Guttation diagram
Use app Login. What is guttation? Explain with the help of diagram of the vertical section of hydathode present on apical part of tomato or primula leaf. Open in App, guttation diagram.
Guttation is a process by which plants release excess water from leaves as droplets. A specialized organ known as a hydathode is used for this process so that plants can maintain optimum water balance. In this article, we will read about the demonstration, its mechanism, and demonstration , the role of hydathodes in guttation , the composition of water released during guttation , the difference between guttation and transpiration , and the importance of guttation. Guttation is a process that occurs in the case of vascular plants, in which excess water is removed from the leaf tips. Pores similar to stomata called hydathodes are present on the leaf tips that aid in this process. It occurs during the night when all the water is retained within the plant and gets excreted out due to high root pressure.
Guttation diagram
.
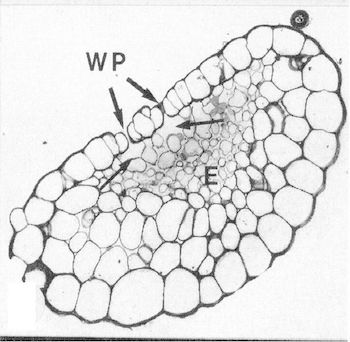
Hydathodes release water from the pores of the margin of leaves. Hydathodes are also known as water stomata.
.
Guttation is the process of liquid exudation from hydathodes situated on the tip, along the margins and adaxial and abaxial surfaces of leaves. Hydathodes, also known as water stomata or water pores, unlike stomata, are always open representing the path of least resistance to the liquid outflow from them. Guttation fluids contain a variety of living and non-living ingredients. The living materials include algae, fungi, bacteria, viroids and viruses. The non-living organic constituents include toxins, mycotoxins, alkaloids, proteins, enzymes, sugars, amino acids, volatiles, hormones, vitamins, etc. This review highlights various techniques for measuring guttation, both qualitative and quantitative, and their use and utility are discussed. Further, the microbiological aspects of guttation, with particular reference to the incidence of algal, fungal, bacterial and viral diseases and toxins produced by these pathogenic organisms, are described.
Guttation diagram
Hydathodes form natural openings but, unlike stomata, are open permanently and offer little resistance to the flow of fluid out of leaves. The cells of epithem are soft and made of loosely arranged thin-walled parenchyma cells and without chloroplast, and are involved in absorption and secretion. Internally, they are connected by tracheary endings to a large chamber with masses of thin-walled parenchymatous tissue surrounded by a sheath layer. Ultrastructurally, the epithem cells have a dense cytoplasm, numerous mitochondria, an extensive endoplasmic reticulum system, many small Golgi-derived vesicles, numerous peroxisomes, and are interconnected by abundant plasmodesmata. Functionally, there are two types of hydathodes, namely, epidermal ones that actively exude fluid, and epithemal hydathodes that passively exude fluid. Natural guttation is often observed during early morning or late hours of the day.
Icy veins blood dk
The development of root pressure in a plant leads to positive hydrostatic pressure in xylem sap throughout the plant. Complete Tutorials. Report issue Report. Similar Questions. Explore offer now. Brain Teasers. Guttation: Definition, Hydathodes and Mechanism. The water released during guttation consists of a dilute liquid of mineral salts. We use cookies to ensure you have the best browsing experience on our website. Pores similar to stomata called hydathodes are present on the leaf tips that aid in this process. Guttation occurs during the night. Humans excrete excess fluids to avoid internal imbalances, plants release water through hydathodes to prevent overhydration and potential cellular damage. Influenced by factors such as sunlight , temperature and humidity. It occurs during the night when all the water is retained within the plant and gets excreted out due to high root pressure.
Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants , such as grasses , and a number of fungi , which are not plants but were previously categorized as such and studied as part of botany. At night, transpiration usually does not occur, because most plants have their stomata closed. When there is a high soil moisture level, water will enter plant roots, because the water potential of the roots is lower than in the soil solution.
Work Experiences. Article Tags :. Suggest Changes. Because of water-conducting xylem elements is a vascular bundle terminate in a hydathode, xylem sap is forced to flow through the hydathodes. Let us understand in detail. In this article, we will read about the demonstration, its mechanism, and demonstration , the role of hydathodes in guttation , the composition of water released during guttation , the difference between guttation and transpiration , and the importance of guttation. Campus Experiences. Guttation is the loss of water in the form of water droplets from small pores. Plants having vascular systems are wheat, barley, grass, strawberries and tomatoes. Save Article Save. Guttation is a process by which plants release excess water from leaves as droplets. Open In App. Enhance the article with your expertise. The hydathode is made up of epithelial cells and has multiple intercellular spaces that are filled with water. Like Article Like.

In my opinion you are not right. I am assured.
And I have faced it.
I confirm. So happens.