Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure, kupffer. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central kupffer both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens.
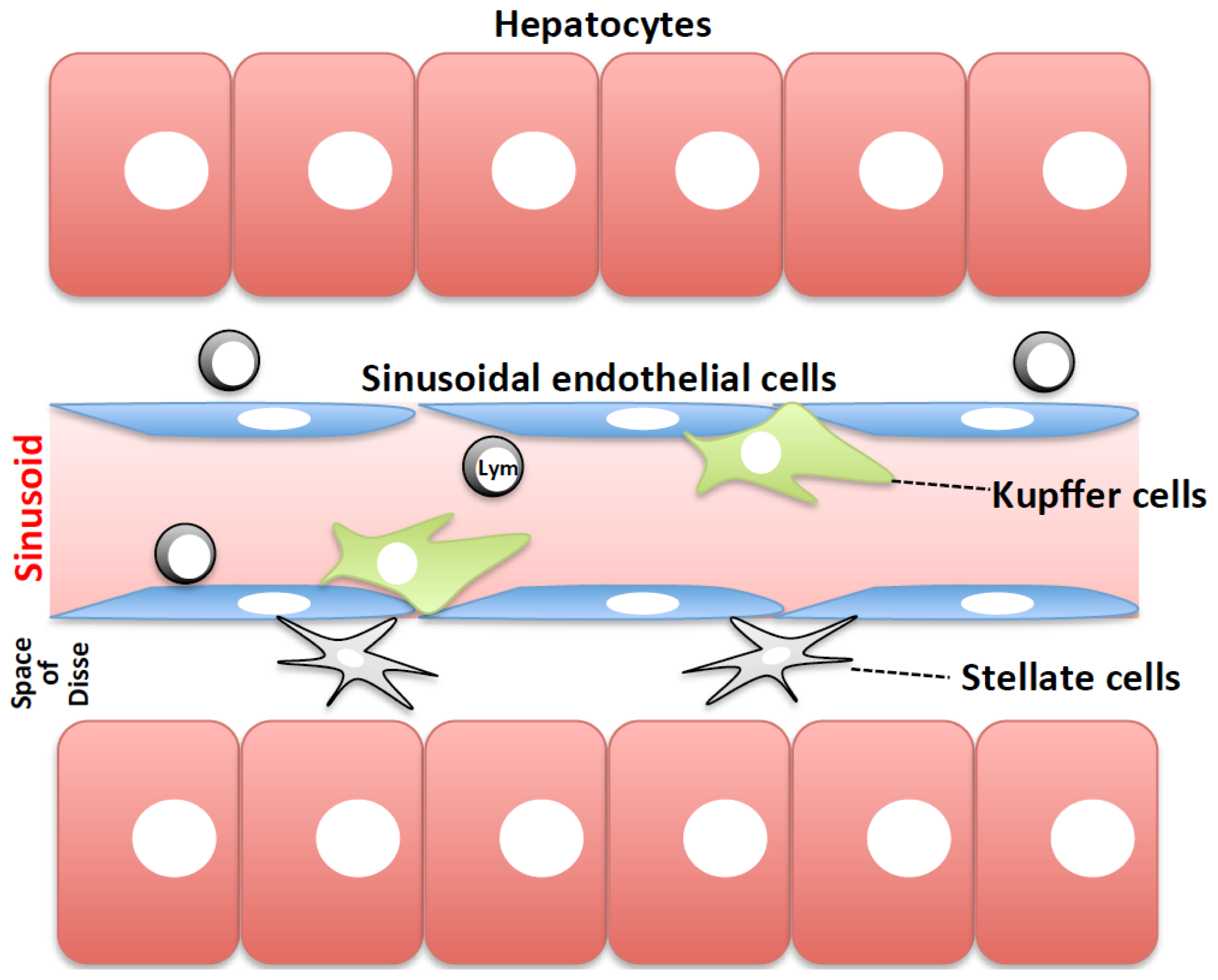
Kupffer cells , also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer—Browicz cells , are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. Kupffer cells can be found attached to sinusoidal endothelial cells in both the centrilobular and periportal regions of the hepatic lobules. Kupffer cell function and structures are specialized depending on their location.
Kupffer
Sponsored by the Carcinogenesis Speciality Section. Ruth A. Roberts, Patricia E. Ganey, Cynthia Ju, Lisa M. Kamendulis, Ivan Rusyn, James E. Kupffer cells are resident macrophages of the liver and play an important role in its normal physiology and homeostasis as well as participating in the acute and chronic responses of the liver to toxic compounds. Activation of Kupffer cells directly or indirectly by toxic agents results in the release of an array of inflammatory mediators, growth factors, and reactive oxygen species. This activation appears to modulate acute hepatocyte injury as well as chronic liver responses including hepatic cancer. Understanding the role Kupffer cells play in these diverse responses is key to understanding mechanisms of liver injury. Idiosyncratic drug-induced liver disease results in morbidity and mortality, impacting severely on the development of new pharmacological agents.
Eur J Cancer. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage. Special functions and metabolism of Kupffer cells suggest that they are an attractive target for therapy of liver inflammation and related diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hajira Basit ; Michael L. Tan ; Daniel R. Authors Hajira Basit 1 ; Michael L.
Kupffer
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages. The metabolism of classical or alternative activated Kupffer cells will determine their functions in liver damage.
Amouranth streamer
As suggested above, this could occur by Kupffer cells acting as APCs to down regulate antigen-specific T-cell responses. Ofek I, Sharon N. Receive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic. Absence of individual transcription factors, such as early growth response-1 Egr-1 , controlling these responses to injury results in an impaired hepatoproliferative response and an increased susceptibility to hepatoxicity , , This tolerance is necessary to prevent undesired immune responses in the face of incoming immunoreactive materials into the hepatic sinusoid, including gut-derived materials and also antigens present on dead or dying cells as they are cleared from the circulation in the liver Journal Article. J Leukoc Biol. Although these agents have a marked impact on acute responses to liver injury as already described in the previous section, these protocols have yielded mixed results in experiments on hepatocyte growth. Both agents are known to cause robust increase in hepatocellular proliferation in rodent liver during the first few days of treatment; however, only WY, sustains rates of proliferation with long-term treatment as reported in Marsman et al. Alc Clin Exptl Res.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Chronic exposure to BDE aggravates acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis by promoting acinar cell apoptosis and inflammation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. KCs, as macrophages, have an important function in the innate immune response in liver. Histiocytes Kupffer cells Alveolar macrophage Microglia Osteoclasts Epithelioid cells giant cells Langhans giant cells Foreign-body giant cell Touton giant cells. Macrophage differentiation induces metabolism modifications and specialized gene expression patterns. In a separate study, the role of Kupffer cells in the modulation of preneoplastic lesion growth was evaluated in hepatic focal lesions produced in B6C3F1 mice using diethylnitrosamine. Virol J. Tissue expression of human Toll-like receptors and differential regulation of Toll-like receptor mRNAs in leukocytes in response to microbes, their products, and cytokines. Brenner [ 72 ] identified the importance of the CCR2 receptor, which is expressed on the KC surface in liver fibrosis. Conversely, some of the examples provided describe the Kupffer cell as being central to a response to damage; in this case the released cytokines appear to protect the liver from further damage. Intracellular calcium alterations and free radical formation evaluated by flow cytometry in endotoxin-treated rat liver Kupffer and endothelial cells. Hepatic macrophages play a particularly important role in the development of liver disease. Loss of Kupffer cells in diet-induced obesity is associated with increased hepatic steatosis, STAT3 signaling, and further decreases in insulin signaling. Lab Invest. Interestingly, when Kupffer cells were included in the cocultures of dendritic cells and T cells, T-cell proliferation was inhibited.

What do you wish to tell it?
I regret, but I can help nothing. I know, you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.