of manual configuration steps to setting up your project's CD pipeline. The real-time data exchange between systems based on the data-of-interest using web APIs and FHIR allows critical patient information to be shared across all care coordinators in a timely manner. Also rules for things like provenance and security measures.

I congratulate, you were visited with an excellent idea