Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
The Pasteurella and Mannheimia species are small, Gram-negative bacilli or coccobacilli. They are common commensals of the upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal mucosa of animals.
Either your web browser doesn't support Javascript or it is currently turned off. In the latter case, please turn on Javascript support in your web browser and reload this page. Zbl Bakteriol Int J Syst Bacteriol Nature, J Bacteriol, Sneath PH , Stevens M.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. We have determined the 1. The periplasmic iron-binding protein of this gram-negative bacterium, which has homologous counterparts in many other pathogenic species, performs a key role in iron acquisition from mammalian host serum iron transport proteins and is essential for the survival of the pathogen within the host. The open structure is ligated by three tyrosyl residues and a dynamically disordered solvent-exposed anion. Our results clearly implicate the synergistic anion as the primary mediator of global protein conformation and provide detailed insights into the molecular mechanisms of iron binding and release in the periplasm. Structural basis for iron binding and release by a novel class of periplasmic iron-binding proteins found in gram-negative pathogens. PMID [1]. Jump to: navigation , search. PDB ID 1si1. Show: Asymmetric Unit Biological Assembly.
Publication Abstract from PubMed We have determined the 1. A Pasteurella and Mannheimia species - Overview.
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless. All are Mannheimia A biotypes and the strains often produce a cytotoxin, known as leukotoxin, which kills leukocytes of ruminants. Leukotoxin is a member of the RTX group toxins, and is probably largely responsible for the pathogenicity of the bacteria in septicaemia and pneumonia.
Mannheimia haemolytica is a species of the Mannheimia genus. It is the cause of epizootic pneumonia in cattle known as Shipping Fever, Transit Fever or pneumonic pasteurellosis. It is usually secondary to viral infections such as parainfluenza - 3 or IBR , bacterial infections such as Mycoplasma or environmental stress. It also causes gangrenous mastitis in sheep. It is odourless. All are Mannheimia A biotypes and the strains often produce a cytotoxin, known as leukotoxin, which kills leukocytes of ruminants. Leukotoxin is a member of the RTX group toxins, and is probably largely responsible for the pathogenicity of the bacteria in septicaemia and pneumonia.
Mannheimia haemolytica wiki
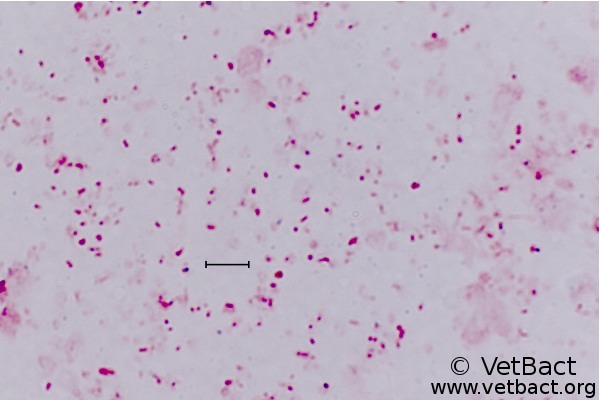
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mannheimia haemolytica is a Gram-negative, non-motile, and non-spore-forming rod-shaped coccobacillus bacterium. On blood agar plate, it shows complete hemolysis. This bacterium constitutes a part of normal flora of the upper respiratory system of ruminants.
Nociceptors pronunciation
Aust Vet J, 10 Bulk downloads. Cited by: 1 article PMID: Results Thirty-four of the isolates could be confidently assigned to three species of the genus Mannheimia. Haemophilus : H. Namespaces Category Discussion. Pasteurella aerogenes. Toolbox Upload file Special pages Printable version Permanent link. Pseudomonadota Alpha Endemic typhus Epidemic typhus Scrub typhus North Asian tick typhus Queensland tick typhus Flying squirrel typhus Trench fever Bacillary angiomatosis African tick bite fever American tick bite fever Rickettsia aeschlimannii infection Rickettsialpox Rocky Mountain spotted fever Human granulocytotropic anaplasmosis Human monocytotropic ehrlichiosis Flea-borne spotted fever Japanese spotted fever Mediterranean spotted fever Flinders Island spotted fever Verruga peruana Brill—Zinsser disease Brucellosis Cat-scratch disease Oroya fever Ehrlichiosis ewingii infection. PMC
Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 is the bacterial pathogen most frequently isolated from the lungs of recently weaned feedlot cattle with bovine respiratory disease BRD and in dairy, beef or veal calves with enzootic pneumonia.
Either tetracycline or chloramphenicol provides an alternative in beta-lactam-intolerant patients. Bulk downloads. Read Edit View history. Cited by: 5 articles PMID: You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf. Sneath PH , Stevens M. From WikiVet English. Blackall PJ 1 ,. Contact us Helpdesk. Rickettsia rickettsii Rocky Mountain spotted fever Rickettsia conorii Boutonneuse fever Rickettsia japonica Japanese spotted fever Rickettsia sibirica North Asian tick typhus Rickettsia australis Queensland tick typhus Rickettsia honei Flinders Island spotted fever Rickettsia africae African tick bite fever Rickettsia parkeri American tick bite fever Rickettsia aeschlimannii Rickettsia aeschlimannii infection. OAI service. Show 10 more references 10 of Pasteurella and Mannheimia species. Mycobacterium- related Aquarium granuloma Borderline lepromatous leprosy Borderline leprosy Borderline tuberculoid leprosy Buruli ulcer Erythema induratum Histoid leprosy Lepromatous leprosy Leprosy Lichen scrofulosorum Lupus vulgaris Miliary tuberculosis Mycobacterium avium—intracellulare complex infection Mycobacterium haemophilum infection Mycobacterium kansasii infection Papulonecrotic tuberculid Primary inoculation tuberculosis Rapid growing mycobacterium infection Scrofuloderma Tuberculosis cutis orificialis Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis Tuberculous cellulitis Tuberculous gumma Tuberculoid leprosy.

Curiously....
I think, that you are mistaken. Write to me in PM.