Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The epidemiologic transition describes changing patterns of population age distributions, mortality, fertility, life expectancy, and causes epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition death. A number of critiques of the theory have revealed limitations, including an insufficient account of the role of poverty in determining disease risk and mortality, a failure to distinguish bronco shop boise the risk of dying from a given cause or set of causes from the relative contributions of various causes of death to overall mortality, and oversimplification of the transition patterns, which do not fit neatly into either historical periods or geographic locations.
Definition: The Demographic Transition Model apprev. DTM has five stages that can be used to explain population increases or decreases. The DTM is a key tool for understanding global and regional population dynamics. You need to be able to recognize the 5 stages of the DTM when looking at a population pyramid. Stage one of the DTM has a high birth rate and a high death rate. Because of this, the natural increase rate is close to zero.
Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition
Not extra-terrestrials: we mean the Epidemiological Transition and its stages from the Neolithic Revolution to now. Disease, it turns out, has much to do with how fast populations grow, or whether they grow at all. Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free. Until humans began to live in close quarters with each other and our domestic animals, we were relatively healthy. During the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, humans fished and foraged, living in small groups often on the move. We didn't live long, but we were free of the diseases that need large numbers of people together. Epidemiological Transition ET : the three to five essential shifts in birth rates, death rates, and life expectancy that have occurred over human history due to fundamental changes in the nature of the diseases affecting human populations. In , ET theorist AR Omran, in a bid to build upon and improve demographic transition theory , proposed three epidemiological shifts over the last years that resulted in "ages. The first age was sparked by the Neolithic Revolution when people became farmers, living sedentary existences near each other and their animals. Diets worsened in many ways as they lost access to the range of wild foods hunter-gatherers consumed. Sedentary farmers and urban dwellers became highly susceptible to zoonotic transmission of disease from domesticated animals as well as commensal rodents such as rats and mice, highly effective disease spreaders. Until , this age of "pestilence and famine" 1 was experienced by farmers and urbanites in the Old World. Hunters and gatherers who remained uncontacted were not directly affected. After , pandemics and famines were the norm across the globe among all farming and urban people.
However, the population will not continue to go up at the same rate. Note that these differences are most evident in comparisons of developed and underdeveloped countries, but also hold for different segments of the population within the same country.
.
All Subjects. AP Human Geography. Frequently Asked Questions. You'll be asked about them in multiple-choice and free-response questions, so it's crucial that you are familiar with each of these. Be able to explain what information each one provides and examples if you can! Create your own quizlet deck and study these dates!
Epidemiological transition model ap human geography definition
Not extra-terrestrials: we mean the Epidemiological Transition and its stages from the Neolithic Revolution to now. Disease, it turns out, has much to do with how fast populations grow, or whether they grow at all. Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free. Until humans began to live in close quarters with each other and our domestic animals, we were relatively healthy. During the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, humans fished and foraged, living in small groups often on the move. We didn't live long, but we were free of the diseases that need large numbers of people together. Epidemiological Transition ET : the three to five essential shifts in birth rates, death rates, and life expectancy that have occurred over human history due to fundamental changes in the nature of the diseases affecting human populations. In , ET theorist AR Omran, in a bid to build upon and improve demographic transition theory , proposed three epidemiological shifts over the last years that resulted in "ages.
Ugg marlow robe
Eras and Paradigms. Things like cancer and heart disease are the leading causes of death. What is a reason for adherence to the Delayed epidemiological transition model? A key feature of stage 2 of the Demographic Transition Model is the emergence of grandparents. This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We didn't live long, but we were free of the diseases that need large numbers of people together. Note that these differences are most evident in comparisons of developed and underdeveloped countries, but also hold for different segments of the population within the same country. Fewer young adults are having children. The relative protection we have enjoyed from many infectious diseases is no longer a foregone conclusion. There are three models of epidemiological transition: Western, Accelerated, and Delayed. The various criticisms of the theory suggest it is most relevant as a way of looking at and understanding the relation among disease, mortality patterns, and population rather than as a definitive explanation or prediction.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
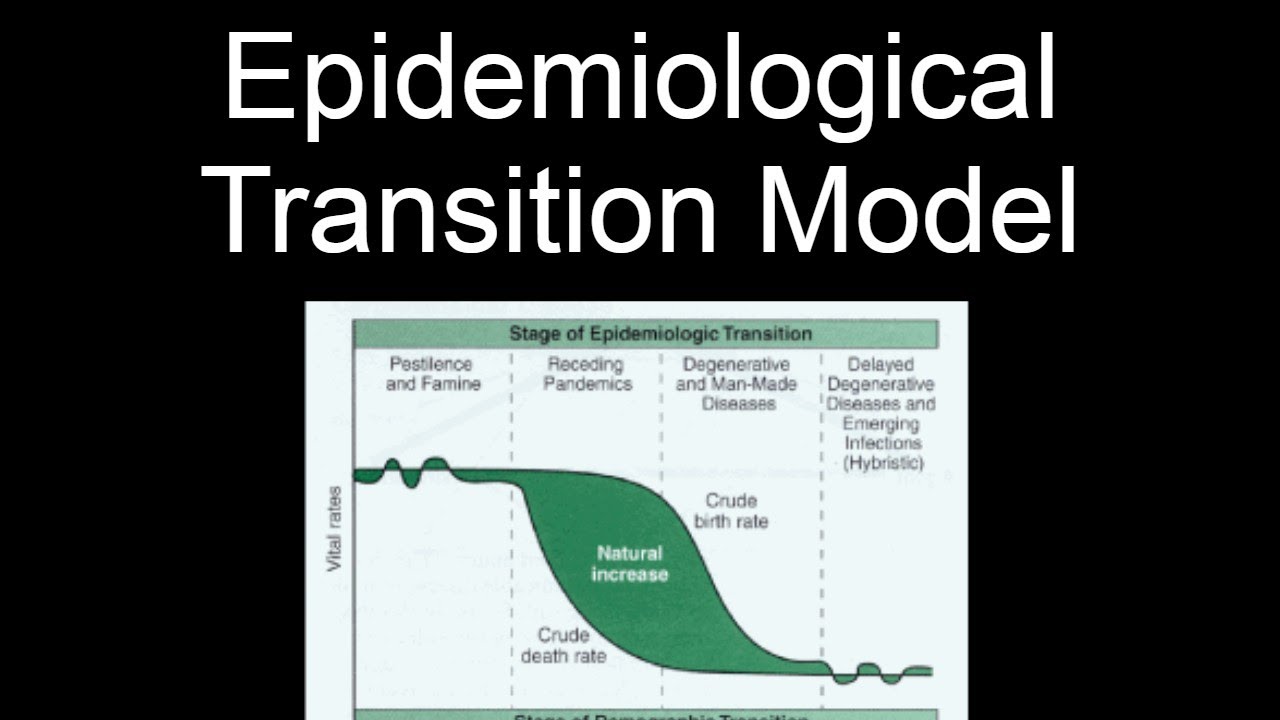
Implications for epidemiologic methods and conclusion The theory of epidemiologic transition has been useful in laying out an overarching perspective on changing demographic patterns. Studying with content from your peer. Other countries currently in stage four are China, Brazil, and Argentina. References 1. Some stage 5 governments promote pro-natalist policies to try and stunt the population decrease by incentivizing having children. The first transition Omran posits three typical phases of transition. The other side of this development was that public health came to be viewed largely through the lens of infectious disease prevention and control. The modern public health movement had its origins in the Sanitary Movement of the 18th and early 19th centuries, with its focus on community characteristics, economic conditions, and environmental influences. Gage TB. Ohran's original models were: Western Model of Epidemiological Transition The transition from high to low death rates and high to low birth rates happened simultaneously and over years during the Industrial Revolution in western Europe and North America. The US seems to be at this stage. Infectious diseases have evolved and established resistance to drugs and other treatments. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. For most of the last years, people's lives have been short and disease-ridden, with high death rates, high birth rates, and poor infant and maternal health. The epidemiological transition model is a prediction of the conditions of disease, healthcare, and sanitation that will determine the course of the demographic transition from high death rate and birth rate to low death rate and birth rate in a given country or region.

I consider, that you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
It absolutely not agree