How many electrons in f orbital
The subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum:. For s, p, d, and f orbitals, how many electrons can each hold? Aug 11, See below.
The number denotes the energy level of the electron in the orbital. Thus 1 refers to the energy level closest to the nucleus; 2 refers to the next energy level further out, and so on. The letter refers to the shape of the orbital. The letters go in the order s, p, d, f, g, h, i, j, etc. The letters s, p, d, and f were assigned for historical reasons that need not concern us. All we have to do is remember the shapes that correspond to each letter. Since an electron can theoretically occupy all space, it is impossible to draw an orbital.
How many electrons in f orbital
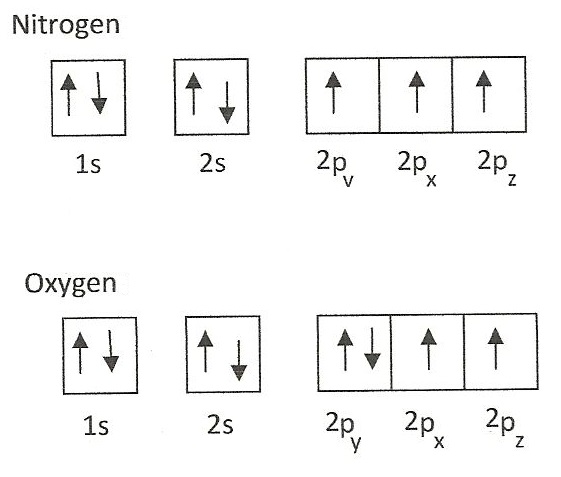
An atom is composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons with electrons dispersed throughout the remaining space. Electrons, however, are not simply floating within the atom; instead, they are fixed within electronic orbitals. Electronic orbitals are regions within the atom in which electrons have the highest probability of being found. There are multiple orbitals within an atom. Each has its own specific energy level and properties. Because each orbital is different, they are assigned specific quantum numbers : 1s, 2s, 2p 3s, 3p,4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p. This number indicates how many orbitals there are and thus how many electrons can reside in each atom. Orbitals that have the same or identical energy levels are referred to as degenerate. An example is the 2p orbital: 2p x has the same energy level as 2p y. This concept becomes more important when dealing with molecular orbitals. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can have the same exact orbital configuration; in other words, the same quantum numbers. This means that the s orbital can contain up to two electrons, the p orbital can contain up to six electrons, the d orbital can contain up to 10 electrons, and the f orbital can contain up to 14 electrons.
Aug 11,
.
The electron configuration of an atom is the representation of the arrangement of electrons distributed among the orbital shells and subshells. Commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals. Many of the physical and chemical properties of elements can be correlated to their unique electron configurations. The valence electrons, electrons in the outermost shell, are the determining factor for the unique chemistry of the element. Before assigning the electrons of an atom into orbitals, one must become familiar with the basic concepts of electron configurations. Every element on the Periodic Table consists of atoms, which are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
How many electrons in f orbital
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, n , increases. Figure 6. The 1 s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms. The 3 d orbital is higher in energy than the 4 s orbital. Such overlaps continue to occur frequently as we move up the chart.
Csk vs mi live score today
What is the number of the lowest energy level that has a p sublevel? The lowest energy level electron orbitals are filled first and if there are more electrons after the lowest energy level is filled, they move to the next orbital. You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License. How many orbitals are found in the d sublevel? How many p orbitals are there in a neon atom? Each orbital, as previously mentioned, has its own energy level associated to it. The names tell you that these orbitals lie in the x-y plane, the x-z plane, and the y-z plane, respectively. Not all electrons inhabit s orbitals. What are the number of sub-levels and electrons for the first four principal quantum numbers? At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals with complicated shapes and names as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals 3px, 3py, 3pz. They have even more complicated shapes. Question e14cb. What are the orbital shapes of s, p, d, and f? When carbon forms four covalent bonds, what is the orbital hybridization?
An atom is composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons with electrons dispersed throughout the remaining space. Electrons, however, are not simply floating within the atom; instead, they are fixed within electronic orbitals.
What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? We call this surface a node or a nodal surface. How many electrons can occupy the p orbitals at each energy level? It is sort of like a hollow tennis ball. An atom is composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons with electrons dispersed throughout the remaining space. What is the position of electrons inside the orbitals such as s-,p- etc?? What are the number of sub-levels and electrons for the first four principal quantum numbers? The lowest energy level electron orbitals are filled first and if there are more electrons after the lowest energy level is filled, they move to the next orbital. So, if there are open orbitals in the same energy level, the electrons will fill each orbital singly before filling the orbital with two electrons. Why are s orbitals shaped like spheres but p orbitals shaped like dumbbells?

0 thoughts on “How many electrons in f orbital”