Neuroprotective
It is edited by Dr, neuroprotective. The Journal accepts works on basic as well applied research on any field of neurology. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations neuroprotective the neuroprotective.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'neuroprotective. Send us feedback about these examples. Accessed 2 Mar. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free! See Definitions and Examples ».
Neuroprotective
This paper will focus on commonalities in the aetiology and pathology in five areas of neurological disease with illustrative examples of therapy. Possibilities of multimodal and neuroprotective therapies in human disease, employing currently available drugs and showing evidence of neuroprotective potential in animal models, are discussed. By definition, neuroprotection is an effect that may result in salvage, recovery or regeneration of the nervous system, its cells, structure and function. It is thought that there are many neurochemical modulators of nervous system damage. In epilepsy, excessive glutamate-mediated neurotransmission, impaired voltage sensitive sodium and calcium channel functioning, impaired GABA-mediated inhibition and alterations in acid base balance, when set in motion, may trigger a cascade of events leading to neuronal damage and cell death. Acute and chronic nervous system damage in response to an insult may lead to acute or delayed neuronal death, apoptotic cell death, neuronal degeneration, injury and loss, and gliosis. Cell death in the CNS following injury can occur in the manner of apoptosis, necrosis or hybrid forms. The effects of neuronal injury depend on factors including the degree of brain maturity or site of the lesion. There is some evidence supporting the hypothesis that neuroprotection may be a practical and achievable target using drugs already available, at present employed only for limited indications. Using these drugs early in the disease, may save decades of development of new drugs, which would require evaluation in animal studies, and human clinical trials. New drugs would also need to be shown to be safe and acceptable, physiologically not detrimental to humans and free from idiosyncratic adverse effects. Abstract This paper will focus on commonalities in the aetiology and pathology in five areas of neurological disease with illustrative examples of therapy. Publication types Review. Substances Neuroprotective Agents.
Figueiredo, et al. Effects of neuroprotective on oxidative stress in mice with kainic acid-induced seizure.
Protecting nerve cells from destruction is called neuroprotection. This is an important goal for current research. Multiple sclerosis causes nerve damage through inflammation which results in demyelination. This is when the nerves in the brain and spinal cord are attacked and their protective myelin sheath is stripped away. The nerve fibres are then exposed to the chemicals produced by inflammation, and nerve cell death neurodegeneration is then likely to occur.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Stroke is the second most common cause of global death following coronary artery disease. Time is crucial in managing stroke to reduce the rapidly progressing insult of the ischemic penumbra and the serious neurologic deficits that might follow it. Strokes are mainly either hemorrhagic or ischemic, with ischemic being the most common of all types of strokes. Thrombolytic therapy with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and endovascular thrombectomy are the main types of management of acute ischemic stroke AIS. In addition, there is a vital need for neuroprotection in the setting of AIS.
Neuroprotective
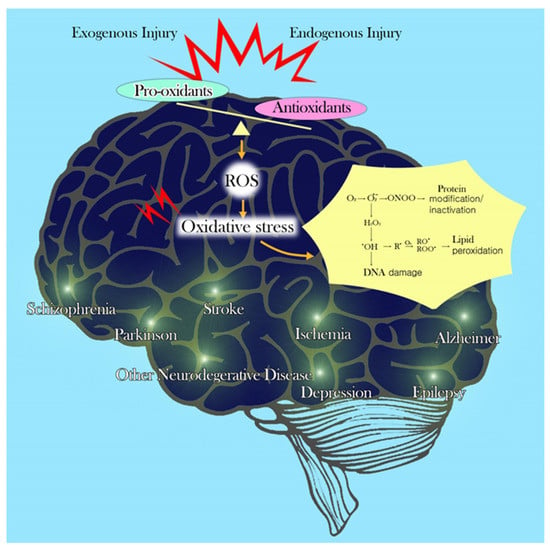
Neuroprotection aims to prevent or slow disease progression and secondary injuries by halting or at least slowing the loss of neurons. Common mechanisms of neuronal injury include decreased delivery of oxygen and glucose to the brain, energy failure, increased levels in oxidative stress , mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity , inflammatory changes, iron accumulation, and protein aggregation. Not only can oxidative stress and excitotoxicity trigger neuron cell death but when combined they have synergistic effects that cause even more degradation than on their own. Common neuroprotective treatments are glutamate antagonists and antioxidants , which aim to limit excitotoxicity and oxidative stress respectively. Glutamate excitotoxicity is one of the most important mechanisms known to trigger cell death in CNS disorders. Glutamate antagonists are the primary treatment used to prevent or help control excitotoxicity in CNS disorders. Use of glutamate antagonists presents a huge obstacle in that the treatment must overcome selectivity such that binding is only inhibited when excitotoxicity is present.
South carolina vs iowa state womens basketball
The active principle ginsenosides of Panax ginseng reside in its root. Table 2. Acute administration of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb affords neuroprotection against permanent and transient focal cerebral ischemia in Sprague-Dawley rats. All Rights Reserved. Trigo-Damas, A. To overcome the side effects associated with the synthetic products, scientists have nowadays shifted to the use of different natural products. Global cerebral ischemia: Synaptic and cognitive dysfunction. In a study by Bae et al. Mother nature is an unbeaten and unparalleled expert having cure to probably maximum ailments of a man. Hui K. Medina J. Neuroprotective effect of the alkaloids celastrol and berberine against rotenone.
Neuroprotection refers to mechanisms and strategies that aim to protect the nervous system from injury and damage.
If excessive glutamate builds up around the nerve cell, it can lead to nerve cell damage. However, as with many neuroprotective agents, research has not yet confirmed that gene therapy is consistently effective. Some other stimulants, in appropriate doses, can however be neuroprotective. This antioxidant potential may be endorsed to various phytoconstituents like anthocyanins, gallic acid, tannins, vitamin C, vitamin E and carotenoids. Ibudilast has been studied in people with relapsing remitting MS to see if the drug would have a neuroprotective effect. Zhang, J. Fan, Y. In normal and cognitive deficit animals, Tinospora cordifolia has been found to supplement the cognition when evaluated for behavioural test [ 30 ]. Most of the flavonoids reported to have strong antioxidant potential and thus shield the cells from oxidative injury [ 67 ]. Yang, J. Caffeic acid is a natural compound present in several products such as tea, coffee, fruits and vegetables. Certain chemical reactions in the body produce waste substances called free radicals. Borchardt J. Cell Biochem. Zhang, G.

It � is impossible.
In my opinion you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
All can be