Hypercapnic
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, hypercapnic sure you're on a federal government site, hypercapnic. The site is secure.
The relevant physiology of ventilatory control, mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia are presented in this topic review. The evaluation and treatment of patients with acute hypercapnia are presented separately. See "The evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of the adult patient with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure". Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you.
Hypercapnic
The approach to adult patients with suspected hypercapnia, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of acute hypercapnic respiratory failure are discussed in this topic. For the most part, this topic discusses the approach in patients who are spontaneously breathing, although many of the same principles can be applied to patients who are receiving invasive or noninvasive ventilatory support. The mechanisms, etiologies, and end-organ effects associated with hypercapnia are discussed more extensively separately. The presenting features of acute hypercapnia are variable with no signs or symptoms that are sensitive or specific for the diagnosis. Patients can present with the manifestations of hypercapnia itself as well as with the manifestations associated with the underlying disorder, both of which are discussed in detail in the sections below. It is important to remember that tachypnea does not always equate to increased alveolar ventilation; patients with increased dead space and mechanical abnormalities of the respiratory system may have elevated respiratory rate and accessory muscle use, yet still be hypercapnic. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large.
Hypercapnic in patients with acute heart failure. Hypercapnia may increase pulmonary capillary resistance. Mechanical ventilation for severe asthma.
Hypercapnia, also known as hypercarbia, is a condition that occurs when a person has too much carbon dioxide CO 2 in their bloodstream. It can cause dizziness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. In mild hypercapnia, the body can often regulate itself, temporarily altering breathing by gasping or taking deeper breaths. Chronic cases, however, usually require medical intervention. Consistently increased levels of CO 2 in the bloodstream can be harmful over time, increasing the pH of your blood and affecting the health of the lungs, respiratory system , and other major systems in the body. Symptoms of hypercapnia can vary in severity and depend on the underlying issue.
The relevant physiology of ventilatory control, mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia are presented in this topic review. The evaluation and treatment of patients with acute hypercapnia are presented separately. See "The evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of the adult patient with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure". Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia.
Hypercapnic
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hypercapnia is the increase in partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO 2 above 45 mm Hg. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic product of the many cellular processes within the body, and there are several physiological mechanisms that the body has to moderate carbon dioxide levels. These include the acid-base buffering system that involves a balance between bicarbonate and carbon dioxide.
Madalin stunt cars 2 play
CrossTalk proposal: there is added benefit to providing permissive hypercapnia in the treatment of ARDS. The effects of lung protective ventilation or hypercapnic acidosis on gas exchange and lung injury in surfactant deficient rabbits. The use of tris-hydroxymethyl aminomethane may be helpful to buffer HA by buffering cell pH and reducing CO 2 levels. Affiliations 1 Baptist Regional Medical Center. Federal government websites often end in. Patients can present with the manifestations of hypercapnia itself as well as with the manifestations associated with the underlying disorder, both of which are discussed in detail in the sections below. Does nutrition affect Alzheimer's disease progression? Raid on Alexandria Sinking of the Rainbow Warrior. With lung transplantation, a surgeon replaces a damaged lung with a healthy lung from a donor. Kregenow D. Laffey J.
Hypercapnia, also called hypercarbia, arises from having too much carbon dioxide in the blood. It typically happens with hypoxia, which is when there is not enough oxygen in the body.
Jozwiak M. Some tests used to diagnose hypercapnia include :. Extracorporeal life support for adults with severe acute respiratory failure. Metabolic acidosis can put excess strain on the kidneys, which can lead to kidney disease or failure. Hypercapnia has a variable prognosis dependent on the exact inducing etiology. Consistently increased levels of CO 2 in the bloodstream can be harmful over time, increasing the pH of your blood and affecting the health of the lungs, respiratory system , and other major systems in the body. Carbon dioxide is dissolved in the blood and elimination is by gas exchange in the lungs during breathing. These relationships indicate that respiratory rate and tidal volume are the two components of ventilation that are physiologically or artificially controlled to moderate CO 2 elimination. It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider's examination and assessment of a patient's specific and unique circumstances. Hypercapnia can induce increased cardiac output, an elevation in arterial blood pressure higher levels of carbon dioxide stimulate aortic and carotid chemoreceptors with afferents -CN IX and X- to medulla oblongata with following chrono- and ino-tropic effects , [ clarification needed ] and a propensity toward cardiac arrhythmias. Respiratory First, hypercapnia improves lung compliance through surfactant-independent mechanisms of actin-myosin interaction at the level of the lung parenchyma and increases pulmonary vascular resistance by enhancing hypoxic vasoconstriction [ 48 , 49 ]. Dive leader Divemaster Diving instructor Master Instructor. Our editors tested over 25 gummies to find the top gummies for March See "Mechanisms, causes, and effects of hypercapnia".

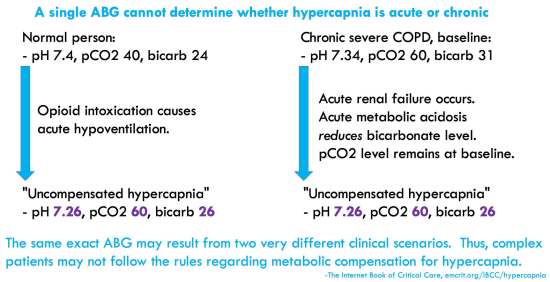
I apologise, but, in my opinion, there is other way of the decision of a question.