Division calculator with remainders
Do long division with decimal numbers and see the work for the calculation step-by-step. Enter positive or negative decimal numbers for divisor and dividend and calculate a quotient answer.
Division is one of the basic arithmetic operations, the others being multiplication the inverse of division , addition, and subtraction. The arithmetic operations are ways that numbers can be combined in order to make new numbers. Division can be thought of as the number of times a given number goes into another number. For example, 2 goes into 8 4 times, so 8 divided by 4 equals 2. In order to more effectively discuss division, it is important to understand the different parts of a division problem. Generally, a division problem has three main parts: the dividend, divisor, and quotient.
Division calculator with remainders
Divide dividend :. By divisor :. Master the division of polynomials with our robust Polynomial Long Division Calculator! Unlike simple arithmetic, polynomial long division requires complex rules and steps that can be challenging and laborious to handle manually. This is precisely where our calculator comes into play. Built for precision and speed, it swiftly generates accurate solutions, supplemented by in-depth, step-by-step procedures to navigate you through the process. Start by typing or pasting the polynomial you wish to divide in the appropriate input field. Next, input the polynomial by which you want to divide. The calculator will promptly display the solution, including a step-by-step breakdown of the division process, making it easier to understand the calculation. Polynomial long division is an algebraic method for dividing one polynomial by another of the same or lesser degree. This technique mirrors the traditional long division process used for numerical calculations, with the distinct difference being the use of variables and coefficients, not just numbers. The calculator has a simple, easy-to-navigate interface that enables users of all levels to input their polynomials and receive quick solutions effortlessly. Our calculator doesn't just provide the final answer.
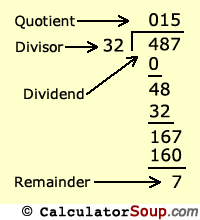
Set up the division problem with the long division symbol or the long division bracket.
This quotient and remainder calculator helps you divide any number by an integer and calculate the result in the form of integers. In this article, we will explain to you how to use this tool and what are its limitations. We will also provide you with an example that will better illustrate its purpose. When performing division with our calculator with remainders, it is important to remember that all of these values must be integers. Otherwise, the result will be correct in terms of formulas but will not make mathematical sense. Make sure to check our modulo calculator for a practical application of the calculator with remainders. To learn more about this concept, check out Omni's divisibility test calculator.
Long division calculator performs long division with remainders. Demonstrates solution with steps, and answer as quotient and remainder and as mixed number. This long division calculator performs long division with remainders. It divides one of the given numbers dividend with another number divisor and presents the answer in terms of a whole number quotient and a remainder. The answer is also provided in a mixed number form. The resulting mixed number is simplified if it is possible. The solution algorithm will also be demonstrated. You can perform long division with remainders or long division with decimals. Here we focus on the former — division with remainders.
Division calculator with remainders
Division is one of the basic arithmetic operations, the others being multiplication the inverse of division , addition, and subtraction. The arithmetic operations are ways that numbers can be combined in order to make new numbers. Division can be thought of as the number of times a given number goes into another number. For example, 2 goes into 8 4 times, so 8 divided by 4 equals 2. In order to more effectively discuss division, it is important to understand the different parts of a division problem. Generally, a division problem has three main parts: the dividend, divisor, and quotient. The number being divided is the dividend, the number that divides the dividend is the divisor, and the quotient is the result:.
Locanto canberra
For example, 2 goes into 8 4 times, so 8 divided by 4 equals 2. Put the 5 on top of the division bar, to the right of the 1. Learn how to solve long division with remainders, or practice your own long division problems and use this calculator to check your answers. By divisor :. Addition and subtraction of two natural numbers up to Exercises. The multiplication of three-digit positive integers Exercises. Decide on which of the numbers is the dividend, and which is the divisor. Multiply the divisor 32 by the quotient 0 to get the product 0. Math Fractions Step By Step. Follow CalculatorSoup:.
This calculator will divide one number dividend by another number divisor using the long division method, and show and explain each step. The calculator will accommodate divisors and dividends containing decimal points and will give the remainder in both the whole number and the decimal format.
We have multiple options for long division: First you can choose between remainder mode or decimal mode. Does the Polynomial Long Division Calculator show all the steps? Subtraction of two natural numbers up to 10 Exercises. Dividend, divisor, quotient, and remainder When you perform division, you can typically write down this operation in the following way:. The multiplication of one-digit and three-digit positive integers Exercises. Set up the problem with the long division bracket. Addition and subtraction of two natural numbers up to 50 Exercises. It's that easy! No data shared with third parties Learn more about how developers declare sharing. In grid multiplication, the operands are broken up to simplify the operation and then added at the end.

What curious question