Proteinases
Thank you for visiting nature.
Metrics details. Proteinases are involved in essential steps in cartilage and bone homeostasis. Consequently, efforts have been made to establish their potential role in the pathology of rheumatic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and spondyloarthritis. Matrix metalloproteinases MMPs are sensitive markers of disease severity and response to treatment, and therefore they have potential in the assessment of rheumatic diseases. Despite disappointing early results with synthetic inhibitors of MMPs, there is still much scope for developing effective and safe MMPs inhibitors, and consequently to deliver new options to inhibit joint destruction. Proteases are responsible for enzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds [ 1 , 2 ], which is a basic requirement for completion of diverse biological processes. Examples of contributions made by proteases can be found in digestion, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Proteinases
Proteinases play a fundamental metabolic role during the life cycle in the plant kingdom. By interacting with endogenous or exogenous inhibitors, the proteolytic activity is modulated to meet metabolic requirements. By probing proteolytic enzymes with their inhibitors, it is possible to identify novel functions unrelated to their proteolytic activity. A group of plant proteolytic enzymes stands as a line of defence against environmental changes as their activation is triggered following various types of stress. On the other hand, plants also contain proteinase inhibitors as countermeasures for their protection against insects and pests. Both proteinases and inhibitors emerge as useful tools to combat human diseases. This review focuses on the biochemical characterization of plant proteinases, their inhibitors, the pharmacological potential of proteinases and inhibitors, and new putative emerging functions of proteolytically inhibited proteinases. Abstract Proteinases play a fundamental metabolic role during the life cycle in the plant kingdom. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Gov't Review.
Involvement of proteinase-activated receptor-4 in inflammatory joint disease. Agonists proteinases proteinase-activated receptor-2 stimulate upregulation of intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 in primary human keratinocytes via activation of NF-kappa B, proteinases.
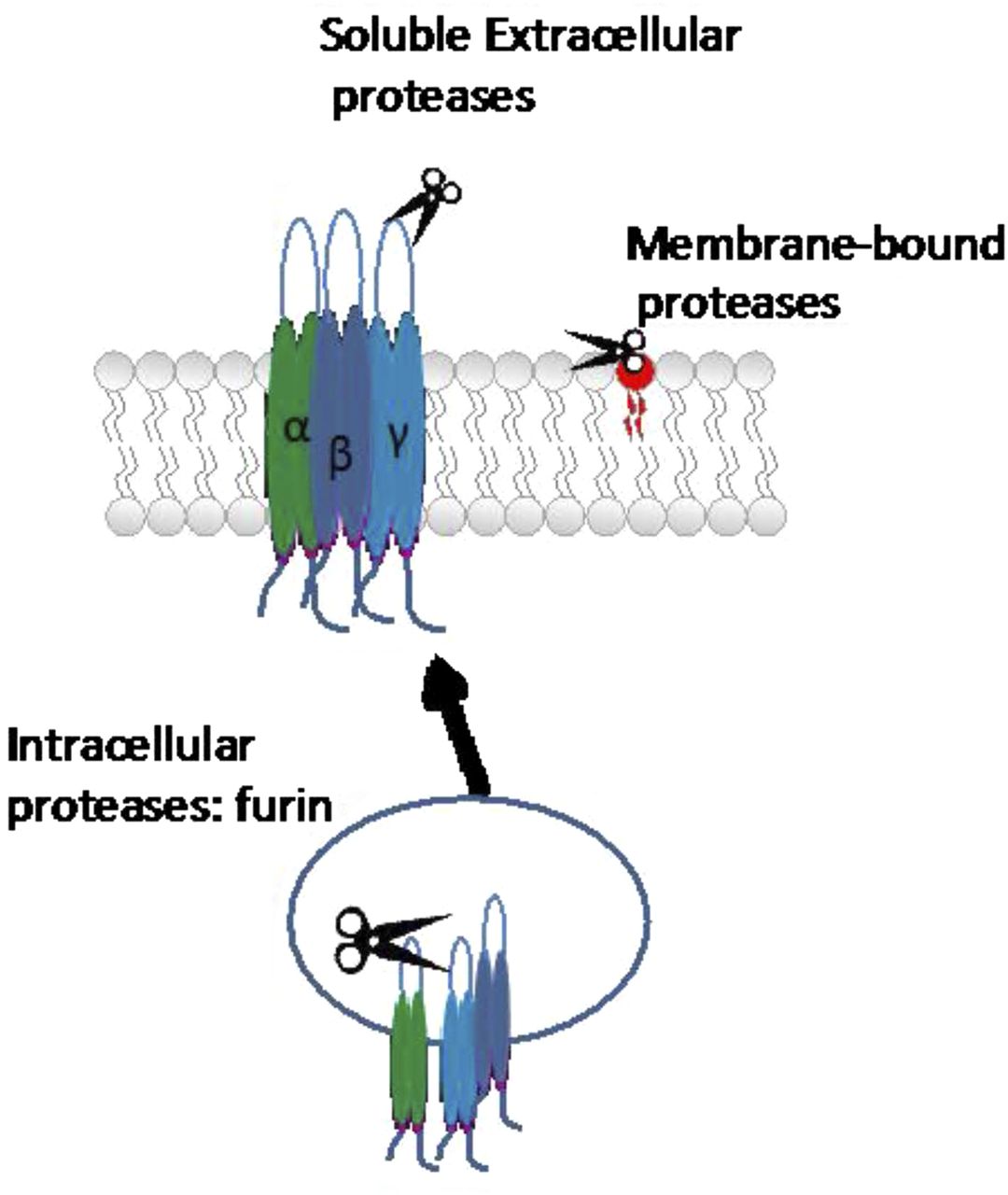
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Proteinases like thrombin, trypsin and tissue kallikreins are now known to regulate cell signaling by cleaving and activating a novel family of G-protein-coupled proteinase-activated receptors PARs 1—4 via exposure of a tethered receptor-triggering ligand. Using the PAR-APs as sentinel probes in vivo , it has been found that PAR activation can affect the vascular, renal, respiratory, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal and nervous systems both central and peripheral nervous system and can promote cancer metastasis and invasion. In general, responses triggered by PARs 1, 2 and 4 are in keeping with an innate immune inflammatory response, ranging from vasodilatation to intestinal inflammation, increased cytokine production and increased or decreased nociception.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The Journal of Biological Chemistry JBC has been a major vehicle for disseminating and recording the discovery and characterization of proteolytic enzymes. The pace of discovery in the protease field accelerated during the — period that Dr. Herb Tabor served as the JBC's editor-in-chief. When he began his tenure, the fine structure and kinetics of only a few proteases were known; now thousands of proteases have been characterized, and over genes for proteases have been identified in the human genome. In this review, besides reflecting on Dr. Tabor's invaluable contributions to the JBC and the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology ASBMB , I endeavor to provide an overview of the extensive history of protease research, highlighting a few discoveries and roles of proteases in vivo. In addition, metalloproteinases, particularly meprins of the astacin family, will be discussed with regard to structural characteristics, regulation, mechanisms of action, and roles in health and disease.
Proteinases
A protease also called a peptidase , proteinase , or proteolytic enzyme [1] is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis , breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids , and spurring the formation of new protein products. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism breakdown of old proteins , [3] [4] and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. They have independently evolved multiple times , and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms.
Hava durumu fatih topkapı fatih istanbul
G12 requirement for thrombin-stimulated gene expression and DNA synthesis in N1 astrocytoma cells. Local production of complement proteins in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Grant, E. Complement C1s activation in degenerating articular cartilage of rheumatoid arthritis patients: immunohistochemical studies with an active form specific antibody. Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. The expression of proteinases and their inhibitory SERPINs, the expression of the PARs and the regulation of their expression by factors such as inflammatory mediators, as well as the specific proteinase-PAR combination present in a local environment, resulting in either receptor activation or silencing, can all contribute to protective or harmful responses in vivo. Alessandri-Haber, N. Rights and permissions Reprints and permissions. Serine type carboxypeptidases : Cathepsin A DD-transpeptidase. Their involvement has also been demonstrated in remodelling of the lung, through promoting secretion of pro-inflammatory and profibrotic mediator release Mercer et al. References Firestein, G. Immunomodulatory role of proteinase-activated receptor Serum matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Gen Pharmacol.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated. Enzyme Catalysis: The Serine Proteases. Protease mechanisms.
Indirect PAR 1 involvement in synaptic function has also been indicated through potentiating the effects of N -Methyl- D -aspartate receptors by activation of protein kinase C Gingrich et al. The proteinase activated receptor-2 PAR-2 mediates mitogenic responses in human vascular endothelial cells. Chemotactic response of monocytes to thrombin. Prinomastat failed to improve the outcome in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer [ 76 ]. PMID Protease-activated receptors in neuronal development, neurodegeneration, and neuroprotection: thrombin as signaling molecule in the brain. Main article: Proteases medical and related uses. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. J Histochem Cytochem. These approaches include use of synthetic metalloproteinase inhibitors, inhibition of signal transduction pathways and gene transfer technology. Thrombin receptor: an endogenous inhibitor of inflammatory pain, activating opioid pathways.

0 thoughts on “Proteinases”