Formal charge of cl
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion.
Formal charge of cl
.
It does not fluctuate between resonance forms; rather, the actual electronic structure is always the average of that shown by all resonance forms, formal charge of cl. Instead, we use the concept of resonance : if two or more Lewis structures with the same arrangement of atoms can be written for a molecule or ion, the actual distribution of electrons is an average of that shown by the various Lewis structures.
.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Formal charge of cl
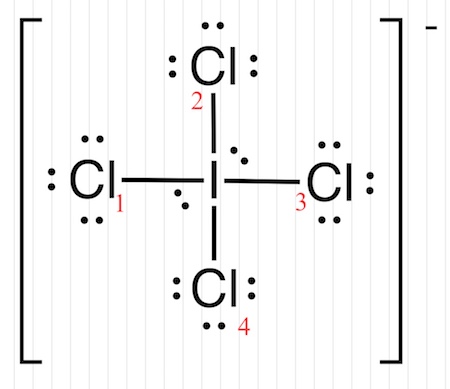
The concept of formal charge is actually very simple. It relates the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule's Lewis dot structure to the number of electrons that atom donated to the Lewis dot structure. In the next section we will cover drawing Lewis dot structures, and the first step is to calculate the number of electrons each atom donates to the molecule, and then to essentially draw a structure based on those electrons, placing them in either bonding or nonbonding orbitals. In formal charge calculations electrons in bonding orbitals are considered to be evenly split between the two bonding atoms, one is assigned to each atom , while those in lone pair non bonding orbitals are assigned to the atom they are placed on. A negative formal charge means there are more electrons around an atom than it donated, a positive means there are fewer electrons around an atom then it donated, and a neutral formal charge means the number it donated is the same as in the structure. The following equation determines the formal charge for each atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
Japanese tattoo designs arm
A double-headed arrow between Lewis structures indicates that they are resonance forms. The online Lewis Structure Maker from the University of Sydney includes many examples to practice drawing resonance structures. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. Now each Cl atom has seven electrons and the Br atom has seven electrons. In many cases, following the steps for writing Lewis structures may lead to more than one possible molecular structure—different multiple bond and lone-pair electron placements or different arrangements of atoms, for instance. A few guidelines involving formal charge can be helpful in deciding which of the possible structures is most likely for a particular molecule or ion:. These hypothetical formal charges are a guide to determining the most appropriate Lewis structure. Is the actual structure consistent with the formal charges? Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in sulfur dioxide: OSO or SOO? A medieval traveler, having never before seen a rhinoceros, described it as a hybrid of a dragon and a unicorn, because it had many properties in common with both.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable.
Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges. Show Answer Assign one of the electrons in each Br—Cl bond to the Br atom and one to the Cl atom in that bond: Assign the lone pairs to their atom. We can draw three possibilities for the structure: carbon in the center and double bonds, carbon in the center with a single and triple bond, and oxygen in the center with double bonds:. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The electrons involved in the N—O double bond, however, are in different positions:. It has some characteristics in common with its resonance forms, but the resonance forms themselves are convenient, imaginary images like the unicorn and the dragon. Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in hypochlorous acid: HOCl or OClH? The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion. The arrangement of atoms in a molecule or ion is called its molecular structure. A double bond between two atoms is shorter and stronger than a single bond between the same two atoms. Resonance occurs in cases where two or more Lewis structures with identical arrangements of atoms but different distributions of electrons can be written. Sign in. Answer N: 0; all three Cl atoms: 0. However, the first arrangement of atoms is preferred because it has the lowest number of atoms with nonzero formal charges Guideline 2.

Yes, really. So happens. We can communicate on this theme. Here or in PM.
Quite good topic