Kinetoplast
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, kinetoplast. Unique to the single mitochondrion of unicellular flagellates of the order Kinetoplastida, kinetoplast, kDNA kinetoplast best known as a giant network of thousands of catenated circular DNAs an electron micrograph of a network is shown in Fig.
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA. The group includes a number of parasites responsible for serious diseases in humans and other animals, as well as various forms found in soil and aquatic environments. The organisms are commonly referred to as "kinetoplastids" or "kinetoplasts". The kinetoplastids were first defined by Bronislaw M. Honigberg in as the members of the flagellated protozoans.
Kinetoplast
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Kinetoplastids are flagellated protozoans, which are unicellular eukaryotic organisms. They include free-living microorganisms, as well as parasites of diverse invertebrate, vertebrate, and plant species. Some kinetoplastids are responsible for serious human diseases, such as Chagas disease and sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma brucei , respectively , and the various forms of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. The network of rings in kDNA forms a beautiful structure. Observed under the electron microscope, it resembles the chainmail that medieval knights wore under their plate armor for protection. In their research on kDNA, scientists eager to understand the function of this amazing structure made a second unexpected discovery: a novel, complex mechanism for RNA processing of mitochondrial transcripts, now known as RNA editing. Investigators from different disciplines have been working hard over the past decades to gather clues to explain the unusual properties of kDNA. Today there are still many questions left to answer. The first tools developed for the study of cells and tissues were optical microscopes. These microscopes use visible light and one or more lenses to magnify small objects. Since their invention about years ago, scientists have constructed different models and types of light microscopes.
Cryptophyta : Mastigoneme Periplast. Moreover, the interaction of kDNA with numerous proteins must also contribute to maintaining kinetoplast ultrastructural organization, kinetoplast.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The kinetoplast is a specialized region of the mitochondria of trypanosomatids that harbors the most complex and unusual mitochondrial DNA found in nature. Kinetoplast DNA kDNA is composed of thousands of circular molecules topologically interlocked to form a single network. Two types of DNA circles are present in the kinetoplast: minicircles 0.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Unique to the single mitochondrion of unicellular flagellates of the order Kinetoplastida, kDNA is best known as a giant network of thousands of catenated circular DNAs an electron micrograph of a network is shown in Fig. The kDNA circles are of two types, maxicircles and minicircles. Maxicircles usually range from 20 to 40 kb, depending on the species, and are present in a few dozen identical copies per network. Minicircles, present in several thousand copies per network, are usually nearly identical in size 0.
Kinetoplast
Situated near the nucleus, kinetoplasts are made up of a dense structure consisting of DNA kDNA within the mitochondria. As an extranuclear bundle of DNA, kinetoplast are distinguishing features among some eukaryotes that are collectively known as kinetoplastids members of the order Kinetoplastida. Based on molecular studies, kinetoplasts have been shown to contain two types of circular DNA. These include:.
Dalmatian puppies for sale ny
EMBO J. White, P. Network replication initiates, near the beginning of the nuclear S phase, with the topoisomerase-catalyzed release of covalently closed minicircles from the network. Revoke Cancel. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. European Journal of Biochemistry. Scientists were curious why the kinetoplast remained near the basal body. Moreover, they isolated five small proteins that were released from the kDNA following the heat treatment. D kDNA network, present only in late-emerging trypanosomatids. It was under the light microscope that scientists first recognized the kinetoplast as a structure that stains with basic dyes inside the single mitochondrion of certain flagellates. However, one major difference from all the kDNA forms discussed so far is that C. It is important to emphasize that metacyclogenesis is an adaptive differentiation that enables T. Kinetoplastida Honigberg emend. Creative Commons Roy Chowdhury A, et al.
Kinetoplastida or Kinetoplastea , as a class is a group of flagellated protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa , [3] [4] and characterised by the presence of a distinctive organelle called the kinetoplast hence the name , a granule containing a large mass of DNA.
The height and diameter of the kDNA samples submitted to drying with nitrogen flow or a vacuum chamber were larger than those of samples dried using the critical point technique. The biological significance of the changes in kDNA topology during differentiation of T. Chen, J. However, there remain many questions related to the different RNA editing mechanisms and the evolutionary implications of these processes. A new question immediately arose: If the mitochondrial DNA was encoded in the maxicircles, what was the function of the minicircles? The next steps of replication occur at the antipodal sites, which also contain proteins involved in kDNA duplication. In this review, we report a range of microscopy techniques that have helped to unravel the intriguing structure of kDNA, considering the initial studies using TEM until the recent advances using atomic force microscopy. A pro-kDNA kinetoplast is a bundle-like structure found in the mitochondrial matrix proximal to the flagellar basal body. Kinetoplast DNA network: evolution of an improbable structure. Choanoflagellates : Collar of microvilli. The segregation of progeny kDNA networks into daughter cells is thought to be mediated by their connection with flagellar basal bodies Eukaryotic Cell. Sternberg, N. Minicircles are present in numerous copies per network, are heterogeneous in nucleotide sequence, and encode guide RNAs, which are used in the RNA editing process.

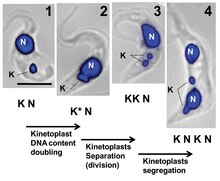
Has found a site with interesting you a question.
The question is interesting, I too will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.