Numerical coefficient of
In mathematics, numerical coefficient of, a coefficient is numerical coefficient of number or any symbol representing a constant value that is multiplied by the variable of a single term or the terms of a polynomial. It is usually a number, but sometimes may be replaced by a letter in an expression. A coefficient refers to a number or quantity placed with a variable. It is usually an integer that is multiplied by the variable and written next to it.
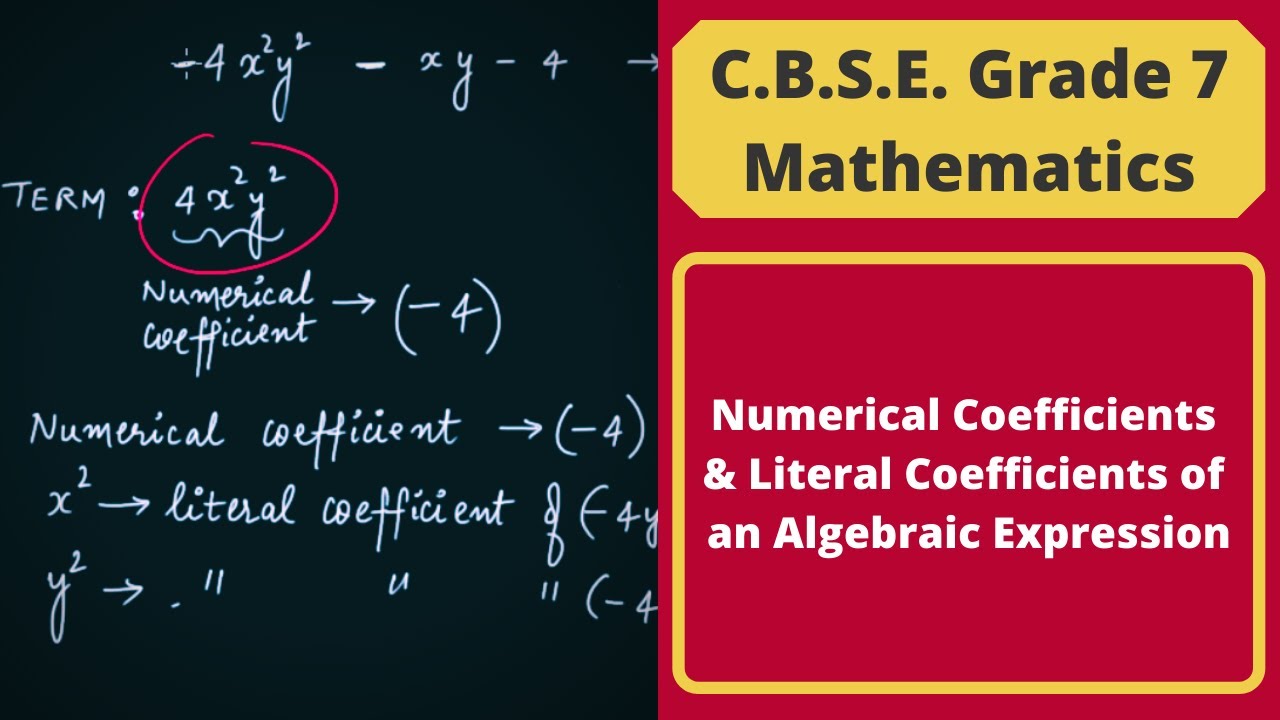
In algebra, a numerical coefficient is a numerical factor associated with a variable in an algebraic expression. It is the constant multiplier that scales or adjusts the variable within the expression. Algebraic expressions typically take the form of a combination of constants, variables, and operators, and the numerical coefficient is the numerical part of a term that multiplies the variable. Understanding numerical coefficients is crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and analyzing the relationships between variables. In more complex algebraic expressions and equations, terms may have different numerical coefficients, contributing to the overall structure and behavior of the mathematical statement.
Numerical coefficient of
.
Terms and Conditions. Why is pi not a rational number?
.
An algebraic expression is a number, a letter, or a collection of numbers and letters along with meaningful signs of operation. Algebraic expressions are often referred to simply as expressions , as in the following examples:. We will study equations in the next section. An important concept that all students of algebra must be aware of is the difference between terms and factors. Any numbers or symbols that are multiplied together are factors of their product. Terms are parts of sums and are therefore joined by addition or subtraction signs. Factors are parts of products and are therefore joined by multiplication signs.
Numerical coefficient of
Constants are the numbers that have a fixed numerical value and variables are the numbers that can take various numerical values. The value of an expression depends upon the values of the variables of an expression. The concept of an algebraic expression is well understood when there is a clear idea about the terms, factors, and coefficients of an algebraic expression. The mathematical statements are written in algebraic expressions. For instance, when we say c is doubled, it is expressed as 2c. Here 2c and t-2 are algebraic expressions. An expression comprises the terms, factors, and coefficient. The terms are the numbers or the variables added together, factors are the numbers or the variables that are multiplied together and the coefficient is the number multiplied to the variable.
156 pounds to kg
Look at the image below showing the leading coefficient in the general form of a polynomial. For example, let us find the coefficients of x and y in the term 5xy. United Kingdom. However, a coefficient can be any natural number , negative number , decimals, or fraction. Hire With Us. In this expression, we can see that there are three terms: 5x 2 , 2y, and Interview Experiences. It is the constant multiplier that scales or adjusts the variable within the expression. Next Unit of Speed. Save Article.
In mathematics, a coefficient is a number or any symbol representing a constant value that is multiplied by the variable of a single term or the terms of a polynomial. It is usually a number, but sometimes may be replaced by a letter in an expression. A coefficient refers to a number or quantity placed with a variable.
How to Calculate the Coefficient of Determination? Help us improve. Answer: Therefore, the coefficients are 1 and 2. We use cookies to ensure you have the best browsing experience on our website. Are whole numbers closed under subtraction? Vote for difficulty :. The leading coefficient is defined as the coefficient of the term with the highest power in a polynomial. Thank you for your valuable feedback! For example, in the term 7x, 7 is the coefficient. In the first term 5x 2 , x 2 is the variable and as we know that a coefficient always comes with the variable, so the coefficient is 5. Is the quotient of two integers always a rational number? A coefficient refers to a number or quantity placed with a variable. The term numerical coefficient is used for the constant multipliers of the variable. Answer: Therefore, the numerical coefficients are 3 and

0 thoughts on “Numerical coefficient of”