Lewis dot na
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom determines lewis dot na chemical characteristics. We visualize valence electrons using Lewis dot structures to locate stable electron configurations. In order to attain stability in any atom like noble gasesthe majority of atoms often lose or gain electrons.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot symbol or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used.
Lewis dot na
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is:. Because the side is not important, the Lewis electron dot diagram could also be drawn as follows:. The next atom, lithium, has an electron configuration of 1 s 2 2 s 1 , so it has only one electron in its valence shell. Its electron dot diagram resembles that of hydrogen, except the symbol for lithium is used:. Beryllium has two valence electrons in its 2 s shell, so its electron dot diagram is like that of helium:. The next atom is boron. Its valence electron shell is 2 s 2 2 p 1 , so it has three valence electrons. The third electron will go on another side of the symbol:. For carbon, there are four valence electrons, two in the 2 s subshell and two in the 2 p subshell.
Thus the electron dot diagrams for the first column of elements are lewis dot na follows:. Beryllium has two valence electrons in its 2 s shell, so its electron dot diagram is like that of helium:.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram or a Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used. For example, the Lewis electron dot diagram for hydrogen is simply.
Why are some substances chemically bonded molecules and others are an association of ions? The answer to this question depends upon the electronic structures of the atoms and nature of the chemical forces within the compounds. Although there are no sharply defined boundaries, chemical bonds are typically classified into three main types: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. In this chapter, each type of bond wil be discussed and the general properties found in typical substances in which the bond type occurs. Each bond classification is discussed in detail in subsequent sections of the chapter.
Lewis dot na
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful. A Lewis electron dot diagram or electron dot diagram, or a Lewis diagram, or a Lewis structure is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. The number of dots equals the number of valence electrons in the atom.
Side part taper fade
Lewis electron dot diagrams use dots to represent valence electrons around an atomic symbol. It is named after Gilbert Lewis , who first proposed it in The second column of the periodic table 5. The valence electron configuration for selenium is 4 s 2 4 p 4. The most electronegative atoms are generally assigned to the lone pairs first. As a result, sodium and chlorine ions both have fully filled valence shells and noble gas configurations. What column of the periodic table has Lewis electron dot diagrams that have six electrons in them? An atom in a molecule can have zero, one or more lone pairs. As a result, each atom acquires a charge. Thus we have. The next atom is boron. Search for:. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. It does not matter what order the positions are used.
In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. To facilitate our understanding of how valence electrons interact, a simple way of representing those valence electrons would be useful.
Again, it does not matter on which sides of the symbol the electron dots are positioned. Is it necessary for the first dot around an atomic symbol to go on a particular side of the atomic symbol? Problem What is the Lewis electron dot diagram for each ion? All of the other atoms or ions will be bound to the core metal atom. The next atom, lithium, has an electron configuration of 1 s 2 2 s 1 , so it has only one electron in its valence shell. In almost all cases, chemical bonds are formed by interactions of valence electrons in atoms. Each atom in the molecule is assigned a pair of lone electrons. The second column of the periodic table 5. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. These dots are arranged to the right and left and above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on a side. As usual, we will draw two dots together on one side, to represent the 2 s electrons. Key Takeaways Lewis electron dot diagrams use dots to represent valence electrons around an atomic symbol.

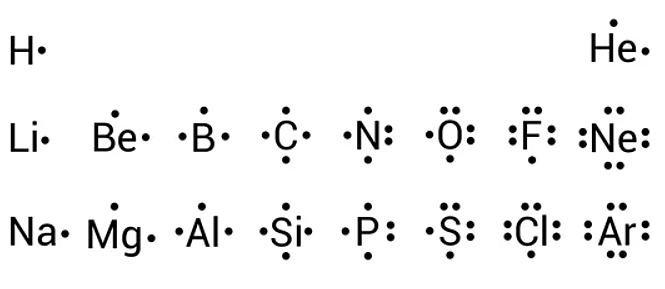
0 thoughts on “Lewis dot na”