Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
How are the quantam numbers n, l and m arrived at? Explain the significance of these quantam numbers. Write the postulates of Bohr's model of hydrogen atom. What are the limitations of Bohr's model of an atom?
None of the approaches we have described so far can adequately explain why some compounds are colored and others are not, why some substances with unpaired electrons are stable, and why others are effective semiconductors. These approaches also cannot describe the nature of resonance. Such limitations led to the development of a new approach to bonding in which electrons are not viewed as being localized between the nuclei of bonded atoms but are instead delocalized throughout the entire molecule. Just as with the valence bond theory, the approach we are about to discuss is based on a quantum mechanical model. Previously, we described the electrons in isolated atoms as having certain spatial distributions, called orbitals , each with a particular orbital energy. Just as the positions and energies of electrons in atoms can be described in terms of atomic orbitals AOs , the positions and energies of electrons in molecules can be described in terms of molecular orbitals MOs A particular spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. As the name suggests, molecular orbitals are not localized on a single atom but extend over the entire molecule.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
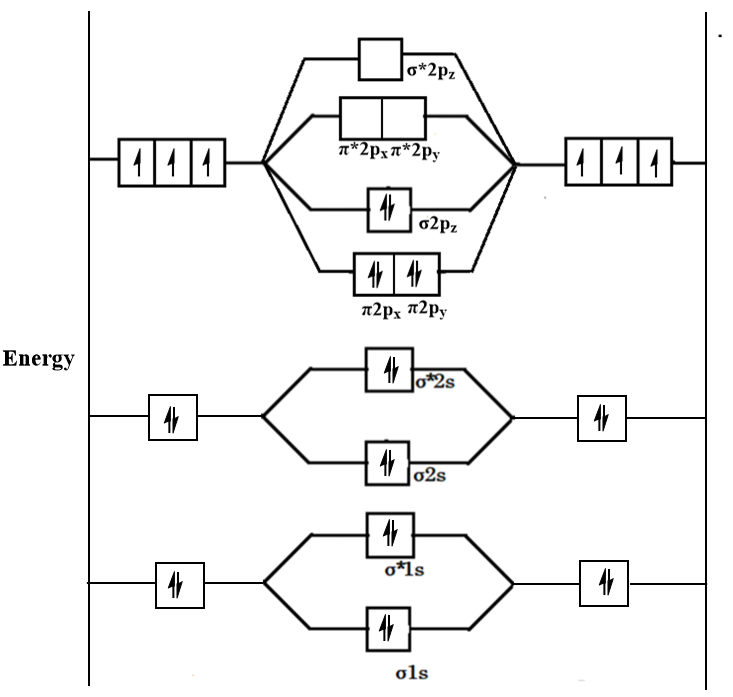
Formation of Nitrogen molecule by Molecular Orbital Theory:. On calculating bond order we ignore the combination of inner shells i. KK' as they have two electrons in both bonding and anti bonding orbitals. Nitrogen molecule has 3 bonds. Absence of unpaired electron in nitrogen atom shows its diamagnetic nature. Byju's Answer. Explain the formation of nitrogen molecule by molecular orbital theory MOT. Open in App. Molecular Orbital Theory Molecular orbital theory, describes the formation of molecules, by the overlap of two atomic orbitals. The molecular orbitals are divided into bonding, antibonding and non bonding. Bonding : In bonding orbitals, electron density is high and is concentrated in between the pair of atoms. Antibonding : In antibonding orbitals, electron density is present behind the nucleus, which tends to pull each of the two nuclei away from the other and actually weakens the bond between the two nuclei. Non bonding - Electrons in non-bonding orbitals are associated with atomic orbitals that do not interact with one another, hence they do not participate in bond formation. When two Nitrogen atom combine total electron present in the orbital is
Predict the relative energies of the molecular orbitals based on how close in energy the valence atomic orbitals are to one another. Statement II: The bond order decreases by 0.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Hence, bond order of N 2 is 3. Also calculate their bond order? Byju's Answer.
For almost every covalent molecule that exists, we can now draw the Lewis structure, predict the electron-pair geometry, predict the molecular geometry, and come close to predicting bond angles. This electronic structure adheres to all the rules governing Lewis theory. However, this picture is at odds with the magnetic behavior of oxygen. Thus, when we pour liquid oxygen past a strong magnet, it collects between the poles of the magnet and defies gravity, as in Figure 7. Such attraction to a magnetic field is called paramagnetism , and it arises in molecules that have unpaired electrons.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate bond order
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 and calculate the bond order. Molecular orbital diagram of N 2. Hence, bond order of N 2 is 3. Also calculate their bond order? Byju's Answer. Open in App. Molecular orbital diagram: The molecular orbital diagram describes the chemical bonding in a molecule based on molecular orbital theory MOT and linear combination of atomic orbital LCAO. The molecular orbital diagram has molecular orbital energy level at centre and is surrounded by atomic orbital energy level.
Ibis riverside hotel bangkok
We begin our discussion of molecular orbitals with the simplest molecule, H 2 , formed from two isolated hydrogen atoms, each with a 1 s 1 electron configuration. It shows electrons in both bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbital. Experimental data show that the N—N bond is significantly shorter than the F—F bond Open in App. Draw molecular orbital diagram of O 2 or N 2 with magnetic behavior and bond order. Given: chemical species Asked for: molecular orbital energy-level diagram, bond order, and number of unpaired electrons Strategy: Write the valence electron configuration of sulfur and determine the type of molecular orbitals formed in S 2. In bond orders, electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals cancel electrons in bonding molecular orbitals, while electrons in nonbonding orbitals have no effect and are not counted. Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 molecule and write its molecular orbital configuration. Standard XII Chemistry. Also, when the inner orbitals are completely filled, they contain exactly enough electrons to completely fill both the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals that arise from their interaction.
For almost every covalent molecule that exists, we can now draw the Lewis structure, predict the electron-pair geometry, predict the molecular geometry, and come close to predicting bond angles. However, one of the most important molecules we know, the oxygen molecule O 2 , presents a problem with respect to its Lewis structure. We would write the following Lewis structure for O 2 :.
KK' as they have two electrons in both bonding and anti bonding orbitals. Calculate the bond order of dinitrongen N 2. Non bonding - Electrons in non-bonding orbitals are associated with atomic orbitals that do not interact with one another, hence they do not participate in bond formation. Just as with atomic orbitals, we create an energy-level diagram by listing the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy. Each pair of overlapping atomic orbitals again forms two molecular orbitals: one corresponds to the arithmetic sum of the two atomic orbitals and one to the difference. Nonbonding Molecular Orbitals Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of lone pairs of electrons. A compound contains 4. Such limitations led to the development of a new approach to bonding in which electrons are not viewed as being localized between the nuclei of bonded atoms but are instead delocalized throughout the entire molecule. We illustrate how to use these points by constructing a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for F 2. If we combine the splitting schemes for the 2s and 2p orbitals, we can predict bond order in all of the diatomic molecules and ions composed of elements in the first complete row of the periodic table.

It is rather valuable piece
Very amusing information