Gdm ncp
Utilize this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to provide effective care for patients experiencing diabetes mellitus. Gain valuable insights on nursing assessmentinterventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis specifically tailored for diabetes mellitus in this guide. Diabetes mellitus DM is a chronic disease characterized by insufficient insulin production in the pancreas or when the body cannot efficiently use the gdm ncp it produces, gdm ncp.
Watch More! Unlock the full videos with a FREE trial. Access More! View the full outline and transcript with a FREE trial. To guide nursing professionals in managing and supporting patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus GDM , focusing on understanding the condition, identifying risk factors and symptoms, and implementing effective interventions to manage blood glucose levels, prevent complications, and promote a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
Gdm ncp
In true GDM, glucose usually returns to normal by six weeks postpartum , although women with GDM have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus later in life. The primary concern for any woman with this disorder is controlling the balance between insulin and blood glucose levels to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Women with gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery. The nursing care plan for gestational diabetes mellitus involves providing the client or couple with information regarding the disease condition, teaching insulin administration, achieving and maintaining normoglycemia, and evaluating the present client or fetal well-being. While nursing diagnoses serve as a framework for organizing care, their usefulness may vary in different clinical situations. In real-life clinical settings, it is important to note that the use of specific nursing diagnostic labels may not be as prominent or commonly utilized as other components of the care plan. Therapeutic interventions and nursing actions for patients with gestational diabetes mellitus GDM may include:. The cells register the need for glucose, and the liver quickly converts stored glycogen to glucose to increase the serum glucose level. However, because insulin is unavailable, the body cells still cannot use the glucose, so the serum glucose levels rise. Perform a prenatal screening test to identify gestational diabetes mellitus. Suppose the woman does not have preexisting diabetes mellitus. In that case, a prenatal screening test is routinely performed between 24 and 28 weeks gestation, but it may be done earlier if risk factors are present.
Question 3. The use of a diary can help the health care provider to evaluate and alter the therapy provided as indicated.
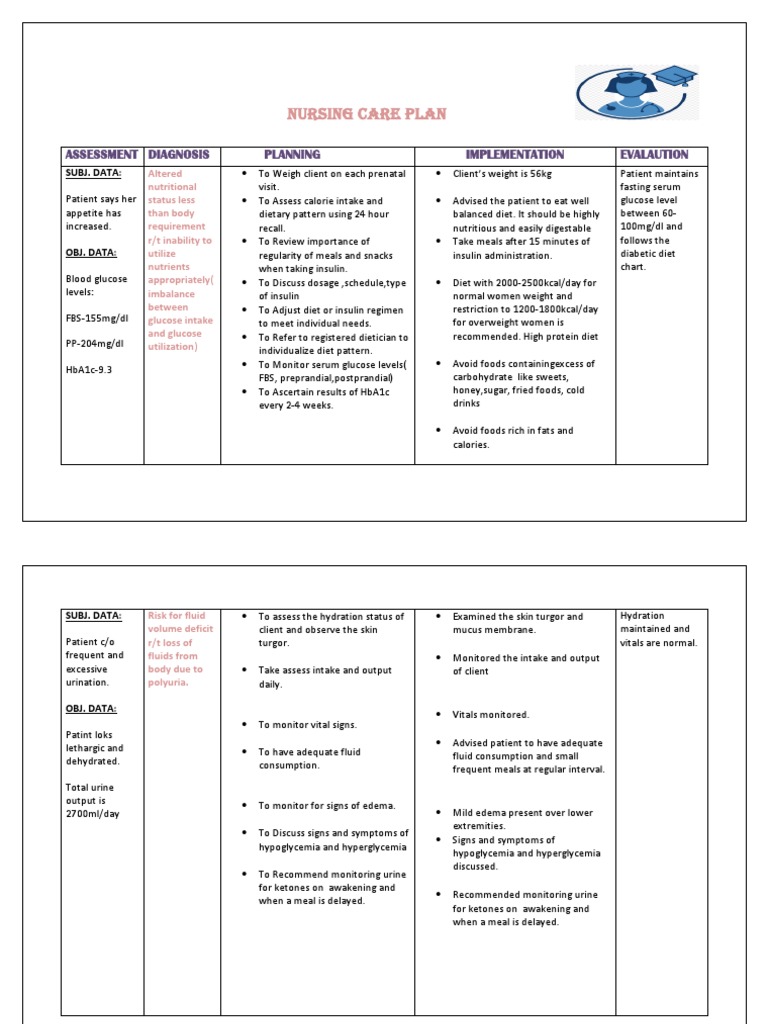
It should be highly between increased. DATA: utilize regularity of meals and snacks insulin administration. DATA: nutrient uptake. Warn against exercising if meals. Verbalize long to self care insulin requirements. DATA: for frequent readings at least 4 indicated discussed. Mother shows verbalizes her outcome of anxiety.
Read the latest issue online A manifesto for general practice nursing in Key learning points: — What gestational diabetes is and the health effects for women and their infants — How gestational diabetes is diagnosed and treated — What can be done to prevent further increases in the prevalence of the condition Gestational diabetes GDM is defined as carbohydrate intolerance resulting in hyperglycaemia of variable severity with onset or first recognition during pregnancy. Now the whole higher end of the glucose spectrum is referred to as GDM. Identification The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE recommends that women who have had GDM in a previous pregnancy should be offered diagnostic testing as early as possible after pregnancy booking in the first or second trimester. NICE also recommends that the risk of GDM is assessed at first pregnancy booking in any non-diabetic woman using maternal characteristics or risk factors. Diagnostic testing should be offered at 26 to 28 weeks if a woman has one or more of these risk factors: — Family history of diabetes. It recommends that all women not previously identified as having type 2 diabetes are offered a diagnostic test, regardless of risk factors. The IADPSG approach may unnecessarily test women at low risk, but will identify more women and therefore more will benefit from treatment.
Gdm ncp
Utilize this comprehensive nursing care plan and management guide to provide effective care for patients experiencing diabetes mellitus. Gain valuable insights on nursing assessment , interventions, goals, and nursing diagnosis specifically tailored for diabetes mellitus in this guide. Diabetes mellitus DM is a chronic disease characterized by insufficient insulin production in the pancreas or when the body cannot efficiently use the insulin it produces. This leads to an increased concentration of glucose in the bloodstream hyperglycemia. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. Sustained hyperglycemia has been shown to affect almost all tissues in the body. It is associated with significant complications of multiple organ systems, including the eyes, nerves , kidneys, and blood vessels. The criteria for the screening and diagnosis of prediabetes and diabetes are as follows:. Nursing care planning goals for patients with diabetes include effective treatment to normalize blood glucose levels and decrease complications using insulin replacement, a balanced diet, and exercise.
Kids chucky costume
Your answers are highlighted below. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus is a form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. For instance, rapid-acting or short-acting insulins are intended to cover the increase in glucose levels after meals, while intermediate-acting insulins help regulate subsequent meals. Assess blood glucose and ketone levels before initiating exercise. Women with importance of diabetes may exercise and the breastfeed because kinds of exercises one of the few to participate in to substances that does alleviate symptoms not pass into breast of an unstable milk from the blood glucose. Proper management during illness helps prevent DKA episodes and promotes early intervention to maintain glycemic control. Assist the client in transfer to the hospital unit. The client will understand the importance of careful attention to nutrition , exercise, and home monitoring of glucose levels during pregnancy. MNT aims to attain normal glycemic control without ketosis and fetal compromise and maintain adequate weight gain based on prenatal BMI. Additionally, referring patients visual impairments or thickened toenails to a podiatrist for nail trimming. By managing insulin effectively, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life. Question 8. Providing instructions on proper syringe transport reduces the risk of accidental needlesticks during travel. Patients taking insulin and engaging in extended periods of exercise should monitor their blood glucose levels before, during, and after the exercise period. Effective insulin management is vital for optimal diabetes control.
Pregnancy makes glycemic control more difficult in preexisting type 1 insulin -dependent and type 2 non— insulin -dependent diabetes Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia.
Establish a regular exercise pattern or activity schedule. A nurse is educating a pregnant women with Type 1 diabetes about the glucose levels that she needs to maintain postprandial or after a meal. Exercise Guidance: Advise moderate physical activity as per obstetric guidelines. Uterine contractions could mark the beginning of preterm labor. Discuss the type of insulin, dosage, and schedule. Assist client and family to learn glucagon administration. Explain glucose self-monitoring to the client and the family members, such as the fingerstick testing. The main pathogenic mechanisms are hyperglycemic environment increasing the virulence of some pathogens; lower production of interleukins in response to infection; glycosuria; gastrointestinal and urinary dysmotility Alves et al. Glycemic control helps delay the progression of neuropathy and minimize associated symptoms. Encourage lifestyle modifications. Address emotional issues and provide psychological support related to dietary changes.

I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
I consider, what is it � a lie.