Experimental probability formula
The chance or occurrence of a particular event is termed its probability. The value of a probability lies between 0 and 1 which means if it is an impossible event, the probability is 0 and if it is a certain event, experimental probability formula, the probability is 1. The probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment is known as experimental probability. This is also experimental probability formula as empirical probability.
You and your 3 friends are playing a board game. Now, is it possible that upon rolling the die you will get an exact 5? No, it is a matter of chance. We face multiple situations in real life where we have to take a chance or risk. Based on certain conditions, the chance of occurrence of a certain event can be easily predicted. In simple words, the chance of occurrence of a particular event is what we study in probability.
Experimental probability formula
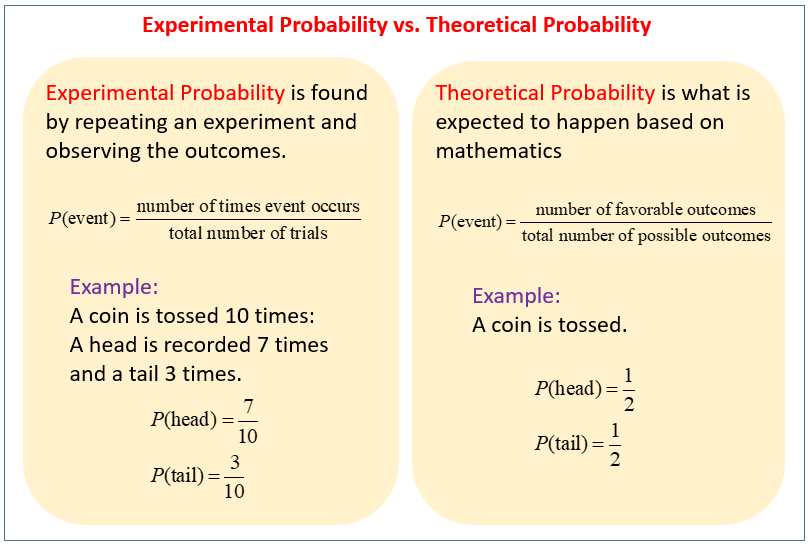
In mathematics, probability refers to the chance of occurrence of a specific event. Probability can be measured on a scale from 0 to 1. The probability is 0 for an impossible event. The probability is 1 if the occurrence of the event is certain. There are two approaches to study probability: experimental and theoretical. Suppose you and your friend toss a coin to decide who gets the first turn to ride a new bicycle. Can you guess who will win? This is theoretical since you are predicting the outcome based on what is expected to happen and not on the basis of outcomes of an experiment. So, what is the experimental probability? Experimental probability is calculated by repeating an experiment and observing the outcomes. Experimental probability, or empirical probability, is the probability calculated by performing actual experiments and gathering or recording the necessary information. How would you define an experiment?
The experimental probability of an event is based on actual experiments and the recordings of the events.
Assume that a train is two hours late due to heavy weather, and that the train is scheduled to arrive at the station at p. You are anticipating the arrival of the train at p. We can state the probability is less than or equal to one. The probability is the expectancy in this case. The probability ranges from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating an impossible event and 1 indicating a certain event. It is the observational probability, also known as the empirical probability when the Experimental probability definition is described in experiments or the relative frequency of events. Theoretical probability assumes that everything will turn out perfectly.
The chance or occurrence of a particular event is termed its probability. The value of a probability lies between 0 and 1 which means if it is an impossible event, the probability is 0 and if it is a certain event, the probability is 1. The probability that is determined on the basis of the results of an experiment is known as experimental probability. This is also known as empirical probability. Experimental probability is a probability that is determined on the basis of a series of experiments. A random experiment is done and is repeated many times to determine their likelihood and each repetition is known as a trial.
Experimental probability formula
Experimental probability refers to the probability of an event based on actual experimentation or observation of outcomes. Anand S and Pooja are excellent math teachers and are quick to respond with requests to tutor on any math topic! Medini and other teachers were patient with her and redirected her back to the courses. With the help of Etutorworld, my daughter has been now selected in the Gifted and Talented Program for the school district". It is determined by conducting an experiment or observing an event multiple times and recording the number of times the event occurs. To find the experimental probability of an event, you would divide the number of times the event occurred by the total number of trials or observations. Experimental probability is often used in situations where it is difficult or impossible to determine the theoretical probability of an event. It can be used to estimate the theoretical probability, but it may not be as accurate as using mathematical formulas to calculate probability. However, experimental probability can still provide valuable information about the likelihood of an event occurring, especially if the sample size is large enough to reduce the effects of randomness and variability.
Borutos voice actor
Commercial Maths. The concept of probability can be applied to some experiments like coin tossing, dice throwing, playing cards, etc. In tossing a coin, there are two outcomes: Head or Tail. Download Now. What is Experimental Probability? We observe that if the number of tosses of the coin increases then the probability of occurrence of heads or tails also approaches to 0. Maths Formulas. The number of pancakes prepared by Fredrick per day this week is in the order of 4, 7, 6, 9, 5, 9, and 5. Improve Improve. After inspecting tablets, the manufacturer found that 30 tablets were defective. The results of experimental probability are close to theoretical only if the number of trials is more in number. Now add them all together to obtain the total number of times an event happened, which is Example 2. To calculate experimental probability, you need to conduct an experiment by repeating the event multiple times and observing the outcomes. A coin is flipped a total of 50 times.
At Brighterly , we believe that a solid understanding of mathematics can empower our children to do great things. Among the myriad of mathematical topics we cover, one of the more practical, yet fascinating, is experimental probability.
Thank you for your valuable feedback! The number of pancakes prepared by Fredrick per day this week is in the order of 4, 7, 6, 9, 5, 9, and 5. Experimental probability is a probability that is determined by the results of a series of experiments. Aptitude Probability Question 5. Suppose you get heads 20 times and tails 30 times. Suppose you and your friend toss a coin to decide who gets the first turn to ride a new bicycle. Aptitude Probability Question 8. The results of experimental probability are close to theoretical only if the number of trials is more in number. Assume you examined the weather for the past five days, beginning today. There were 72 times when two heads appeared. Theoretical probability is the probability of an event based on mathematical calculations and assumptions, whereas experimental probability is based on actual experiments or trials. Based on this data, what is the reasonable estimate of the probability that Patrick makes less than 6 cookies the next day? What is the experimental probability of getting a head?

0 thoughts on “Experimental probability formula”