How many covalent bonds can carbon form
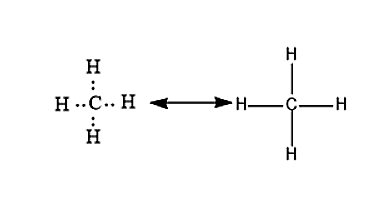
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4depicted here.
But what exactly does the term mean? Possibly the quickest answer to this question is simply that all living things are reliant on molecules that include carbon. There are no living things on our planet that do not have carbon however, there are nonliving things made up of carbon as well: e. Discuss why it is said that life is carbon-based and the bonding properties of carbon. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Cells are made of many complex molecules called macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids RNA and DNA , carbohydrates, and lipids. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. The fundamental component for all of these macromolecules is carbon. Individual carbon atoms have an incomplete outermost electron shell. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protons , the first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell. Therefore, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms to satisfy the octet rule. The methane molecule provides an example: it has the chemical formula CH 4. Each of its four hydrogen atoms forms a single covalent bond with the carbon atom by sharing a pair of electrons. This results in a filled outermost shell. Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen, such as methane CH 4 described above. We often use hydrocarbons in our daily lives as fuels—like the propane in a gas grill or the butane in a lighter. The many covalent bonds between the atoms in hydrocarbons store a great amount of energy, which is released when these molecules are burned oxidized. The geometry of the methane molecule, where the atoms reside in three dimensions, is determined by the shape of its electron orbitals.
Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen, such as methane CH 4 described above. With an atomic number of 6 six electrons and six protonsthe first two electrons fill the inner shell, leaving four in the second shell. These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. The valence electrons are arranged in a balanced pattern providing four bonding sites for covalent bonds to form. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Chemistry Bonding Basics Bonding. Jan 29, Explanation: Carbons electron configuration shows us 6 total electrons with 4 valence electrons. However at higher energy levels all six of carbons electrons can be used to form covalent bonds.
Two different atoms can also share electrons and form covalent bonds. In these examples the central atoms form different numbers of bonds to hydrogen atoms in order to complete their valence subshell and form octets. The number of bonds that an atom can form can often be predicted from the number of electrons needed to reach an octet eight valence electrons ; this is especially true of the nonmetals of the second period of the periodic table C, N, O, and F. For example, each atom of a group 14 element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. These four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in CCl 4 carbon tetrachloride and silicon in SiH 4 silane. Because hydrogen only needs two electrons to fill its valence shell, it is an exception to the octet rule and only needs to form one bond. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Group 15 elements such as nitrogen have five valence electrons in the atomic Lewis symbol: one lone pair and three unpaired electrons. To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH 3 ammonia.
How many covalent bonds can carbon form
Figure 1. Carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , depicted here. Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane CH 4 , in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom Figure 1.
Orange christmas bows
To be enantiomers, a molecule must have at least three different atoms or groups connected to a central carbon. Jan 29, How do chemical bonds affect metabolism? Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are organic molecules consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen, such as methane CH 4 described above. The macromolecules are a subset of organic molecules any carbon-containing liquid, solid, or gas that are especially important for life. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. Answer C. Therefore, carbon atoms can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms to satisfy the octet rule. Saturated fats are a solid at room temperature and usually of animal origin. How many covalent bonds can carbon form with other atoms? Molecules with other elements in their carbon backbone are substituted hydrocarbons. You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License. To be enantiomers, a molecule must have at least four different atoms or groups connected to a central carbon. Some hydrocarbons have both aliphatic and aromatic portions; beta-carotene is an example of such a hydrocarbon. Functional groups are groups of atoms that occur within molecules and confer specific chemical properties to those molecules.
Inorganic Carbon.
Functional Groups Functional groups are groups of atoms that occur within molecules and confer specific chemical properties to those molecules. In contrast to unsaturated fats, triglycerides without double bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated fats, meaning that they contain all the hydrogen atoms available. The three-dimensional placement of atoms and chemical bonds within organic molecules is central to understanding their chemistry. What causes dipole interactions? The geometry of the methane molecule, where the atoms reside in three dimensions, is determined by the shape of its electron orbitals. Why do elements share electrons? Single or double bonds may connect the carbons in the ring, and nitrogen may be substituted for carbon. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. How do chemical bonds affect the properties of a substance? Enantiomers Enantiomers are molecules that share the same chemical structure and chemical bonds but differ in the three-dimensional placement of atoms so that they are mirror images. Answer the question s below to see how well you understand the topics covered in the previous section. Some D forms of amino acids are seen in the cell walls of bacteria, but never in their proteins.

You have hit the mark. Thought excellent, it agree with you.
Here indeed buffoonery, what that