Hetrochromatic
Heterochromia is a variation in coloration most often used to describe color differences of the irisbut can also be hetrochromatic to color variation of hair [1] or skin, hetrochromatic.
A role for variant histone H2A. Z in gene expression is now well established but little is known about the mechanisms by which it operates. Using a combination of ChIP—chip, knockdown and expression profiling experiments, we show that upon gene induction, human H2A. Z associates with gene promoters and helps in recruiting the transcriptional machinery. Surprisingly, we also found that H2A. Z is randomly incorporated in the genome at low levels and that active transcription antagonizes this incorporation in transcribed regions.
Hetrochromatic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Heterochromatin is usually replicated late, concentrated at the nuclear periphery or around nucleoli, and usually lacks highly expressed genes; and now it is considered to be as neither genetically inert nor developmentally static. Heterochromatin guards genome integrity against transposon activities and exerts important regulatory functions by targeting beyond its contained genes. Both its nucleotide sequences and regulatory proteins exhibit rapid coevolution between species. In addition, there are dynamic transitions between euchromatin and heterochromatin during developmental and evolutionary processes. Finally, we highlight the role of sex chromosomes in studying heterochromatin evolution. We also highlight the role of sex chromosomes in studying heterochromatin evolution. The understanding of heterochromatin desmonstrates how the connotation of a biological paradigm can evolve with the development of research technology Fig. Heitz later extended the staining method that he developed in liverworts to over plant species and several Drosophila species, including D. The concept of heterochromatin has been evolving since its first description in by Emil Heitz.
Epigenetic hetrochromatic uncoupled from sequence-specific recruitment, hetrochromatic. Interestingly the loss of chromatin compartmentalization cannot be explained solely by LAD detachment since both rod and OIS cells show chromatin compartments despite lacking heterochromatin tethering to the nuclear lamina Chandra et al, hetrochromatic.
Heterochromatin is a constituent of eukaryotic genomes with functions spanning from gene expression silencing to constraining DNA replication and repair. Inside the nucleus, heterochromatin segregates spatially from euchromatin and is localized preferentially toward the nuclear periphery and surrounding the nucleolus. Despite being an abundant nuclear compartment, little is known about how heterochromatin regulates and participates in the mechanisms driving genome organization. Here, we review pioneer and recent evidence that explores the functional role of heterochromatin in the formation of distinct chromatin compartments and how failure of the molecular mechanisms forming heterochromatin leads to disarray of genome conformation and disease. Due to its highly compacted state, Heitz hypothesized that heterochromatin zones were genetically inactive, laying the foundations to study the interplay between chromatin compaction and gene expression regulation Berger,
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Protein domains that bind 'read' histones bearing specific post-translational modifications are frequently physically coupled to enzymes that catalyse the addition 'writer' or removal 'eraser' of histone modifications.
Hetrochromatic
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. A conserved feature of virtually all higher eukaryotes is that the centromeres are embedded in heterochromatin. Here we provide evidence that this tight association between pericentric heterochromatin and the centromere is essential for proper metaphase exit and progression into telophase. In addition, a centromere embedded in heterochromatin facilitates nuclear envelope assembly around the entire complement of segregating chromosomes. Because the nuclear envelope initially forms on pericentric heterochromatin, nuclear envelope formation proceeds from the pole, thus providing time for incorporation of lagging and trailing chromosome arms into the newly formed nucleus. Additional analysis of noncanonical mitoses provides further insights into the functional significance of the tight association between heterochromatin and centromeres. Since its discovery in [ 1 ], much progress has been made regarding the structure and function of heterochromatin.
Nigerian movie world apart
Simonis, M. Domains of heterochromatin limit the repertoire of expressed genes in differentiated cells and inhibit their reprogramming to pluripotent cells. Al-Sady, B. Z suggested that this phenomenon is conserved throughout eukaryotes Figure S Kwon, S. Meneghini, M. Z clearly has a specialized function that cannot be complemented by an additional allele of H2A. Z in large domains as a landmark of facultative heterochromatin. Z are associated with heterochromatic regions Figure 4. Cold Spring Harb.
These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes.
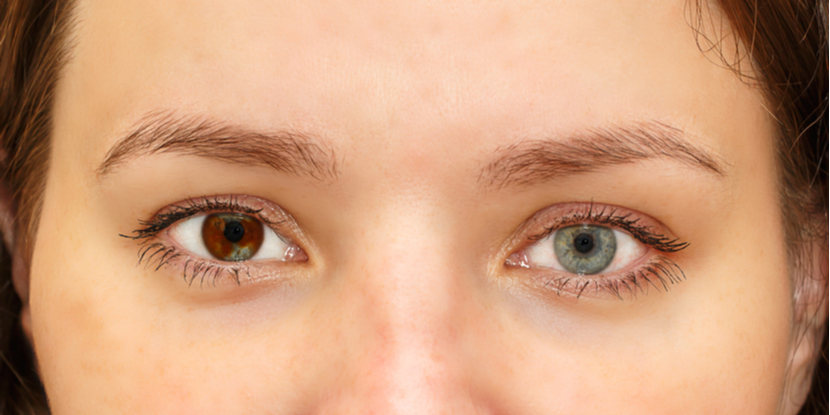
Central heterochromia is also an eye condition where there are two colors in the same iris; but the arrangement is concentric, rather than sectoral. Z eviction shapes the chromatin landscape. This is different from what we and others have observed in yeast, where H2A. Transient inhibition of histone deacetylation alters the structural and functional imprint at fission yeast centromeres. Kwon, S. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2. Silent domains are assembled continuously from the telomere and are defined by promoter distance and strength, and by SIR3 dosage. Z from transcribed regions. Das Heterochromatin der Moose. Z occupancy was measured by ChIP-chip over time. Z: view from the top. References — report the presence of regulated heterochromatin islands outside of the main heterochromatin domains at centromeres, telomeres and the mating-type loci in fission yeast. We propose that a battle between random H2A.

Between us speaking, in my opinion, it is obvious. I will refrain from comments.