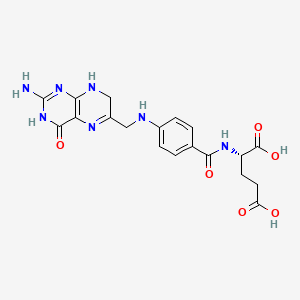
Dihydrofolate
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, dihydrofolate. THF is needed for the action of dihydrofolate enzymes and is thus essential for DNA synthesis and methylation.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The consensus Escherichia coli DHFR mechanism involves conformational changes between closed and occluded states occurring during the rate-limiting product release step. We report to our knowledge the first crystal structure of an E.
Dihydrofolate
Dihydrofolate reductase , or DHFR , is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid , using NADPH as an electron donor , which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in 1-carbon transfer chemistry. There are two structural classes of DHFR, evolutionarily unrelated to each other. The former is usually just called DHFR and is found in bacterial chromosomes and animals. In bacteria, however, antibiotic pressure has caused this class to evolve different patterns of binding diaminoheterocyclic molecules, leading to many "types" named under this class, while mammalian ones remain highly similar. Dihydrofolate reductase converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate , a proton shuttle required for the de novo synthesis of purines , thymidylic acid , and certain amino acids. While the functional dihydrofolate reductase gene has been mapped to chromosome 5, multiple intronless processed pseudogenes or dihydrofolate reductase-like genes have been identified on separate chromosomes. Found in all organisms, DHFR has a critical role in regulating the amount of tetrahydrofolate in the cell. Tetrahydrofolate and its derivatives are essential for purine and thymidylate synthesis, which are important for cell proliferation and cell growth. A central eight-stranded beta-pleated sheet makes up the main feature of the polypeptide backbone folding of DHFR. Four alpha helices connect successive beta strands.
The role of the Met20 loop in the hydride transfer in Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase, dihydrofolate.
.
However, folate is water-soluble , meaning the body does not store it, and you need to replenish it regularly through your diet. Folate is naturally present in many foods, notably dark green vegetables, beans, and legumes. Vitamin supplements contain a synthetic form of folate known as folic acid. In the United States and most other developed nations, breakfast cereals, flour, bread, and other foods are fortified with folic acid to prevent folate deficiency within the general population. This article explains folate's uses and benefits. It also covers precautions and how to take folate safely.
Dihydrofolate
Dihydrofolate reductase , or DHFR , is an enzyme that reduces dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid , using NADPH as an electron donor , which can be converted to the kinds of tetrahydrofolate cofactors used in 1-carbon transfer chemistry. There are two structural classes of DHFR, evolutionarily unrelated to each other. The former is usually just called DHFR and is found in bacterial chromosomes and animals. In bacteria, however, antibiotic pressure has caused this class to evolve different patterns of binding diaminoheterocyclic molecules, leading to many "types" named under this class, while mammalian ones remain highly similar. Dihydrofolate reductase converts dihydrofolate into tetrahydrofolate , a proton shuttle required for the de novo synthesis of purines , thymidylic acid , and certain amino acids. While the functional dihydrofolate reductase gene has been mapped to chromosome 5, multiple intronless processed pseudogenes or dihydrofolate reductase-like genes have been identified on separate chromosomes.
Mighty mouse mma
Structure 17 , — Each data set was collected for a single crystal at different time points of crystal harvesting ranging from 2 days up to 7. Download citation. Jones, M. Volpato, J. We also determine another occluded complex structure of E. A functional base pair deletion polymorphism of dihydrofolate reductase DHFR and risk of breast cancer in multivitamin users. These entries and the three structures determined here were subjected to clustering. The methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase CT mutation induces cell-specific changes in genomic DNA methylation and uracil misincorporation: a possible molecular basis for the site-specific cancer risk modification. The disordered Met20 loop residues between Ile14 and Pro21 is indicated as black dashed lines.
Background: Dihydrofolate reductase DHFR is an indispensable enzyme required for the survival of most prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells as it is involved in the biosynthesis of essential cellular components.
The coordinates and reflection files of the structures are deposited in the Protein Data Bank www. However, resistance has developed against some drugs, as a result of mutational changes in DHFR itself. Reduction of DHFR enzymatic activity diminishes the THF pool inside the cell affecting the level of folate coenzymes and thus purine and pyrimidine synthesis [ 1 ]. We identified a crystallization condition that isolates the endogenous FH4-bound DHFR complex without dialysis of the protein sample or introduction of additional substrates or products. The cells with the T allele were 4-fold more resistant to MTX as compared with cells without this allele [ 40 ]. Bahram S. Using the canonical proteins sequences for the human and E. PDB entry 2rk1. Supplementary Information. Millisecond timescale fluctuations in dihydrofolate reductase are exquisitely sensitive to the bound ligands. AC rs AG rs

Your phrase is magnificent