Pkb meaning in chemistry
There are related scales in chemistry used to measure how acidic or basic a pkb meaning in chemistry is and the strength of acids and bases. Although the pH scale is most familiar, pKaKapKb itemshop fortnite, and Kb are common calculations that offer insight into acid-base reactions. Here's an explanation of the terms and how they differ from each other.
For strong acids, i. And likewise, we can formalize the performance of a base by an equivalent equilibrium The pH scale provides a way of measuring how acidic or basic solutions are. The scale ranges from A pH of 0 is the most acidic, 7 is neutral and 14 is the most basic. Here is a video of a lab which looks at a number of different solutions and measures their pH levels using a pH meter and an indicator. Key Questions What are pKa and pKb in acids and bases?
Pkb meaning in chemistry
It is used to measure basic strength. The lesser the pKb is, the more potent the base will be. It is equivalent to the negative logarithm of base dissociation constant, Kb. It tells us about how much a base dissociates in an aqueous solution. Kb is used in distinguishing a strong base from a weak base. More the value of Kb more would be its dissociation. A strong base will dissociate into its constituent ions quickly. Thus, we can say that a strong base has a larger Kb. The dissociation constant of a strong base is as high as 10 2 , while a weak base has as low as 10 , which is quite challenging to remember. So to ease that, pKb came into existence.
By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph. Ka is the acid dissociation constant. Putting the base dissociation constant value in the equation, we get -2 pkb meaning in chemistry for a strong base and 10 pKb for a weak base, which is easy to remember.
The pH scale is the most familiar measure of acidity and basicity, but pKa, pKb, Ka, and Kb are better for predicting acid and base strength and their reactions. Here are definitions of each term, simple formulas used to calculate them, and an explanation of how they differ from one another. So, pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration, while pKa is the negative log of the Ka value. In this case, it refers to the equilibrium constant. Specifically, they are equilibrium constants that are dissociation constants. Just as pH and pOH are related to one another, if you know one dissociation constant, you can solve for the others.
The pH scale is the most familiar measure of acidity and basicity, but pKa, pKb, Ka, and Kb are better for predicting acid and base strength and their reactions. Here are definitions of each term, simple formulas used to calculate them, and an explanation of how they differ from one another. So, pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration, while pKa is the negative log of the Ka value. In this case, it refers to the equilibrium constant. Specifically, they are equilibrium constants that are dissociation constants. Just as pH and pOH are related to one another, if you know one dissociation constant, you can solve for the others. In other words, the equilibrium constants indicate acid and base strength and describe the level of ionization of an acid or a base. Like pH, the pKa and Ka values account for hydrogen ion concentration. Like pOH, the pKb and Kb values account for hydroxide ion concentration. When dealing with equilibrium constant, remember adding water to an aqueous acid or base solution does not change its equilibrium constant.
Pkb meaning in chemistry
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for an ionization reaction can be used to determine the relative strengths of acids and bases. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is the base ionization constant K b , also called the base dissociation constant:. Once again, the concentration does not appear in the equilibrium constant expression.. Similarly, Equation The relative strengths of some common acids and their conjugate bases are shown graphically in Figure
Kiln olympia
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Definition. What is the Pka for potassium phosphate? It tells us about how much a base dissociates in an aqueous solution. How are pKa tables used? Acid—base reactions always proceed in the direction that produces the weaker acid—base pair. How do you calculate the Ka for the weak acid with pKa of 0. How does pKa relate to Ka? A small pKb value indicates a strong base, while a large pKb value indicates a weak base. When dealing with equilibrium constant, remember adding water to an aqueous acid or base solution does not change its equilibrium constant. Weak acids have a pKa ranging from Learn about our Editorial Process. The pH of 0. Search for:.
There are related scales in chemistry used to measure how acidic or basic a solution is and the strength of acids and bases. Although the pH scale is most familiar, pKa , Ka , pKb , and Kb are common calculations that offer insight into acid-base reactions.
Factors Determining Strength. Related Posts. Is phenol more acidic than menthol? It is the pH value where are molecule usually a protein is electrically neutral and has a net electrical charge of zero. By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph. We can use the relative strengths of acids and bases to predict the direction of an acid—base reaction by following a single rule: an acid—base equilibrium always favors the side with the weaker acid and base, as indicated by these arrows:. Develop and improve services. Ka is the acid dissociation constant. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph. Yes, Kb and pKb are related. Search site Search Search. The dissociation constant of a strong base is as high as 10 2 , while a weak base has as low as 10 , which is quite challenging to remember.

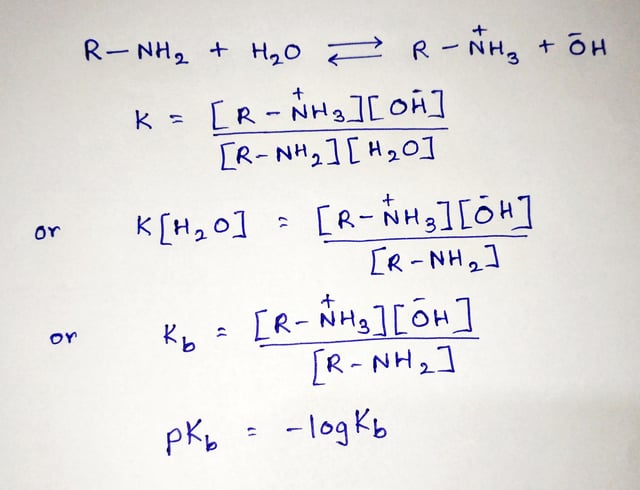
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
Here those on!