Enzymes byjus
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Without the presence of enzymes the biochemical reactions would take years to complete. These enzymes are successfully produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications. Lets look at some enzymes byjus its applications below.
Stay tuned for updated notes by subscribing to the newsletter! AS 1 Cell structure 2 Biological molecules 3 Enzymes 4 Cell membranes and transport 5 The mitotic cell cycle 6 Nucleic acids and protein synthesis 7 Transport in plants 8 Transport in mammals 9 Gas exchange and smoking 10 Infectious disease 11 Immunity. Paper 3 Paper 5 notes are included with theory. Flashcards 1. A2-Level flashcards.
Enzymes byjus
What are enzymes and what do they do in our bodies? Enzymes are basically proteins that are produced by living organisms to bring about certain metabolic and biochemical reactions in the body. They are biological catalysts that speed up reactions inside the body. Enzymes, as mentioned above, are biological catalysts. While they hasten or speed up a process, they are actually providing an alternative pathway for the process. But, in the process, the structure or composition of the enzymes remain unaltered. Enzymes are actually made up of s of amino acids that are linked in a specific way to form different enzymes. The enzyme chains fold over to form unique shapes and it is these shapes that provide the enzyme with its characteristic chemical potential. Most enzymes also contain a non-protein component known as the co-facto r. The biochemical reactions occurring in the body are basically of 6 types and the enzymes that bring about these reactions are named accordingly:. For any reaction to occur in the universe, there is an energy requirement. In cases where there is no activation energy provided, a catalyst plays an important role to reduce the activation energy and carried forward the reaction. This works in animals and plants as well.
The enzyme Oxidoreductase catalyzes the oxidation reaction where the electrons tend to travel from one form of a molecule to the other.
The human body is composed of different types of cells, tissues and other complex organs. For efficient functioning, our body releases some chemicals to accelerate biological processes such as respiration, digestion, excretion and a few other metabolic activities to sustain a healthy life. Hence, enzymes are pivotal in all living entities which govern all the biological processes. Let us understand what are enzymes, types, their structure, mechanism and various factors that affect its activity. The majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes.
Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. The exceptions are a class of RNA molecules known as ribozymes, of which most act upon themselves i. In this book and most textbooks in this field , unless otherwise specified, the term enzyme refers to one made of protein. Enzymes confer extraordinary specificity to a chemical reaction: a reaction that might occur between a variety of potential substrates in an uncatalyzed situation may only be allowed between two specific substrates when catalyzed by an enzyme. Enzymes allow cells to run chemical reactions at rates from a million to even a trillion times faster than the same reactions would run under similar conditions without enzymes. In some cases, the enzymes al - low reactions to proceed that would normally i. Finally, and perhaps most importantly for life, enzymes can be regulated. This is crucial for the cell, since it must be able to react to different situations, such as availability of energy, accumulation of toxic byproducts, the need to reproduce, etc. Not only can enzymes be modified either covalently or noncovalently to increase or decrease their activity, the cell can also regulate production of the enzymes, providing another level of control over particular cellular biochemical reactions. All enzymes now have both recommended names for common usage, often reflecting historical naming, and a systematic name, which is highly specific.
Enzymes byjus
Isozymes are present in the serum and tissues of mammals, amphibians, birds, insects, plants and unicellular organisms. The difference between some isozymes are due to differences in the quarternary structure of the enzymes, e. Only the tetrameric molecule possesses catalytic activity. Therefore, each consists of a single subunit. Medical discovery in had shown that the relative proportions of several lactate dehydrogenase isozymes of human serum were changed significantly in some pathologic conditions. The isozymes have different charges at this pH and migrate to 5 regions of the electrophoretogram. In certain solid tumors, there is an increase in serum LD 1 and LD 2. These isoenzymes are also present in the blood of patients with acute leukemia.
Free lina twitter
The applications of enzymes include:. Microbial Biotransformation Vasundhara Kakade Pisal. The most frequent active site amino acid residues out of the 20 amino acids forming the protein are polar amino acids, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, histidine, Serine, and lysine. Very little desorption enzyme strongly bound 2. Inclusion in gels: Poly acrylamide gel, Poly vinyl alcohol gels. Search site Search Search. Get ready for all-new Live Classes! This model also describes why enzymes are so specific in their action because they are specific to the substrate molecules. Enzymes are actually made up of s of amino acids that are linked in a specific way to form different enzymes. Enzymes immobilization. Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions. Login To View Results. Download Now. Catalysis of all reactions taking place in metabolic pathways is carried out by intracellular enzymes.
Perhaps you are unaware but your digestive system is like one big chemical lab. There are hundreds of reactions that occur in your body to absorb the nutrients from your food.
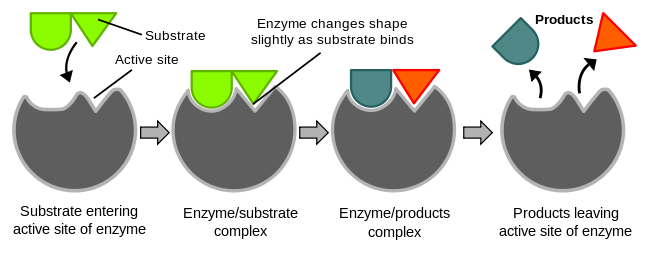
What is the induced fit theory? What are the types of enzymes present? This model also describes why enzymes are so specific in their action because they are specific to the substrate molecules. A small number of ribozymes exist which serve as an RNA-based biological catalyst. Denaturation of enzymes can also take place when enzymes are incubated for long durations. Enzymes reduce the reactions and activation energy to progress towards equilibrium quicker than the reactions that are not catalyzed. These enzymes are successfully produced in large quantities by using microorganisms and have various commercial applications. The induced structural rearrangements in this type of catalysis produce strained substrate bonds that attain transition state more easily. Customize your course in 30 seconds Which class are you in? This concept is used for treating bacterial infectious diseases. Another key characteristic of the ping-pong mechanism is that one product is formed and released before the second substrate binds.

I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also idea excellent, I support.