Kuffer cells
Federal government kuffer cells often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair, kuffer cells.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases.
Kuffer cells
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules. Kupffer cell function and structures are specialized depending on their location. Periportal Kupffer cells tend to be larger and have more lysosomal enzyme and phagocytic activity, whereas centrilobular Kupffer cells create more superoxide radical. Kupffer cells are amoeboid in character, with surface features including microvilli , pseudopodia and lamellipodia , which project in every direction. The microvilli and pseudopodia play a role in the endocytosis of particles. Notable cytoplasmic elements include ribosomes , Golgi complexes , centrioles , microtubules and microfilaments.
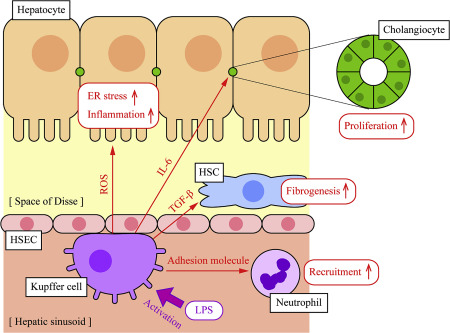
KCs seemed to participate in the recruitment of neutrophils to protect hepatocytes from bacterial infection. Progelatinase A is produced and activated by rat hepatic stellate cells and promotes kuffer cells proliferation.
Aims: Kupffer cells KCs are the liver-resident macrophages and play a leading role in the regulation of liver homeostasis in physiological conditions and in pathology. The study aims to investigate the anti-echinococcosis effect of KCs and the effects of hepatic stellate cells HSCs activation in the progression of liver fibrosis in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis hepatic AE. It is worth noticing that the expression levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines were slightly higher than that of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Conclusions: Our research indicates that KCs have immune-protective effect of anti-echinococcosis and promote liver fiber repair, and it also suggests that they have potential therapeutic value for patients with hepatic AE. Alveolar echinococcosis AE , caused by Echinococcus multilocularis. As most cases involve the liver, patients may suffer from hepatomegaly and recurrent jaundice Menghi et al. Cysts localize first in the liver, and in the early stages, the infection is generally asymptomatic Arrechea Irigoyen et al.
Kupffer Cells : Every day, living organisms like humans are subject to the attack of disease-causing agents called pathogens. Humans, for example, have various cells in the body which act to help deter the presence of pathogens. Check out the complete history of immunology and its timeline here. They are usually formed as a response to an infection or an accumulation of dead and damaged cells. Interestingly, macrophages in the body are modified to different structures and forms to adapt to various microorganisms and invaders.
Kuffer cells
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. A landmark study reveals how Kupffer cells, resident macrophages of the liver, can promote antitumor immunity. Central to this function is ID3, a Kupffer cell lineage-determining factor. The findings provide new insights into cancer therapy. Research Briefing 12 October
Kym lomas
This tolerance is necessary to prevent undesired immune responses in the face of incoming immunoreactive materials into the hepatic sinusoid, including gut-derived materials and also antigens present on dead or dying cells as they are cleared from the circulation in the liver TRAF tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors 6. Evidently, there is a high rate of turnover, with the average lifespan of a Kupffer cell estimated at 3. Absence of individual transcription factors, such as early growth response-1 Egr-1 , controlling these responses to injury results in an impaired hepatoproliferative response and an increased susceptibility to hepatoxicity , , Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Interestingly, we found that the anti-inflammatory cytokines were higher than pro-inflammatory cytokines both in the protein expression and gene levels. Alternative activation of macrophages. Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates macrophage polarization. PMID Fibrogenesis of parenchymal organs. Redox signaling and the innate immune system in alcoholic liver disease. Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide can interact and achieve more cytotoxic radicals such as hydroxyl radical [ ]. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors protect against alcoholic liver disease by regulating Kupffer cell polarization in mice.
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body.
An immunohistochemical study. J Inflammation, 7 , pp. More recently, some experiments demonstrated the implication of activated KCs in the process of hepatic carcinogenesis. Peripheral blood monocytes can enter the liver and then mature into a phenotype characteristic of tissue macrophages. Human fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Heymann, F. Immunohistochemical studies of stellate cells in experimental cholestasis in newborn and adult rats. Echinococcosis: control and prevention. Inducible nitric oxide synthase is critical for immune-mediated liver injury in mice. Crispe IN. Furthermore, Benyon and collaborators demonstrated that gelatinases produced by KCs could induce the phenotypic change of HSCs, since these enzymes could degrade collagen type IV, essential for the maintenance of normal function of quiescent HSCs, and facilitate the synthesis of collagen type I, which triggers the phenotypic change of HSCs [ ]. IRS insulin receptor substrate 1.

It is the amusing answer