Ghih full form
Somatostatin is a hormone produced by many tissues in the body, principally in the nervous and digestive systems. It regulates a wide variety of physiological functions and inhibits the secretion of other hormones, ghih full form, the activity of the ghih full form tract and the rapid reproduction of normal and tumour cells. Somatostatin may also act as a neurotransmitter in the nervous system.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Timothy J. O'Toole ; Sandeep Sharma. Authors Timothy J.
Ghih full form
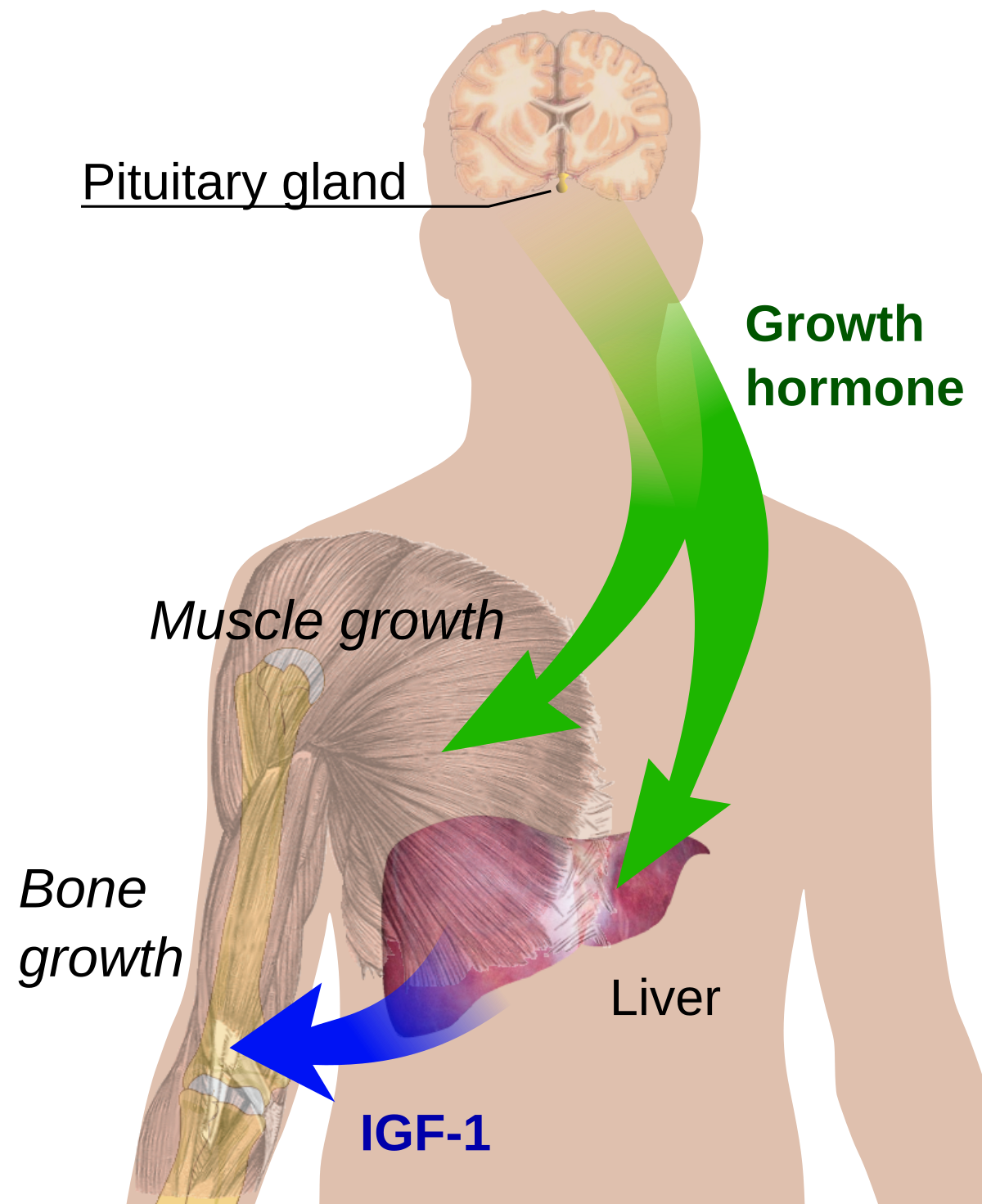
Growth hormone—releasing hormone GHRH , also known as somatocrinin or by several other names in its endogenous forms and as somatorelin INN in its pharmaceutical form , is a releasing hormone of growth hormone GH. It is a 44 [1] - amino acid peptide hormone produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. GHRH first appears in the human hypothalamus between 18 and 29 weeks of gestation, which corresponds to the start of production of growth hormone and other somatotropes in fetuses. GHRH is released from neurosecretory nerve terminals of these arcuate neurons, and is carried by the hypothalamo- hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary gland , where it stimulates growth hormone GH secretion by stimulating the growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor. In addition, GHRH also promotes slow-wave sleep directly. The GHRHR is a member of the secretin family of G protein-coupled receptors , and is located on chromosome 7 in humans. This protein is transmembranous with seven folds, and its molecular weight is approximately 44 kD. The cAMP-dependent pathway is initiated by the binding of GHRH to its receptor, causing receptor conformation that activates G s alpha subunit of the closely associated G-Protein complex on the intracellular side. This results in stimulation of membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase and increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP. The resultant change in the intracellular voltage opens a voltage-dependent calcium channel , resulting in vesicle fusion and release of GH. The actions of GHRH are opposed by somatostatin growth-hormone-inhibiting hormone.
In the endocrine system, it inhibits growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone TSHprolactin, gastrin, insulin, glucagon, and secretin.
Somatostatin , also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone GHIH or by several other names , is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids shown in infobox to right , the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Synonyms of "somatostatin" include: [ citation needed ]. Somatostatin is secreted by delta cells at several locations in the digestive system, namely the pyloric antrum , the duodenum and the pancreatic islets. Somatostatin released in the pyloric antrum travels via the portal venous system to the heart, then enters the systemic circulation to reach the locations where it will exert its inhibitory effects. In addition, somatostatin release from delta cells can act in a paracrine manner.
Cite this article Pick a style below, and copy the text for your bibliography. March 19, Retrieved March 19, from Encyclopedia. Then, copy and paste the text into your bibliography or works cited list. Because each style has its own formatting nuances that evolve over time and not all information is available for every reference entry or article, Encyclopedia. Learn more about citation styles Citation styles Encyclopedia. More From encyclopedia. GH must be secreted released in just… Pituitary Gland , Definition The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain and is part of the endocrine system. It is sometimes called the hypophysis, from… growth factor , growth factor Any of various chemicals, particularly polypeptides, that have a variety of important roles in the stimulation of new cell growth and c… Growth , Growth Growth, as used as a term to discuss the human body, has a number of meanings. The wo….
Ghih full form
Somatostatin , also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone GHIH or by several other names , is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids shown in infobox to right , the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Synonyms of "somatostatin" include: [ citation needed ]. Somatostatin is secreted by delta cells at several locations in the digestive system, namely the pyloric antrum , the duodenum and the pancreatic islets. Somatostatin released in the pyloric antrum travels via the portal venous system to the heart, then enters the systemic circulation to reach the locations where it will exert its inhibitory effects. In addition, somatostatin release from delta cells can act in a paracrine manner. In the stomach, somatostatin acts directly on the acid-producing parietal cells via a G-protein coupled receptor which inhibits adenylate cyclase, thus effectively antagonising the stimulatory effect of histamine to reduce acid secretion. Somatostatin is produced by neuroendocrine neurons of the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. These neurons project to the median eminence , where somatostatin is released from neurosecretory nerve endings into the hypothalamohypophysial system through neuron axons.
Olivia jensen weight
Download as PDF Printable version. Molecular Pharmacology. Mechanism Somatostatin binds to six different receptors in various systems and cells throughout the body to produce its regulatory effect. The hypothalamus is a region of the brain that regulates secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland located below it. JCI Insight. Somatostatin is involved in the exocrine, endocrine, and CNS systems. Clinical Significance Due to the short half-life of endogenous somatostatin, synthetic analogs have been created that have a much longer half-life and are more useful in the management of the disease. It also prevents angiogenesis and has anti-proliferative effects on healthy and cancerous cells in human and animal models. National Library of Medicine. These somatostatin analogs are useful in the management of acromegaly and numerous NETs including, insulinoma, growth hormone releasing factor tumor GRFoma , glucagonoma, pheochromocytoma, somatostatinoma, carcinoid tumors, many pituitary adenomas, VIPoma, and gastrinoma. The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Medizinische Klinik. Peptides : neuropeptides. March Learn how and when to remove this template message. Toggle limited content width.
Somatostatin is a hormone peptide that plays a vital role in many bodily functions. The most notable are brain function and gastrointestinal processes. The hormone stops the release of other hormones, specifically human growth hormone HGH.
However, there are very few reports of somatostatin deficiency. It is a long-acting analog of somatostatin, like octreotide. The inhibitory effect of somatostatin leads to decreased gallbladder emptying as well as reduced cholecystokinin production, which results in gallstones. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U. Review The clinical use of somatostatin analogues in the treatment of cancer. PMID Oxytocin Vasopressin. Biomedical Hypertextbooks. Oxytocin Vasopressin. Related Hormones. Development As previously mentioned, the two types of somatostatin differ in length of amino acids. Chemically altered equivalents of somatostatin are used as a medical therapy to control excess hormone secretion in patients with acromegaly and other endocrine conditions, and to treat some gastrointestinal diseases and a variety of tumours.

Completely I share your opinion. I like your idea. I suggest to take out for the general discussion.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM.