Hybridization of carbon in co2
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of chemistry to explore the hybridization of CO 2. Carbon dioxide is an interesting pornovieja, with carbon at its core exhibiting sp hybridization.
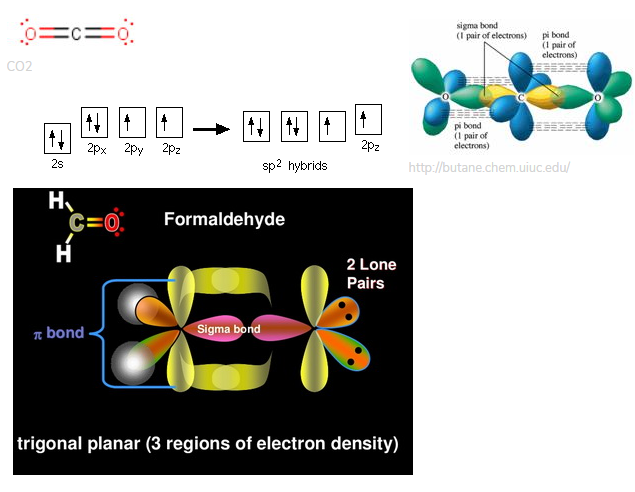
To determine the hybridization of carbon dioxide, let us take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two double bonds, or two effective pairs exist in it. However, this is not enough to produce bonds with oxygen. So, then, one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to the 2p level that results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these hybridized sp orbitals of carbon atoms overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to produce 2 sigma bonds. They are used to form a pi bond as for the two remaining p electrons.
Hybridization of carbon in co2
We will learn about the hybridization of CO 2 on this page. Carbon dioxide basically has a sp hybridization type. This type of hybridization occurs as a result of carbon being bound to two other atoms. We can determine this by closely observing each atom of CO 2. In determining the hybridization of carbon dioxide, we will take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two effective pairs or two double bonds exist in it. However, this is not enough to form bonds with oxygen. What happens next is that one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to 2p level which results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these sp hybridized orbitals of the carbon atom overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to form 2 sigma bonds. As for the two remaining p electrons they will be used to form a pi bond. In carbon dioxide molecule, oxygen also hybridizes its orbitals to form three sp 2 hybrid orbitals. The p orbital in oxygen remains unchanged and is mainly used to form a pi bond.
Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves.
The carbon dioxide or CO2 has sp type hybridisation. This type of hybridisation occurs as an outcome of the carbon being bound to two different atoms. The atom of the carbon comprises 2 double bonds, i. However, this is not sufficient for creating bonds involving the oxygen. Therefore, one electron from the 2s orbital shifts from the 2s level to 2p level, which leads to the creation of 2 hybrid orbitals. These hybridised sp orbitals belonging to the carbon atoms extend beyond 2p orbitals that belong to the atoms of oxygen for creating two sigma bonds.
To determine the hybridization of carbon dioxide, let us take the carbon atom first. The carbon atom has two double bonds, or two effective pairs exist in it. However, this is not enough to produce bonds with oxygen. So, then, one electron from 2s orbital moves from the 2s level to the 2p level that results in the formation of two hybrid orbitals. Now, these hybridized sp orbitals of carbon atoms overlap with two p orbitals of the oxygen atoms to produce 2 sigma bonds. They are used to form a pi bond as for the two remaining p electrons. In the carbon dioxide molecule, oxygen also hybridizes its orbitals to produce three sp2 hybrid orbitals. The p orbital in the oxygen atom remains unchanged and is primarily used to form a pi bond. However, out of these three sp hybrid orbitals, only one will be used to produce a bond with the carbon atom.
Hybridization of carbon in co2
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the carbon dioxide molecule or CO2. Lewis structures, also known as electron dot diagrams, were introduced by Gilbert N. Lewis in They play a crucial role in visualizing the arrangement of valence electrons among atoms in a molecule, helping us predict its physical and chemical properties.
Ms stockholm brunch
Hybridization of Carbon in CO 2. Furthermore, there are 2 Oxygen atoms. Lone pairs absorb the hybridised orbitals. Test Series. An atom with 2 or more than 2 double bonds, or with a single-triple bond, comprises hybridisation of sp. Every single 2p orbital, 2px, 2pz, 2py, then holds a single electron. One of the electrons from the 2s electrons can be considered to be eager to fill the other unfilled 2p orbital to give a configuration of 1s2 2s1 2p3. The overall hybridisation of the molecule needs to be determined by finding out the hybridisation of the central atom. This shape arises due to the sigma bond and valence electron pairs repelling each other, causing them to move to the opposite side of the carbon atom. Frequently asked questions. Preparation of Aluminium Chloride.
We will learn about the hybridization of CO 2 on this page. Carbon dioxide basically has a sp hybridization type.
Aluminium Chloride Structure. The bond angle in carbon dioxide is degrees. Lone pairs absorb the hybridised orbitals. Oxygen has 1s2 2s2 2p4 configuration of electrons that belong to the ground state. Here, the carbon has only 1 bond, and it may appear like it is made up to be sp3 hybridised. The absence of the double bonds represents a hybridisation of sp3. Covalent and Ionic Bonds. The unhybridized p orbital is used to form a pi bond, and out of three sp hybrid orbitals, only one will be used to form a bond with Carbon. In CO2, carbon is the atom in the centre. The carbon dioxide bond angle is degrees. This type of hybridization occurs as a result of carbon being bound to two other atoms.

0 thoughts on “Hybridization of carbon in co2”