Electron pair geometry of sf4
The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between them electron pair geometry of sf4 in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. The new orbitals in this form are known as hybrid orbitals. Like pure orbitals the hybrid orbitals are used in Bond formation.
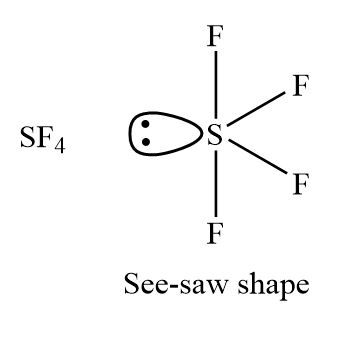
Let us learn about the SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The structure of SF4 molecular geometry may be predicted using VSEPR theory principles: A nonbonding lone pair of electrons occupy one of the three equatorial locations. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. The SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles of molecules having the chemical formula AX4E are trigonal bipyramidal. The equatorial orientations of two fluorine atoms establishing bonds with the sulphur atom are shown, while the axial locations of the other two are shown.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
The molecular formula of sulfur tetrafluoride SF 4 indicates that the compound has one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms. Sulfur is located in Group 16 of the periodic table and has six valence electrons. Fluorine is located in Group 17 and has seven valence electrons. Fluorine requires one electron to complete its octet and achieve the electron configuration of its nearest neighbor, neon. Sulfur and fluorine will combine to form four S-F single bonds. Sulfur will use four valence electrons to bond with the four fluorine atoms. Hence, it will have one lone pair of electrons, while each fluorine atom will have six []. Lewis structure is used to show the bond formation in sulfur tetrafluoride. Sulfur is the least electronegative of the two. So, it will lie at the center of the molecule. Dash lines represent the four S-F single covalent bonds. Dots represent the lone pairs. According to this theory, the central sulfur atom has a steric number of 5. It has five valence atomic orbitals forming five sp3d hybridized orbitals — one 3s orbital, three 3p orbitals, and one 3d orbital.
Ans : Not all ligands peripheral groups in trigonal bipyramidal molecules or complexes are equidi
.
Thus far, we have used two-dimensional Lewis structures to represent molecules. However, molecular structure is actually three-dimensional, and it is important to be able to describe molecular bonds in terms of their distances, angles, and relative arrangements in space Figure 7. A bond angle is the angle between any two bonds that include a common atom, usually measured in degrees. A bond distance or bond length is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms along the straight line joining the nuclei. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure. The VSEPR model assumes that electron pairs in the valence shell of a central atom will adopt an arrangement that minimizes repulsions between these electron pairs by maximizing the distance between them.
Electron pair geometry of sf4
The SF4 Lewis structure refers to the arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule of sulfur tetrafluoride. In this structure , there is one sulfur atom bonded to four fluorine atoms. The Lewis structure helps us understand the bonding and electron distribution in a molecule. It shows the connectivity of atoms and the placement of lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons.
Minecraft floor designs
Chemistry Learner It's all about Chemistry. Now, on the other hand, the molecule might be nonpolar with an even number of electrons. SF4 only contains one lone pair and four F sigma bonds. Partially ionic links are referred to as polar covalent bonds. Is SF4 a polar gas? The five valence atomic orbitals of the S atom are hybridised in the middle to produce five sp3d hybrid orbitals. In the 2P-orbitals, 4 hybrid orbitals are overlapped, and the fifth orbital has a lone pair. The 3-dimensional arrangement of atoms or fragments which create a molecule by getting together is called Molecular Geometry. The process of mixing of atomic orbitals belonging to the same atom of slightly different energies so that a redistribution of energy takes place between them resulting in the formation of new sets of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape is called hybridization. JEE Main Highlights. Let us learn about the molecule XeF2, its molecular geometry and bond examples, and XeF2 Lewis structure.
Drawing and predicting the SF4 molecular geometry is very easy.
Partially ionic links are referred to as polar covalent bonds. It can be specified regarding the bond lengths or bond angles. Fluorine requires one electron to complete its octet and achieve the electron configuration of its nearest neighbor, neon. The form will be equatorial since the lone pair is in the equatorial plane. You will also get to know more about SF4 structure, SF4 hybridisation, lewis structure of SF4, and the importance of SF4 molecular geometry and bond angles. The advantage of this structure is that it shows the bonding and chemical connectivity of all the particles that are associated with the reactivity and atoms of a molecule. As a result, there are two types of F ligands in the molecule: axial and equatorial. But before any final decision, it is suggested to check the VSEPR structure and then decide based on the diagram. JEE Advanced Syllabus. Sulfur will use four valence electrons to bond with the four fluorine atoms.

0 thoughts on “Electron pair geometry of sf4”