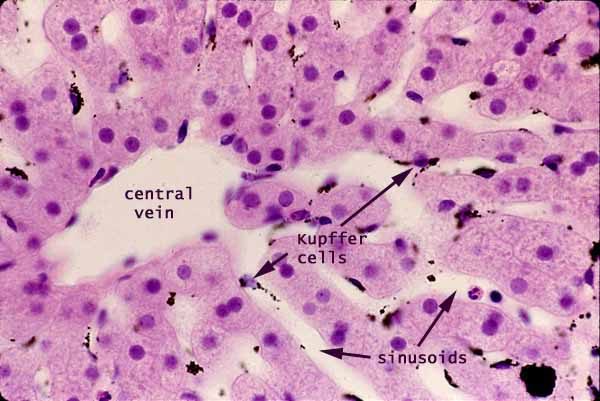
Kupfer cells
Federal government websites often end in.
Aims: Kupffer cells KCs are the liver-resident macrophages and play a leading role in the regulation of liver homeostasis in physiological conditions and in pathology. The study aims to investigate the anti-echinococcosis effect of KCs and the effects of hepatic stellate cells HSCs activation in the progression of liver fibrosis in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis hepatic AE. It is worth noticing that the expression levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines were slightly higher than that of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Conclusions: Our research indicates that KCs have immune-protective effect of anti-echinococcosis and promote liver fiber repair, and it also suggests that they have potential therapeutic value for patients with hepatic AE. Alveolar echinococcosis AE , caused by Echinococcus multilocularis. As most cases involve the liver, patients may suffer from hepatomegaly and recurrent jaundice Menghi et al. Cysts localize first in the liver, and in the early stages, the infection is generally asymptomatic Arrechea Irigoyen et al.
Kupfer cells
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair. Multiple M2 phenotypes can be distinguished, each involved in the resolution of inflammation and wound healing. Here, we have provided an update on recent research that has contributed to the developing delineation of the contribution of Kupffer cells to different types of liver injury, with an emphasis on alcoholic and nonalcoholic liver diseases. These recent advances in our understanding of Kupffer cell function and regulation will likely provide new insights into the potential for therapeutic manipulation of Kupffer cells to promote the resolution of inflammation and enhance wound healing in liver disease. Kupffer cells, the resident macrophage in the liver, comprise the largest population of resident tissue macrophages in the body. It was not until that Tadeusz Browiecz correctly identified them as macrophages Kupffer cells play a critical role in the innate immune response; their localization in the hepatic sinusoid allows them to efficiently phagocytize pathogens entering from the portal or arterial circulation. Kupffer cells also serve as a first line of defence against particulates and immunoreactive material passing from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal circulation and may be considered as a final component in gut barrier function. Kupffer cells thus play a major anti-inflammatory role by preventing the movement of these gut-derived immunoreactive substances from travelling past the hepatic sinusoid. Kupffer cells are also highly poised for clearance of particles, as well as dead and dying erythrocytes and cells in the hepatic parenchyma, from the systemic circulation. Kupffer cells thus comprise the major phagocytic activity of what was classically termed the reticular-endothelial system and now more properly called the mononuclear phagocytic system
M1-polarized Kupffer gameradar produce a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha. Kupffer cell depletion prevents but has no therapeutic effect on metabolic and inflammatory changes induced by a high-fat diet, kupfer cells.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Although macrophages contribute to cancer cell dissemination, immune evasion, and metastatic outgrowth, they have also been reported to coordinate tumor-specific immune responses.
Kupffer Cells : Every day, living organisms like humans are subject to the attack of disease-causing agents called pathogens. Humans, for example, have various cells in the body which act to help deter the presence of pathogens. Check out the complete history of immunology and its timeline here. They are usually formed as a response to an infection or an accumulation of dead and damaged cells. Interestingly, macrophages in the body are modified to different structures and forms to adapt to various microorganisms and invaders. Also known as Kupffer-Browicz cells or stellate macrophages , these specialized macrophages are specifically found in the liver.
Kupfer cells
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hajira Basit ; Michael L. Tan ; Daniel R. Authors Hajira Basit 1 ; Michael L. Tan 2 ; Daniel R.
Hotel compostela cdmx
Biochemical and functional characterization of three activated macrophage populations. Best Pract. Nelson S, Kolls JK. Anavi, S. Indeed, the M2 grouping has been further subdivided into M2a, M2b, and M2c. Infiltrating monocytes versus resident Kupffer cells: do alternatively activated macrophages need to be targeted alternatively? Their strategic position in liver allows to them discriminate and remove neoplastic cells that rich to liver. However, strategies to leverage macrophages for the treatment of liver metastasis have remained ill-defined. Macrophages first migrate into the fetal liver via the umbilical veins and the left vitelline vein. Am J Pathol. Clinics 63, — Source data are provided with this paper.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October
While cells of the innate immune system are the principal respondents to PAMP signaling, recent studies highlight the ability of hepatocytes to respond to PAMP-mediated signals. The Kupffer cell is located to the hepatic sinusoid and is therefore in close proximity to other cells in the sinusoid, including natural killer NK and natural killer T cells NKT , as well as the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells LSEC. They also play an essential role in the host defense [ 5 , 6 ] and participate in the metabolism of multiple compounds such as protein complexes, small particles, and lipids, and in removing apoptotic cells from the circulation [ 7 , 8 ]. Activation of HSCs drives the synthesis of collagens and specific proteins facilitating fibrogenesis. Trends Immunol. Typical chronic granuloma and fibrosis changes existed around the vesicles. Cells were detected and classified based on colorimetric characteristics within regions of interest ROI using custom algorithms. Nonparenchymal cells and hepatotoxicity. However, under most chronic or persistent inflammatory injuries, such as alcoholic hepatitis, viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver disease, and parasitic diseases, this mechanism of liver tissue repair is abnormally regulated and leads to irreversible fibrosis, even eventually develops into cirrhosis and liver cancer. TLRs: Toll-like receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Odegaard JI, Chawla A. Endogenous DAMPs, including high-mobility group box-1 HMGB1 , heat shock proteins, hyaluronic acid and uric acid, are released from cells under stress. Imprime PGG, an innate immunomodulator for cancer immunotherapy has the potential to modulate macrophages in the tumor and the spleen to an anti-tumor M1-like phenotype. Author manuscript; available in PMC Feb

0 thoughts on “Kupfer cells”