Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s
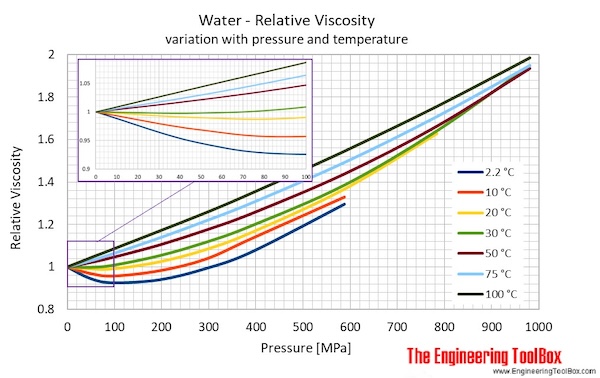
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress. For further definitions, go to Absolute dynamic and kinematic viscosity. Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s, transient or turbulent. The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures.
In this calculator, you will learn what the absolute viscosity of water is commonly known as its dynamic viscosity and how to convert it to kinematic viscosity. You will also learn how to calculate the viscosity of water and the effect of temperature on the viscosity of water using various methods. This water viscosity calculator provides you with a water viscosity to temperature chart and table so you can reference the effects that temperature has on water's viscosity and density of water. Although our charts and tables are in SI units, in this calculator, you will also learn how we can express the viscosity of water in English units. Keep on reading to learn more!
Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s
This is dynamic viscosity. The other way is to measure the resistive flow of a fluid under the weight of gravity. The result is kinematic viscosity. Measuring Kinematic Viscosity. There are several ways to find the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, but the most common method is determining the time it takes a fluid to flow through a capillary tube. The time is converted directly to kinematic viscosity using a calibration constant provided for the specific tube. A basic difference between the dynamic and kinematic viscosity measurements is density. Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. The formula for the conversion is:. For a given sample, with a density greater than one, dynamic viscosity will always be the higher number. Density is the ratio of the mass or weight of the sample divided by the volume of the sample. Think about an ice cube and a cube of steel. They may be the same size, but the steel cube weighs more than the ice cube.
People also viewed….
Water is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature and pressure, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state, steam water vapor. It is vital for all known forms of life. Water plays an important role in the world economy as it functions as a solvent for a wide variety of chemical substances and facilitates industrial cooling and transportation. We use cookies on our website.
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress. For further definitions, go to Absolute dynamic and kinematic viscosity. Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent. The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures. See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties.
Kinematic viscosity of water ft2/s
Water is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature and pressure, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state, steam water vapor. It is vital for all known forms of life. Water plays an important role in the world economy as it functions as a solvent for a wide variety of chemical substances and facilitates industrial cooling and transportation. We use cookies on our website. Some of them are necessary e. In this case your data may potentially be accessed by US Authorities for surveillance purposes and you may not be able to exercise effective legal remedies. You can accept or reject all cookies by clicking on the respective button or define your cookie settings using the link "Customize your cookie settings".
Saucony guide 16 review
In the metric system, the unit of kinematic viscosity is the square centimeter per second or the stoke. Chapter 2 Document 73 pages. Volume 1. How do I determine the viscosity of water? Volume m 3 liters in 3 ft 3 us gal. When choosing between the two viscosities, it is worth noting that dynamic viscosity tells us about the force required to move the fluid at a certain speed. Cold honey will flow even slower than honey at room temperature. Weight 1. Aside from calculating the dynamic viscosity of water, we may also need to determine the kinematic viscosity of water at any temperature. Distillation Principles Document 71 pages. Using the chart, simply:.
Membership Services.
There are several ways to find the kinematic viscosity of a fluid, but the most common method is determining the time it takes a fluid to flow through a capillary tube. How do I determine the viscosity of water? Some of them are necessary e. Analysis 0 We collect and combine data on our visitors and their behavior on our website. The centistoke one hundredth of a stoke is more generally used. How do I convert kinematic viscosity to dynamic viscosity? Viscosity-Tables Substances Water Document 3 pages. Search inside document. Density actually provides a way to convert between a kinematic and a dynamic viscosity measurement. Necessary cookies 0 Necessary cookies enable the basic functioning of the website. Only accept necessary cookies Save settings and close.

There is nothing to tell - keep silent not to litter a theme.
Bravo, this magnificent idea is necessary just by the way