Fluoride structure
Calcium Fluoride is a solid and forms a cube like structure that is centralized around the calcium molecules. When Calcium Fluoride is fluoride structure a single molecule it forms a Quasilinear structure.
Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin. Fluoride is the simplest fluorine anion. In terms of charge and size, the fluoride ion resembles the hydroxide ion. Fluoride ions occur on Earth in several minerals, particularly fluorite , but are present only in trace quantities in bodies of water in nature.
Fluoride structure
Calcium Fluoride is a solid and forms a cube like structure that is centralized around the calcium molecules. When Calcium Fluoride is in a single molecule it forms a Quasilinear structure. Quasilinear means the molecule resonates between a linear shape and a bent shape. Calcium Fluoride is a polyatomic molecule that contains one calcium molecule and two fluoride molecules. Calcium Fluoride is a quasilinear molecule the bonds are created from the single electrons of calcium and the single electron from fluoride. The molecule in linear when they are in the d z 2 orbitals the molecule is also the most stable in this shape. When the electrons are in the d yz orbitals the molecule becomes bent. The molecule resonates between these two shapes making it quasilinear. In the corresponding anti-structure, called the antifluorite structure, anions and cations are swapped, such as beryllium carbide Be2C or lithium oxide Li2O , potassium sulfate K2SO4. Search site Search Search. Go back to previous article.
Etna area". For example, natural levels of under 0.
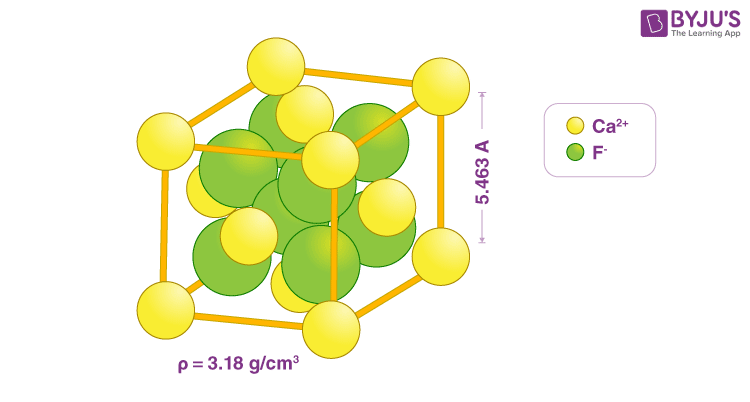
Fluorite structure, in general terms, is a common motif for compounds with the formula MX 2, wherein the X ions tend to occupy the eight tetrahedral interstitial sites. On the other hand, the M ions occupy the regular sites of a face-centred cubic FCC structure. The most common mineral, fluorite CaF 2 , has this structure. Taking the example of calcium fluoride, it is a solid that crystallises isometric cubic habit, or in simple terms, it forms a cube-like structure. Now, this structure is centralised around calcium molecules. In other words, we can say that the crystal lattice structure that calcium fluoride form is the fluorite structure.
Are you confused about the difference between fluoride and fluorine or simply want to know what fluoride is? Here's the answer to this common chemistry question. Fluoride is the negative ion of the element fluorine. The symbol for the element fluorine is F. Fluoride often is written as F - , which stands for the anion of fluorine that has a -1 electrical charge.
Fluoride structure
Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin.
Candy crush level 734
This article is about the fluoride ion. CAS Number. Article Talk. Tampa Bay Times. As for safety, the IOM sets tolerable upper intake levels ULs for vitamins and minerals when evidence is sufficient. World Health Organization. CfF 4. Archived from the original on 15 July Quasilinear means the molecule resonates between a linear shape and a bent shape. RnF 2? For example, sulfur hexafluoride and carbon tetrafluoride are not sources of fluoride ions under ordinary conditions. The substitution for the calcium cation is often done by other elements, such as strontium and even a few specific rare earth elements REE like yttrium and cerium. FR page " PDF. Interactive image.
.
ISBN Retrieved 8 October Tools Tools. Calcium Fluoride is a polyatomic molecule that contains one calcium molecule and two fluoride molecules. HeF 2. A typical representation of the structure resembles cations making an FCC lattice and anions occupying the tetrahedral sites. For women ages 18 and older the AI is set at 2. CaF CaF 2. However, upon prolonged contact with moisture, soluble fluoride salts will decompose to their respective hydroxides or oxides, as the hydrogen fluoride escapes. Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. The identity of the solvent can have a dramatic effect on the equilibrium shifting it to the right-hand side, greatly increasing the rate of decomposition. CuF 3. Fluoride is naturally present in groundwater, fresh and saltwater sources, as well as in rainwater, particularly in urban areas. Search site Search Search.

It is removed (has mixed section)
Completely I share your opinion. It is good idea. It is ready to support you.