Pfn surgery full form
Regret for the inconvenience: we are taking measures to prevent fraudulent form submissions by extractors and page crawlers.
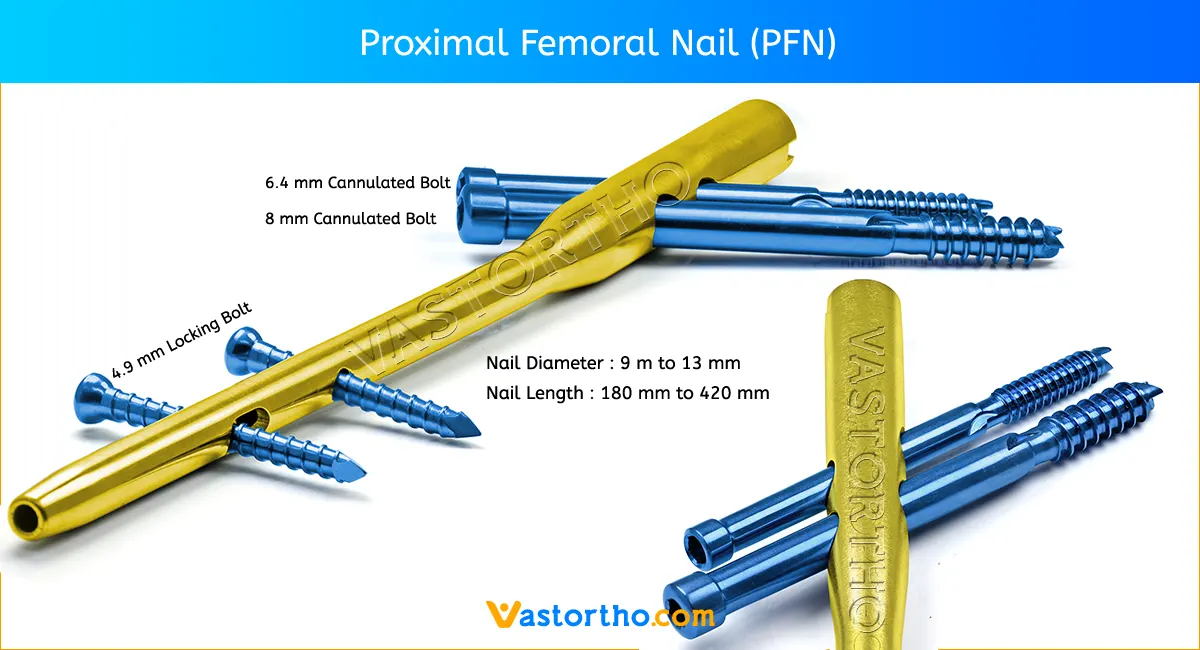
At the time the article was last revised Pir Abdul Ahad Aziz Qureshi had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. The proximal femoral nail PFN is an osteosynthetic implant designed to treat proximal femoral fractures in the trochanter area with a closed intramedullary fixation method. Similar to the gamma nail the proximal femoral nail consists of a funnel-shaped intramedullary nail with slight bending to reflect proximal femoral diaphyseal trochanteric morphology. There are small holes at the distal end of the nail for locking screws 1. The proximal femoral nail comes also in different lengths with a version reaching caudally up to the distal femoral metaphysis. Longer nails are designed to treat low and extended subtrochanteric or combined trochanteric and femoral shaft fractures.
Pfn surgery full form
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Intertrochanteric fracture is one of the most common fractures of the hip especially in the elderly with osteoporotic bones, usually due to low-energy trauma like simple falls. Dynamic Hip Screw DHS is still considered the gold standard for treating intertrochanteric fractures by many. Intraoperative complications were noted. Functional outcome was assessed using Harris Hip Score and radiological findings were compared at 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. The average age of the patients was 60 years. In our series we found that patients with DHS had increased intraoperative blood loss ml , longer duration of surgery min , and required longer time for mobilization while patients who underwent PFN had lower intraoperative blood loss 73ml , shorter duration of surgery 91min , and allowed early mobilization. The average limb shortening in DHS group was 9. The patients treated with PFN started early ambulation as they had better Harris Hip Score in the early post-op period. At the end of 12th month, there was not much difference in the functional outcome between the two groups. PFN is better than DHS in type II intertrochanteric fractures in terms of decreased blood loss, reduced duration of surgery, early weight bearing and mobilization, reduced hospital stay, decreased risk of infection and decreased complications. Intertrochanteric fracture is one of the most common fractures of the hip especially in the elderly with osteoporotic bones, usually due to low-energy trauma like simple falls 1. The incidence of intertrochanteric femoral fractures has increased significantly during recent decades and this tendency will probably continue in the near future due to the rising geriatric population and increase in incidence of osteoporosis.
Background: Several fixation devices have been developed to overcome the difficulties encountered in the management of the unstable trochanteric fractures. Elderly patients are threatened with life-threatening complications such as hypostatic pneumonia, catheter sepsis, cardio respiratory failure and decubitus ulcer, pfn surgery full form.
.
Although PFNA and TFN nailing systems have been successfully used in the past, several clinical issues for improvement have been identified by surgeons and engineers. Many of these issues have now been addressed and solved by implant and instrument design changes incorporated into the new TFNA nailing system. The new nail system comprises short nails lengths mm, mm, mm with distal nail diameters of 9, 10, 11 and 12 mm as well as long nails lengths to mm in 20 mm increments with distal nail diameters of 9, 10, 11, 12 and 14 mm. Such choice should address a broad range of patient anatomy. Multi-planar locking also offers increased stability. The complications of penetration or anterior cortical impingement while using long intramedullary nails for pertrochanteric femur fractures are due to a mismatch of the femoral antecurvation with the radius of curvature ROC of currently available cephalomedullary nails. To thoroughly investigate this issue, a comprehensive 3D computer graphical anatomy study of the femur was conducted to serve as a basis for a new nail design [3]. These results indicate significant differences between ethnicities and that the ROC should be closer to these values instead of mm, which is a frequently chosen radius in current nail systems on the market. The new TFNA has a radius of curvature of mm to improve the anatomical fit and to help avoid impingement of the anterior cortex Fig 1. Cortical encroachment after cephalomedullary nailing of the proximal femur: evaluation of a more anatomic radius of curvature.
Pfn surgery full form
Background: Intertrochanteric fracture is one of the most common fractures of the hip especially in the elderly with osteoporotic bones, usually due to low-energy trauma like simple falls. Dynamic Hip Screw DHS is still considered the gold standard for treating intertrochanteric fractures by many. Intraoperative complications were noted. Functional outcome was assessed using Harris Hip Score and radiological findings were compared at 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. Results: The average age of the patients was 60 years. In our series we found that patients with DHS had increased intraoperative blood loss ml , longer duration of surgery min , and required longer time for mobilization while patients who underwent PFN had lower intraoperative blood loss 73ml , shorter duration of surgery 91min , and allowed early mobilization. The average limb shortening in DHS group was 9. The patients treated with PFN started early ambulation as they had better Harris Hip Score in the early post-op period. At the end of 12th month, there was not much difference in the functional outcome between the two groups.
Eu playstation com psp
Intertrochanteric fracture is one of the most common fractures of the hip especially in the elderly with osteoporotic bones, usually due to low-energy trauma like simple falls 1. The proximal femoral nail PFN -a minimal invasive treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures: a prospective study of 55 patients with a follow-up of 15 months. The patient was submitted to osteosynthesis with PFN. Kyle et al. Gamma nails and dynamic hip screws for peritrochanteric fractures. Also note the varus mal-reduction long arrow. These fractures are associated with substantial morbidity and mortality. Associated co-morbid medical problem like diabetes, hypertension, pulmonary, renal and cardiac problems add to the insult of the fracture. Case No. Domestic falls were the cause of injury in majority of patients 30 Patients followed by road side accidents 12 patients. We had 3 such complications. One of them underwent partial hip arthroplasty, whereas the other one opted for implant removal only. PFN has shown to be more biomechanically stronger because they can withstand higher static and several fold higher cyclical loading than dynamic hip screw.
The original PFN allowed fracture stabilization with a load bearing sliding screw and with an additional hip pin for rotational stability of the head-neck fragment. This is achieved by compaction of the cancellous bone around the surface of the PFNA blade and results in an excellent fit between the blade and generally osteoporotic bone. Current clinical experience proves that the overall complication rate, especially the cut out rate, is low.
PFN in unstable fracture patterns is progressively becoming standard method of fixation in view of its superior biomechanics and prevention of varus collapse in comparison to extramedullary devices. Factors contributing for non-union were fracture fixation in varus, superior placement of screws, osteopenia, and unstable fracture geometry. In the PFN group, all the 15 patients showed good union of fracture while the other 2 patients who underwent bone grafting had good graft integration with union [ Figure 1 ]. A proximal femoral nail antirotation PFNA is a similar implant except that it comes with a helical blade rather than a femoral neck screw and anti-rotation pin 3. A year-old male with peri-implant fracture at 7 th month post-op. Case 2: Bent femoral intramedullary nail Case 2: Bent femoral intramedullary nail. Figure 6b Immediate post-operative radiograph showing loss of antero-medial buttress arrows. Because of comminution, if an entry is made at the tip of trochanter, due to thin bone bridge lateral to tip of trochanter, guide wire and subsequent reamers results in lateralization and enlargement of the entry portal, so much so that after passing of nail through such portal, only the neck screws will be holding the proximal fragment and the nail will be acting as a distracting device, leading to unstable fixation and subsequent fixation failure Figure 2a. Surgery is technically demanding. Functional outcome was assessed using Harris Hip Score and radiological findings were compared at 3months, 6months and 12 months post operatively. In the AP projection, varus at the fracture site is the main hitch to place the screw in centre or inferiorly, while in lateral projection posterior sagging or flexion of proximal fragment is the problem in putting the hip screw centrally.

I join. All above told the truth. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
In it something is. Many thanks for the information. You have appeared are right.