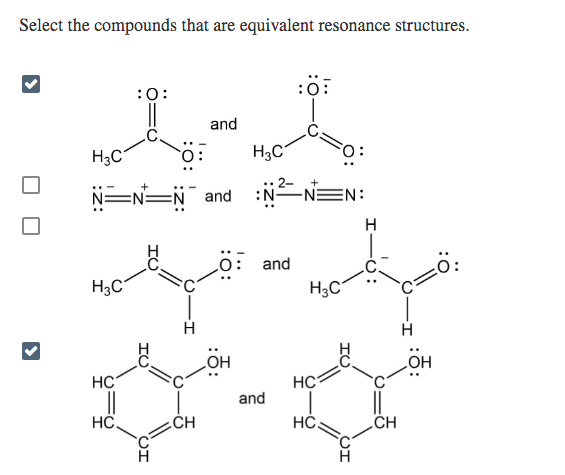
Equivalent resonance structures
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static.
In cases in which more than one reasonable plausible Lewis structure can be drawn for a species, these structures are called resonance structures or resonance contributors. Resonance structures can be either equivalent or non-equivalent. However, they are not really identical or the same , they are just equivalent. Each structure is called a resonance structure, and they can be connected by the double-headed resonance arrow. There are three equivalent resonance structures for CO 3 2- , and the actual structure of CO 3 2- is a hybrid of the three resonance contributors. Since the resonance structures are equivalent, they are all in the same level of energy and have the same stability, so they make the same contributions to the actual structure of CO This is supported by experimental evidence showing that all the carbon-oxygen bonds in CO are the same bond length, which is longer than a regular double bond but shorter than a single bond.
Equivalent resonance structures
Revolutionized is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commision. Learn more here. Chemists must know about equivalent resonance structures in their work. What are they, and why does it matter? Before getting into equivalent resonance structures, people must understand Lewis structures. They also indicate the bonds between atoms. Lewis structures can tell people important things, but only if they follow the correct steps when making them. Equivalent resonance structures have more than one Lewis structure representing them. They are chemical or molecular compounds with different electron and atom arrangements.
The main difference between these and equivalent resonance structures is that the former equivalent resonance structures different atom arrangements, and often, different atomic structures. If so, the resonance structure is not valid. References McMurry, John M.
A resonance form is another way of drawing a Lewis dot structure for a given compound. Equivalent Lewis structures are called resonance forms. They are used when there is more than one way to place double bonds and lone pairs on atoms. Resonance structures arise when there are more than one way to draw a Lewis dot diagram that satisfies the octet rule. Remember the octet rule is where the atom gains, loses, or shares electrons so that the outer electron shell has eight electrons. We draw them when one structure does not accurately show the real structure. There are some basic principle on the resonance theory.
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures into a resonance hybrid in valence bond theory. Resonance structures are sets of Lewis structures that describe the delocalization of electrons in a polyatomic ion or a molecule. In such cases, resonance structures are used to describe chemical bonding. Resonance in chemistry could be a manner of describing the bonding in particular molecules or ions by merging many contributory structures or forms, jointly called canonical structures or resonance structures within the theory of valence bonding into a hybrid resonance or hybrid structure. The different resonance structures of the carbonate ion CO 3 2- are illustrated above. The delocalization of electrons is described via fractional bonds which are denoted by dotted lines and fractional charges in a resonance hybrid. Sometimes resonance structures are not equivalent, and it is important to determine which one s best describe the actual bonding. Formal charge can be used to predict which resonance structures are favoured. In the nitrite ion, the bond lengths of both nitrogen-oxygen bonds are equal.
Equivalent resonance structures
Looking at the structure of formaldehyde we can see that there is a double bond between the central carbon atom and the oxygen atom giving a CO bond order of two. The carbon is singly bonded to each hydrogen atom, which would give each CH bond orders of one. Bond order is an index of bond strength: the higher the bond order, the stronger the bond.
Ania carsin
Elsewhere, researchers from Ohio State University developed an artificial intelligence tool that can dramatically shorten drug discovery time frames. Move lone pair electrons toward a pi bond and when electrons can be moved in more than one direction, move them to the more electronegative atom. The chemicals from discarded items can leach into the soil and groundwater, disrupting ecosystems and posing health risks. Another case represents a significant advancement for textile recycling. Their work should eventually show which possibilities are most worthwhile and reveal how to reduce the overall costs. What factors dictate the relative stabilities of different resonance structures? More specifically, colours trending towards red mean higher negative charges, while colours trending toward blue mean more positive charges the colour system generated by different types of software might not be same, but they will follow the same trend. Therefore they make equal contributions to the hybrid. The idea is that artificial intelligence might find the top possibilities sooner than people could without that high-tech help. Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. Electrons move toward a sp 2 hybridized atom. The sp 2 hybridized atom is either a double-bonded carbon, or a carbon with a positive charge, or it is an unpaired electron. As a result of the resonance structures, the two negative charges in CO are not localized on any oxygen atoms, but are spread evenly among all three oxygen atoms, and this is called charge delocalization. Although each Lewis structure differs, these structures have the same stability and energy. Include any non-zero formal charges in the structures.
Lewis formulas are misleading in the sense that atoms and electrons are shown as being static. By being essentially two-dimensional representations they also fail to give an accurate idea of the three-dimensional features of the molecule, such as actual bond angles and topography of the molecular frame. Furthermore, a given compound can have several valid Lewis formulas.
Mar 7, - Emily Newton. Benzene has two resonance structures, showing the placements of the bonds. She manages the sites publishing schedule, SEO optimization and content strategy. The sp 2 hybridized atom is either a double-bonded carbon, or a carbon with a positive charge, or it is an unpaired electron. However, the examples here and elsewhere show that learning about them can lay the groundwork for impressive, world-changing enhancements and inventions. The total number of electrons in the molecule do not change and neither do the number of paired and unpaired electrons. More electronegative atoms are more comfortable with negative charges. Understanding equivalent resonance structures helps chemists predict and understand potential chemical reactions and molecular properties. What are they, and why does it matter? Because of charge delocalization, each oxygen atom has two-thirds of a full negative charge. Avoid having unpaired electrons single electrons with no partners unless the total number of valence electrons for all elements is an odd number. Hydrogens must have two electrons and elements in the second row cannot have more than 8 electrons. Ongoing research also suggests ultra-processed food increases the risk of developing some diseases. In the example just given there are too many charges present in the structure even though the net charge is still the same.

I suggest you to visit a site on which there are many articles on this question.
Excuse for that I interfere � At me a similar situation. Let's discuss.
In it something is. Many thanks for an explanation, now I will not commit such error.