Haplogroup
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, haplogroup. Figure S2.
As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup or paragroup. As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy , in which each set haplogroup is also a subset of a single broader set as opposed, that is, to biparental models, such as human family trees. Haplogroups can be further divided into subclades.
Haplogroup
A haplogroup is a genetic population group of people who share a common ancestor on the patriline or the matriline. Top-level haplogroups are assigned letters of the alphabet, and deeper refinements consist of additional number and letter combinations. For Y-DNA, a haplogroup may be shown in the long-form nomenclature established by the Y Chromosome Consortium , or it may be expressed in a short-form using a deepest-known single-nucleotide polymorphism SNP. SNPs are locations on the DNA where one nucleotide has "mutated" or "switched" to a different nucleotide. Because a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes , it is possible to predict a haplogroup from the haplotype. A SNP test is required to confirm the haplogroup prediction. Not all the testing companies offer SNP testing, and consequently their customers' haplogroup predictions are sometimes inaccurate. For advice on SNP testing it is recommended that you join the appropriate Y-DNA haplogroup project and seek advice from the volunteer project administrators. The tree is updated as and when new branch-defining SNPs are discovered. The criteria for inclusion of SNPs in the tree are published here.
In Hadley D. Other languages:. The Viking presence in England?
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The Y chromosome contains the largest nonrecombining block in the human genome. By virtue of its many polymorphisms, it is now the most informative haplotyping system, with applications in evolutionary studies, forensics, medical genetics, and genealogical reconstruction. However, the emergence of several unrelated and nonsystematic nomenclatures for Y-chromosomal binary haplogroups is an increasing source of confusion.
In this article, we intend to educate you about haplogroups, whilst answering some of the most frequent questions surrounding them. Welcome back! Ah, the big question. Well, to simplify, according to the International Society of Genetic Genealogy, a haplogroup is a genetic population group of people who share a common ancestor on either their paternal or maternal line. Particular haplogroups are associated with well-known ancestral groups such as the Vikings , Aboriginal Australians, and the Celts. While Living DNA can't tell you whether your haplogroup is associated with these ancestries, there are resources available online to aid your further research and put together the pieces. Haplogroups follow male and female descendancy lines, with Y-DNA passing from father to son, and mtDNA passing from mothers to both daughters and sons. All haplogroups started as the original haplogroup in Africa, and as the many millennia have passed by, more and more haplogroups have come to be.
Haplogroup
A macrohaplogroup, its descendant lineages are distributed across many continents. Like its sibling macrohaplogroup M , macrohaplogroup N is a descendant of the haplogroup L3. M and N are the signature maternal haplogroups that define the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans and subsequent early human migrations around the world. The global distribution of haplogroups N and M indicates that there was likely at least one major prehistoric migration of humans out of Africa, with both N and M later evolving outside the continent. There is widespread agreement in the scientific community concerning the African ancestry of haplogroup L3 haplogroup N's parent clade. The out of Africa hypothesis has gained generalized consensus.
Morning star koh phangan
Lineages defined solely by the presence of a derived marker are monophyletic. Genome Research , 5 1 , 42— Wiley-Blackwell, American Journal of Biological Anthropology , 2 , — Y chromosome sequence variation and the history of human populations. Related Stories Ancestry. Found in almost all European countries, but most common in Gagauzia , southeastern Romania , Greece , Italy , Spain , Portugal , Tyrol , and Bohemia with highest concentrations on some Mediterranean islands; uncommon in Northern Europe. In addition, early branching subhaplogroup J1b mtDNAs Top-level haplogroups are assigned letters of the alphabet, and deeper refinements consist of additional number and letter combinations. Paternal Haplogroups and Women A woman can infer her paternal haplogroup if a male relative on her paternal line has been genotyped by 23andMe. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources at this section. The Y chromosome contains the largest nonrecombining block in the human genome. Systematic Biology , 52 5 , —
The clade arose from haplogroup R , likely during the early Upper Paleolithic.
Receive the latest from your DNA community. Population genomics of bronze age Eurasia. This means the Y chromosome and mtDNA share specific properties. The Viking world. Subhaplogroups J1c4 5. R — Large group found within the N type. Several of the highly conserved haplogroup J polymorphisms were correlated with an increase of energy deficiency and longevity. February The phylogeography of Y chromosome binary haplotypes and the origins of modern human populations. Until , there were only 11 known binary polymorphisms that could be genotyped by PCR-based methods Hammer ; Seielstad et al. Within J2, subhaplogroups J2b and J2b1

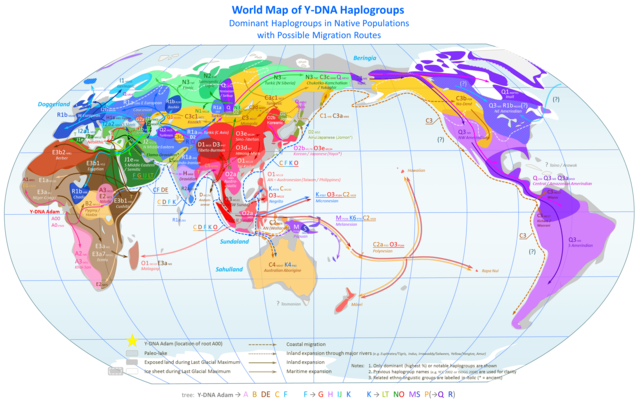
0 thoughts on “Haplogroup”