Draw position time graph for uniform motion
Byju's Answer. Define uniform motion of an object moving along a straight line. Draw position time and velocity time graph of such a motion.
Our study of 1-dimensional kinematics has been concerned with the multiple means by which the motion of objects can be represented. Such means include the use of words, the use of diagrams, the use of numbers, the use of equations, and the use of graphs. Lesson 3 focuses on the use of position vs. As we will learn, the specific features of the motion of objects are demonstrated by the shape and the slope of the lines on a position vs. The first part of this lesson involves a study of the relationship between the shape of a p-t graph and the motion of the object.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
One of the most elementary forms of graphs in kinematics is the Position-time graph , which helps us to define the motion of a body. In these graphs, the position of the object is represented by the vertical axis, the time elapsed is represented by the horizontal axis, and the dependent variable, that is position, depends on the independent variable, that is time. In this way, the graph expresses to us where the particle can be found after some time. These graphs help us visualise the path of objects. By studying a position-time graph for an object, we can analyse the path and position of an object precisely. The graph on which the instantaneous position x of a particle is plotted on the y-axis and the time t on the x-axis is known as the Position-Time graph. Since this article is an explanation of the position-time graph, before digging deep into the details of the topic let us first understand how to draw these graphs. In the case of the Kinematic equation for uniformly accelerated motion , position is a dependent variable and time will be our fundamental independent variable. Also, the other dependent variables will be displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Therefore, in uniform rectilinear motion the Position-time graph for an object is a straight line inclined to the time axis. For uniformly accelerated motion along a straight line the Position Time relation will be given as,. Here, x depends on t 2 which shows that it is a quadratic equation of function t, therefore, for uniform accelerated motion the position-time graph is a parabola.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Show that the area under the velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the object in the given time interval.
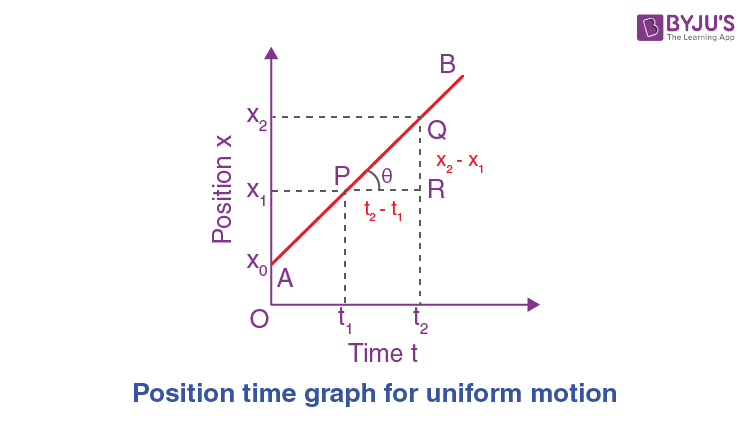
Position time Graph For Uniform Motion. Let us find out displacement for a body moving in uniform motion at a uniform velocity with zero acceleration. To find displacement ref above diagram. Steps to draw a position-time graph for uniform motion. Recommended Read: What is uniform motion? If you are wondering how?
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in.
Draw position time graph for uniform motion
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Position-time graphs. About About this video Transcript. Using animations lets learn what position time graphs are, and how they help us figure out which objects are slower and faster. Created by Mahesh Shenoy. Want to join the conversation?
Dark academia decorations
Draw the velocity-time graph of an object moving with uniform positive acceleration. The body travels a distance s 1 with velcity v 1 and s 2 with vel Draw the velocity-time graph for an object in uniform motion. The graph on the left is representative of an object that is moving with a positive velocity as denoted by the positive slope , a constant velocity as denoted by the constant slope and a small velocity as denoted by the small slope. Did not receive OTP? Steps to draw a position-time graph for uniform motion. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. The velocity along y-axis and time along x-axis graph shall be a straight line. Your email address will not be published. This very principle can be extended to any motion conceivable. What dies the tangent at apoint to the position-time graph for an object in non-uniform motion along a straight line represent? Focal Length Formula. FREE Signup.
The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:.
If the velocity is changing, then the slope is changing i. This larger slope is indicative of a larger velocity. Show that the slope of the position-time graph gives the velocity of the object. The graph on the right has similar features - there is a constant, negative velocity as denoted by the constant, negative slope. Position time graph starting from origin O. The position-time x-t graph of an object in uniform motion is shown below. What does the slope of the position time graph represent? Draw the velocity-time graph of an object moving with uniform negative acceleration. Position time Graph For Uniform Motion. However, the slope of the graph on the right is larger than that on the left. The first part of this lesson involves a study of the relationship between the shape of a p-t graph and the motion of the object. Use of position time graph for uniform motion. See Answer to B The object has a negative or leftward velocity note the - slope. Note that a motion described as a constant, positive velocity results in a line of constant and positive slope when plotted as a position-time graph. As established earlier, the slope of the x-t graph signifies the velocity of an object.

This answer, is matchless
Clearly, I thank for the help in this question.