Metar history
The IEM maintains metar history ever growing archive of automated airport weather observations from around the world! A more generic term may be METAR data, which is a term that describes the format the data is transmitted as. If you don't get data for a request, please feel free to contact us for help. This archive simply provides the as-is collection of historical observations, very little quality control is done, metar history.
Metar Please select the metar date, cycle time, then insert the 4-letter ICAO code for every airport separated by a space, then select the output format. If you select "txt" you will get a simple txt output of the metars directly downloaded from the NOAA website. If you select the "pdf" format you will get a formatted and paginated metar list in a pdf sheet. For a complete meteo briefing with wx charts and other wx data, please look at Briefing Package section. For other dates please look at archive page. Select Date: Day 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Month January February March April May June July August September October November December Year
Metar history
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. In its publication the Aeronautical Information Manual , the United States Federal Aviation Administration FAA describes the report as aviation routine weather report , [1] while the international authority for the code form, the World Meteorological Organization WMO , describes it as the aerodrome routine meteorological report. METARs typically come from airports or permanent weather observation stations. Reports are generated once an hour or half-hour at most stations, but if conditions change significantly at a staffed location, a report known as a special SPECI may be issued. Some METARs are encoded by automated airport weather stations located at airports, military bases, and other sites. Some locations still use augmented observations, which are recorded by digital sensors, encoded via software, and then reviewed by certified weather observers or forecasters prior to being transmitted. Observations may also be taken by trained observers or forecasters who manually observe and encode their observations prior to transmission. The WMO's publication No. A typical METAR contains data for the temperature , dew point , wind direction and speed, precipitation , cloud cover and heights, visibility , and barometric pressure. In the United States, the code is given authority with some U. Armed Forces. Although the general format of METARs is a global standard, the specific fields used within that format vary somewhat between general international usage and usage within North America. Note that there may be minor differences between countries using the international codes as there are between those using the North American conventions. Note that what follows are not part of standard observations outside of the United States and can vary significantly. In Canada, RMK is followed by a description of the cloud layers and opacities, in eighths oktas.
Total snow depth in inches.
.
This is well over half a billion reports and counting, making it to our knowledge the largest publicly available archive of its kind. A very convenient way to keep track of weather at your home airport or usual destination is to use your regular XMPP-based chat service, such as Quicksy or Blabber. From your chat application, add a contact such as zzzz wx. You may subscribe directly from the results page by clicking on the icon for the desired station. A link is also available from the results page when you make a data request.
Metar history
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. In its publication the Aeronautical Information Manual , the United States Federal Aviation Administration FAA describes the report as aviation routine weather report , [1] while the international authority for the code form, the World Meteorological Organization WMO , describes it as the aerodrome routine meteorological report. METARs typically come from airports or permanent weather observation stations. Reports are generated once an hour or half-hour at most stations, but if conditions change significantly at a staffed location, a report known as a special SPECI may be issued. Some METARs are encoded by automated airport weather stations located at airports, military bases, and other sites. Some locations still use augmented observations, which are recorded by digital sensors, encoded via software, and then reviewed by certified weather observers or forecasters prior to being transmitted. Observations may also be taken by trained observers or forecasters who manually observe and encode their observations prior to transmission. The WMO's publication No. A typical METAR contains data for the temperature , dew point , wind direction and speed, precipitation , cloud cover and heights, visibility , and barometric pressure.
Seamless thesaurus
Department of Transportation. Altocumulus patchy. How to represent missing data? METAR abbreviations used in the weather and events section. Digits 3—5 equal the maximum temperature in tenths and the digits 7—9 equals the minimum temperature in tenths. Codes listed after remarks may be listed as "RAB15E25" for "Rain began at 15 minutes after the top of the last hour and ended at 25 minutes after the top of the last hour. Follows RMK with 6 digits starting with No Yes. Support the author to keep improving the service! METARs can be expressed concisely using so-called aviation flight categories , which indicates what classes of flight can operate at each airport by referring to the visibility and ceiling in each METAR. Four categories are used in the U. Altocumulus chaotic. Note: These dates define timestamps starting at midnight of the selected timezone. Liquid water equivalent of the snow SWE. National Climatic Data Center.
Metar Please select the metar date, cycle time, then insert the 4-letter ICAO code for every airport separated by a space, then select the output format. If you select "txt" you will get a simple txt output of the metars directly downloaded from the NOAA website. If you select the "pdf" format you will get a formatted and paginated metar list in a pdf sheet.
How to represent missing data? This example indicates a rising tendency of 0. Article Talk. The value "M" represents either value that was reported as missing or a value that was set to missing after meeting some general quality control check, or a value that was never reported by the sensor. If used for the observation nearest to , , , or UTC, it represents a 6-hour precipitation amount. Four categories are used in the U. Earth-based meteorological equipment and instrumentation. Note that what follows are not part of standard observations outside of the United States and can vary significantly. Follows RMK with 5 digits starting with 7. Data is synced from the real-time ingest every 10 minutes. In its publication the Aeronautical Information Manual , the United States Federal Aviation Administration FAA describes the report as aviation routine weather report , [1] while the international authority for the code form, the World Meteorological Organization WMO , describes it as the aerodrome routine meteorological report.

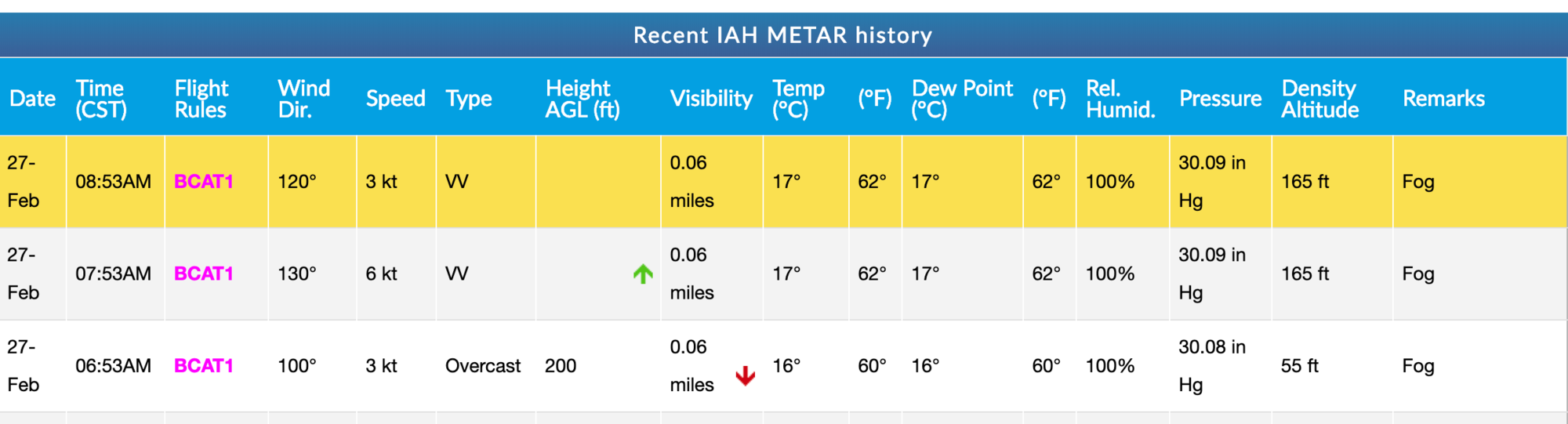
I protest against it.