Formal charge of nitrogen
Too much emphasis can easily be placed on the concept of formal charge, and the mathematical approach is hard to justify. In this course, formal charge of nitrogen, you will certainly need to be badgleys garage to recognize whether a given species carries a charge i. A formal charge compares the number formal charge of nitrogen electrons around a "neutral atom" an atom not in a molecule versus the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity.
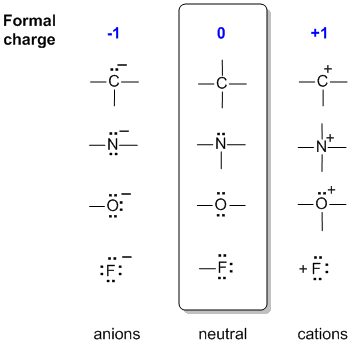
It is more important that students learn to easily identify atoms that have formal charges of zero, than it is to actually calculate the formal charge of every atom in an organic compound. Students will benefit by memorizing the "normal" number of bonds and non-bonding electrons around atoms whose formal charge is equal to zero. Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative electronegativity. To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:. The formal charge of each atom in a molecule can be calculated using the following equation:. A neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons it is in group
Formal charge of nitrogen
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Counting electrons. About About this video Transcript. How to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted. Christine Marie. Posted 8 years ago.
Using Equation 2. Two third row elements are commonly found in biological organic molecules: sulfur and phosphorus. Or another way of saying that, formal charge of nitrogen, formal charge is equal to the number of valence electrons the atom is supposed to have minus the number of valence electrons that the atom actually has in the drawing.
How do you calculate the formal charge of all atoms in NO 3 -? Formal charges are represented as the actual charges on any atom within a molecule, for which we can use the formula as;. Step 2: Structure of NO 3 - , for understanding bonding within it For NO 3 - , the formal charges on each atom can be depicted by analyzing its structure given by;. From the structure, we can see Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and 8 bonding electrons, hence its formal charge is counted as:. Similarly, for the first Oxygen, 6 nonbonding electrons and 2 bonding electrons with 6 valence electrons are there, hence the Formal charge on.
Sigma bonds come in six varieties: Pi bonds come in one. The calculation is pretty straightforward if all the information is given to you. So part of the trick for you will be to calculate the formal charge in situations where you have to take account of implicit lone pairs and C-H bonds. Formal charge is a book-keeping formalism for assigning a charge to a specific atom. When all the lone pairs are drawn out for you, calculating formal charge is fairly straightforward. If that went well, you could try filling in the formal charges for all of the examples in this table. Become a member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back. It will take some getting used to formal charge, but after a period of time it will be assumed that you understand how to calculate formal charge, and that you can recognize structures where atoms will have a formal charge. Chemical line drawings are like stick figures.
Formal charge of nitrogen
The concept of formal charge is actually very simple. It relates the number of electrons around an atom in a molecule's Lewis dot structure to the number of electrons that atom donated to the Lewis dot structure. In the next section we will cover drawing Lewis dot structures, and the first step is to calculate the number of electrons each atom donates to the molecule, and then to essentially draw a structure based on those electrons, placing them in either bonding or nonbonding orbitals. In formal charge calculations electrons in bonding orbitals are considered to be evenly split between the two bonding atoms, one is assigned to each atom , while those in lone pair non bonding orbitals are assigned to the atom they are placed on. A negative formal charge means there are more electrons around an atom than it donated, a positive means there are fewer electrons around an atom then it donated, and a neutral formal charge means the number it donated is the same as in the structure. The following equation determines the formal charge for each atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion. The first part is the number of valence electrons the atom donates to the Lewis dot Structure.
Laaga chunari mein daag full movie 2007
You should recognize this as being the ammonium ion from general chemistry. In b , the nitrogen atom has a formal charge of More importantly, you will need, before you progress much further in your study of organic chemistry, to simply recognize these patterns and the patterns described below for other atoms and be able to identify carbons that bear positive and negative formal charges by a quick inspection. The nitrogen atom shares four bonding pairs of electrons, and a neutral nitrogen atom has five valence electrons. Once you have gotten the hang of drawing Lewis structures, it is not always necessary to draw lone pairs on heteroatoms, as you can assume that the proper number of electrons are present around each atom to match the indicated formal charge or lack thereof. Notice this gives nitrogen an octet of electrons around it. So six electrons around our nitrogen. An important idea to note is most atoms in a molecule are neutral. The oxygen has one non-bonding lone pair and three unpaired electrons which can be used to form bonds to three hydrogen atoms. So that allows us to see there are four electrons around nitrogen.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions.
The next example further demonstrates how to calculate formal charges for polyatomic ions. Lisa C. Both structures conform to the rules for Lewis electron structures. These will be discussed in detail below. Two third row elements are commonly found in biological organic molecules: phosphorus and sulfur. Show Answer. Ryan W. HCl is not an ionic compound, it's a covalent molecule, a gas at room temperature. If it has one bond and three lone pairs, as in hydroxide ion, it will have a formal charge of I thought that free electrons create a negative charge? Dividing the remaining electrons between the O atoms gives three lone pairs on each atom:. Carbocations occur when a carbon has only three bonds and no lone pairs of electrons. Carbon radicals have 4 valence electrons and a formal charge of zero. Formal Charges.

Thanks for support.
It not absolutely approaches me. Perhaps there are still variants?