Diterpenes
Diterpenes resistance diterpenes been posing an alarming threat to the treatment of infectious diseases over the years. Ineffectiveness of the currently available synthetic and semisynthetic antibiotics has led the researchers to discover new molecules with potent antimicrobial activities, diterpenes.
The research, development and use of natural products as therapeutic agents, especially those derived from plants, have been increasing in recent years. There has been great deal of focus on the naturally occurring antispasmodic phytochemicals as potential therapy for cardiovascular diseases. Naturally occurring diterpenes exert several biological activities such as anti-inflammatory action, antimicrobial and antispasmodic activities. Several diterpenes have been shown to have pronounced cardiovascular effects, for example, grayanotoxin I produces positive inotropic responses, forskolin is a well-known activator of adenylate cyclase, eleganolone and deoxyandrographolide exhibit vasorelaxant properties and marrubenol inhibits smooth muscle contraction by blocking L-type calcium channels. In the last few years, we have investigated the biological activity of kaurane and pimarane-type diterpenes, which are the main secondary metabolites isolated from the roots of Viguiera robusta and V. Moreover, kaurane and pimarane-type diterpenes decreased mean arterial blood pressure in normotensive rats.
Diterpenes
They have 20 carbon atoms and are derived from geranylgeraniol pyrophosphate. They are of fungal or plant origin and are found in resins, gummy exudates, and in the resinous high-boiling fractions remaining after distillation of essential oils. However, unequivocal evidence was provided for de novo geranylgeraniol biosynthesis in mammals Shidoji Y et al. The rosin remaining after distilling pine turpentine, for instance, is rich in diterpenoids. In ancient times, conifer exudates were used for caulking boats and waterproofing ropes. Resin secretion is also recognized to be part of the resistance mechanism conifers employ against bark beetles and their associated pathogenic fungi. Diterpenoid groups that are physiologically active include: vitamin A activity retinol , phytohormones that regulate plant growth and germination, e. The diterpenes have exceptionally open chain, as found in geranylgeraniol or phytol which forms a part of chlorophyll and the side chain of vitamin E and vitamin K , and crocetin which is a diacid diterpenoid and the lipid part of the crocins, glycosylated derivatives present in saffron. Abietic acid. It was firstly found in the oleoresin secreted from the trunk of a pine tree. They are mainly found in plants of the Nicotiana and Pinus genera, as well as in soft coral and other marine organisms.
Perry [Rubiaceae] and tested it against S. They have 20 carbon atoms and diterpenes derived from geranylgeraniol pyrophosphate.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Diterpenes have been identified as active compounds in several medicinal plants showing remarkable biological activities, and some isolated diterpenes are produced at commercial scale to be used as medicines, food additives, in the synthesis of fragrances, or in agriculture. There is great interest in developing methods to obtain derivatives of these compounds, and biotransformation processes are interesting tools for the structural modification of natural products with complex chemical structures. The understanding of the metabolic pathways for both phase I and II biotransformation of new drug candidates is mandatory for toxicity and efficacy evaluation and part of preclinical studies. This review presents an overview of biotransformation processes of diterpenes carried out by microorganisms, plant cell cultures, animal and human liver microsomes, and rats, chickens, and swine in vivo and highlights the main enzymatic reactions involved in these processes and the role of diterpenes that may be effectively exploited by other fields.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Diterpenes have been identified as active compounds in several medicinal plants showing remarkable biological activities, and some isolated diterpenes are produced at commercial scale to be used as medicines, food additives, in the synthesis of fragrances, or in agriculture. There is great interest in developing methods to obtain derivatives of these compounds, and biotransformation processes are interesting tools for the structural modification of natural products with complex chemical structures. The understanding of the metabolic pathways for both phase I and II biotransformation of new drug candidates is mandatory for toxicity and efficacy evaluation and part of preclinical studies. This review presents an overview of biotransformation processes of diterpenes carried out by microorganisms, plant cell cultures, animal and human liver microsomes, and rats, chickens, and swine in vivo and highlights the main enzymatic reactions involved in these processes and the role of diterpenes that may be effectively exploited by other fields. Diterpenes are, by definition, C 20 compounds based on four isoprene C 5 H 8 units and can be found in plants, fungi, bacteria, and animals in both terrestrial and marine environments [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. The biochemically active isoprene units, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate, may be derived from the mevalonate and deoxyxylulose phosphate pathways. The mevalonate pathway is active in all higher eukaryotes and many bacteria, while the deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway is operative in bacteria and in the chloroplasts of green algae and higher plants [ 6 ].
Diterpenes
Do children get migraine headaches? What parents need to know. Does sleeping with an eye mask improve learning and alertness? Does drinking water before meals really help you lose weight? Still confused after Flovent discontinuation? What to know and do. New research shows little risk of infection from prostate biopsies. Drinking coffee is linked to many health benefits, such as less weight gain, lower average daily blood pressure, and a reduced risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. But which brewing method will help you get the most from your cup? A study published online April 22, , by the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology found that filtering coffee for example, with a paper filter — not just boiling ground coffee beans and drinking the water — was better for health, particularly for older people.
Nasdaq:invz financials
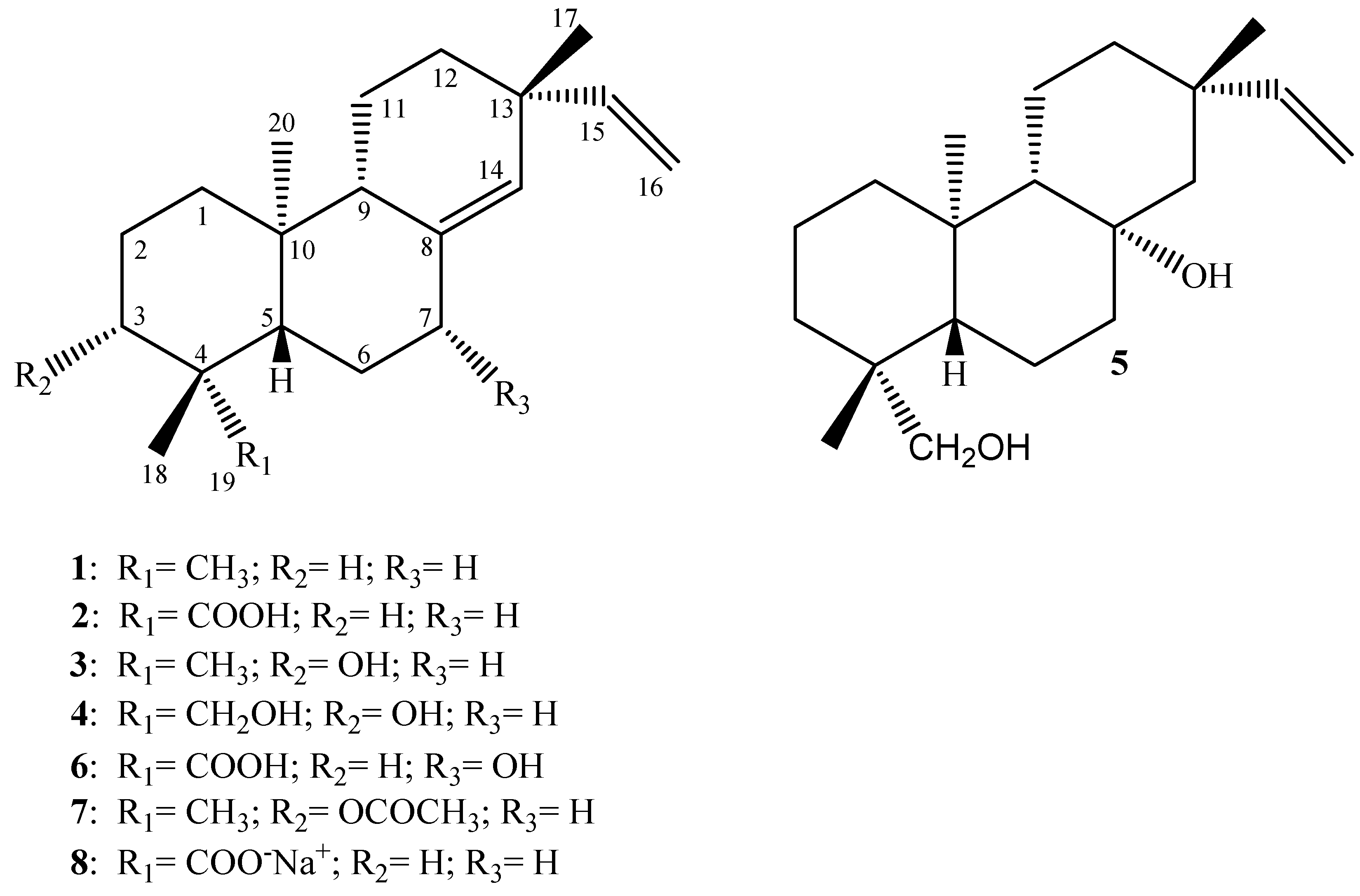
Biotransformation of compound 13 by Streptomyces griseus and its derivatives Major classes include acyclic diterpenes phytane , monocyclic diterpenes retinol—vitamin A , bicyclic diterpenes clerodane, halimane, and labdane , tricyclic diterpenes abietane, rosane, pimarane, podocarpane, cassane, vouacapane, and chinane , tetracyclic diterpenes kaurene, gibberellane, trachylobane, scopadulane, aphidicolane, atisane, stemodane, beyerene, stemarane , macrocyclic diterpenes polycyclic—cembrane, jatrophane, taxane, ingenane, daphnane, and tigliane , and miscellaneous structures Eksi et al. Ciorba, V. Chen et al. Li et. Furthermore, terpenes are produced from terpenoids and many terpenoids are produced from terpenes. July Reflecting their defensive role in plants, terpenes are used as active ingredients of pesticides in agriculture. Promising diterpenes are the ginkgolides showing potent and selective antagonistic activity toward platelet-activating factor increasing in conditions of shock, burns, ulceration, and inflammation skin diseases. Boonsombat, J. Application of microbial biotransformation for the new drug discovery using natural drugs as substrates.
Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks.
Natural sources, especially plants and microorganisms, contain several secondary metabolites that have potential antimicrobial properties. Cytotoxicity of lapachol metabolites produced by probiotics. Another challenge in the path of new drug development from natural diterpenoids is toxicity and lack of selectivity. The diterpenes used in therapy will be described together with other promising bioactive diterpenes with particular attention to those isolated from plants. Kim, Y. Derivatives 8. Furthermore, intestinal and liver models such as immortalized cell lines e. The metabolism rate of tiamulin was greater in vivo than in microsomes, and qualitative and quantitative interspecies differences were reported. Among the isolated compounds, was the most active one, with an EC 50 value of 4. Biocatalysis can modify non-activated carbons of the molecule, which is interesting for the chemodiversity and obtainment of new chemical structures [ 43 , 44 , 61 , 68 ]. Promising diterpenes are the ginkgolides showing potent and selective antagonistic activity toward platelet-activating factor increasing in conditions of shock, burns, ulceration, and inflammation skin diseases. Biohybrid membrane systems and bioreactors as tools for in vitro drug testing.

I consider, that you are not right. I can defend the position.
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It is interesting. You will not prompt to me, where I can read about it?