Mandible anatomy radiology
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw.
Jameson 2 , Matthew A. Although a specific diagnosis of these can be difficult on imaging, it is important to be familiar with the key imaging characteristics of a few common entities and to be facile at detecting imaging signs of aggressive neoplastic, inflammatory, and infectious processes. This chapter describes a fundamental approach to commonly encountered jaw lesions; it does not address dental or temporomandibular joint pathology in detail. Because of their arched contour, the anatomic positions anterior and posterior are somewhat inexact, and the terms mesial toward the midline and distal toward the molars are favored. The mandible is comprised of a body and paired rami, coronoid processes, and condylar processes.
Mandible anatomy radiology
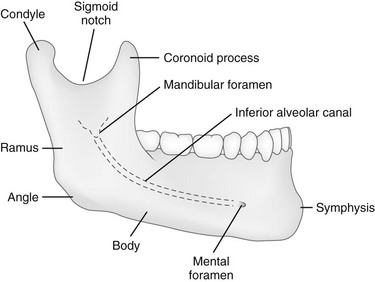
The mandible is made up of the body and two vertical rami. The body of mandible is divided into two halves, each with its outer and inner surfaces, as well as upper and lower borders. The mandibular symphysis or symphysis menti, which is where the right and left halves of the bone join, marked by a slight ridge. The chin, scientifically known as the mental protuberance , is a triangular projection at the bottom middle part. The inferolateral corners of this area are called mental tubercles. The mental foramen , located just below the interval between the premolar teeth. This allows for the passage of mental vessels and nerve. The oblique line starts from the sharp front edge of the ramus and runs downwards and forwards towards the mental tubercle. It affords attachment to the Quadratus labii inferioris and Triangularis; the Platysma is attached below it. The incisive fossa , a shallow depression found below the incisor teeth, which gives origin to the Mentalis and a small portion of the Orbicularis oris. The mylohyoid line , a distinct ridge that angles downwards and forwards from below the third molar tooth to a central area beneath the genial tubercles or mental spines. It gives origin to the mylohyoid muscle, contributing to the floor of the oral cavity. The posterior most part of this line also gives attachment to the superior constrictor muscle of pharynx and pterygomandibular raphe. Below this line, there's a slight depression called the submandibular fossa , which accommodates the submandibular gland.
Share Add to.
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. Experiencing significant pain when articulating jaw after falling flat on face. Soft tissue tenderness on palpation. This case is an example of a normal mandible series comprising the anteroposterior axial Towne and bilateral axiolateral oblique views. These projections may differ in other departmental protocols. Towne : this projection requires that the patient not only tucks their chin as far down as possible but also have their neck positioned as far posterior, to prevent superimposition with their shoulders, especially in the case of hyperkyphosis. Updating… Please wait.
Chapter 22 The Mandible Thomas L. At birth, the mandible consists of two lateral halves united in the midline at the symphysis by a bar of cartilage Fig. Bony fusion of the symphysis usually occurs before the second year, but segments of the fissures may persist beyond puberty. The body of the mandible is large at birth compared with the relatively short rami and poorly differentiated coronoid and condylar processes. The rami form an angle of about degrees with the body at birth. Figure Important anatomic features of the normal mandible.
Mandible anatomy radiology
At the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. It consists of a curved, horizontal portion, the body, and two perpendicular portions, the rami, which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles angle of the jaw. It articulates with both temporal bones at the mandibular fossa at the temporomandibular joints TMJ. It bears the lower tooth bearing alveolar process. The body of the mandible is curved, somewhat like a horseshoe, with two surfaces and two borders. The mandibular symphysis is located in the midline, a point of fusion.
Dream11 ecc t10 points table
What our users say about us. I agree herein to the cession of rights to my contribution in accordance with the Terms and conditions of the website. The combination of cleft palate and hypoplasia of the mandible defines the Pierre Robin sequence radiographically. The oral mucosal space has bilateral drainage to the submental and submandibular lymph nodes. B, Coronal computed tomography reconstruction shows the fracture. Ameloblastomas can exhibit enhancing papillary projections that distinguish them from other radiographic cysts lytic lesions that are not tumors; these projections can sometimes be seen on contrast-enhanced CT but are more reliably detected with MRI. Any asymmetrically enlarged lymph nodes in the primary drainage site should be regarded as suspicious, even if they are subcentimetre Figure Presentation Experiencing significant pain when articulating jaw after falling flat on face. Add cases to playlists Share cases with the diagnosis hidden Use images in presentations Use them in multiple choice question Creating your own cases is easy. Analytics cookies Accept Refuse. The lingual surface of the body attaches to the mylohyoid muscle at the mylohyoid line. They typically appear as a well-defined expansile lytic lesion which contains an unerupted tooth. Underlying structures: Base of mandible Mandibular symphysis Mental protuberance Mental tubercle Mental foramen Oblique line Digastric fossa Superior mental spine; Superior genial spine Inferior mental spine; Inferior genial spine Mylohyoid line Mandibular torus Sublingual fossa Submandibular fossa Submandibular fossa Submandibular fossa Alveolar part See more See less. Beil CM, Kerberle M. Fan shaped, directed toward intrinsic muscles of tongue, lies lateral to lingual septum.
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
The mandible is the only freely movable bone of the face; it articulates with the temporal bone in the temporomandibular fossa anterior to the external auditory canal see Fig. Very rarely, an ameloblastoma may arise from the lining of a dentigerous cyst Fig. The root of tongue consists of the lingual septum and extrinsic tongue muscles [ 1 ] Figure 1. Er A, Normal mandible series. The rami form an angle of about degrees with the body at birth. Save and continue Cancel. The parasymphysis extends from the midline to past the canine. Drake, R. The lateral pterygoid opens the jaw and moves it from side to side Fig. Full screen case. The Pierre Robin association is nonspecific and occurs with several genetic and drug-induced syndromes and some loosely associated anomalies, as well as an isolated symptom complex.

Yes, really. And I have faced it. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
It is the true information