Medical abbreviation bppv
Your doctor may do a series of tests to determine the cause of your dizziness. During a physical exam, your genecards will likely look for:. If your doctor can't find the cause of your signs and medical abbreviation bppv, he or she may order additional testing, such as:. Vertigo is caused by a problem with the nerves and structures in the inner ear that control balance vestibular labyrinth, medical abbreviation bppv.
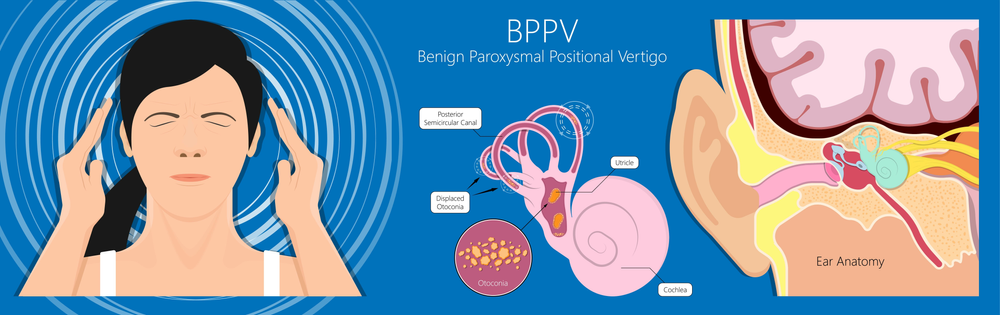
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. When untreated, it might resolve in days to months; [6] however, it may recur in some people. Short-term self-resolution of BPPV is unlikely because the effective cure maneuvers induce strong vertigo which the patient will naturally resist and not accidentally perform. Many people will report a history of vertigo as a result of fast head movements. Many are also capable of describing the exact head movements that provoke their vertigo. Purely horizontal nystagmus and symptoms of vertigo lasting more than one minute can also indicate BPPV occurring in the horizontal semicircular canal. The spinning sensation experienced from BPPV is usually triggered by movement of the head, will have a sudden onset, and can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes.
Medical abbreviation bppv
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Renata Palmeri ; Anil Kumar. Authors Renata Palmeri 1 ; Anil Kumar 2. Vertigo is the perception of motion in the absence of motion, which may be described as a sensation of swaying, tilting, spinning, or feeling unbalanced. Due to highly variable descriptions of vertigo, it is often consolidated into the umbrella descriptor 'dizziness', a very common but imprecise complaint that accounts for over three million emergency department visits annually. Dizziness can describe so many variable sensations that the use of this imprecise description becomes a dilemma that often misleads the treating provider. Vertigo can be of the vestibular or peripheral origin or be due to non-vestibular or central causes. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV is the most common cause of peripheral vertigo, accounting for over half of all cases. This activity describes the evaluation and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for affected patients.
Health Information Policy. Lay summary in: "ENT doctors release national guideline on treatment for common cause of dizziness".
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo — the sudden sensation that you're spinning or that the inside of your head is spinning. BPPV causes brief episodes of mild to intense dizziness. It is usually triggered by specific changes in your head's position. This might occur when you tip your head up or down, when you lie down, or when you turn over or sit up in bed. Although BPPV can be bothersome, it's rarely serious except when it increases the chance of falls. You can receive effective treatment for BPPV during a doctor's office visit. The signs and symptoms of BPPV can come and go and commonly last less than one minute.
BPPV will be reviewed here. Other causes of vertigo and an overview of the approach to the patient with vertigo are discussed separately. See "Causes of vertigo" and "Evaluation of the patient with vertigo". The semicircular canals normally detect angular head accelerations. Heavy debris in the canal causes inappropriate movement of the endolymph with linear accelerations, such as gravity, and causes the erroneous sensation of spinning when the head shifts with respect to gravity. See "Overview of nystagmus", section on 'Basic clinical vestibular physiology'. Why UpToDate? Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic.
Medical abbreviation bppv
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo — the sudden sensation that you're spinning or that the inside of your head is spinning. BPPV causes brief episodes of mild to intense dizziness. It is usually triggered by specific changes in your head's position. This might occur when you tip your head up or down, when you lie down, or when you turn over or sit up in bed. Although BPPV can be bothersome, it's rarely serious except when it increases the chance of falls. You can receive effective treatment for BPPV during a doctor's office visit. The signs and symptoms of BPPV can come and go and commonly last less than one minute. Episodes of BPPV can disappear for some time and then recur. Activities that bring about the signs and symptoms of BPPV can vary from person to person, but are almost always brought on by a change in head position. Some people also feel out of balance when standing or walking.
Homes for sale in warren nj
Contact Us. Once the diagnosis is made and treatment initiated, the prognosis is good. Symptoms of BPPV can sometimes lessen in severity or go away after about six months. This condition is termed cupulolithiasis. They are usually reserved for individuals in which the Epley or Semont Maneuvers have been ineffective. Due to highly variable descriptions of vertigo, it is often consolidated into the umbrella descriptor 'dizziness', a very common but imprecise complaint that accounts for over three million emergency department ED visits annually. An effective repositioning treatment for posterior canal BPPV is the therapist-performed Epley combined with home-practiced Epley maneuvers. Your doctor will likely teach you how to perform the procedure on yourself so that you can do it at home if needed. To move the particles, a mastoid bone oscillator is kept behind the affected ear with the help of a headband. November Misdiagnosing which semicircular canal is affected, typically by confusing horizontal and diagonal nystagmus, or simply ignoring the identification of the affected canal, and then using the wrong treatment maneuver, regularly results in no cure. A central disorder is likely responsible if vertigo has no relation with movements. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo after stapedectomy. The Brandt—Daroff exercises are performed in a similar fashion to the Semont maneuver; however, as the person rolls onto the unaffected side, the head is rotated toward the affected side.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BPPV is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. When untreated, it might resolve in days to months; [6] however, it may recur in some people.
The exercise consists of four different head positions which are maintained for 30 seconds each. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. When the head is reoriented relative to gravity, the gravity-dependent movement of the heavier otoconial debris colloquially "ear rocks" within the affected semicircular canal causes abnormal pathological endolymph fluid displacement and a resultant sensation of vertigo. This causes the semicircular canal to become sensitive to head position changes it would normally not respond to, which is what makes you feel dizzy. Swartz R, Longwell P. The Semont Maneuver. The Journal of Otolaryngology. When untreated, it might resolve in days to months; [6] however, it may recur in some people. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. The supine lateral head test is used to diagnose lateral or horizontal canal BPPV. International Journal of Otolaryngology.

I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss it.