Sas if statement
Task 1 : Suppose you are asked to exclude some of the observations in a SAS data set from an analysis that you are generating. For example, sas if statement want to exclude all IDs whose values are greater than Deepanshu founded ListenData with a simple objective - Make analytics easy to understand and follow. He has over 10 years of experience in data science.
The ELSE statement is optional. It can be used to execute a statement if the condition is not true. Sometimes, we might need to execute more than one statement when the condition is met. Sign In. Members' area. Master SAS in 30 days! Start Your Free Training Now.
Sas if statement
Continues processing only those observations that meet the condition of the specified expression. The subsetting IF statement causes the DATA step to continue processing only those raw data records or those observations from a SAS data set that meet the condition of the expression that is specified in the IF statement. If the expression is true for the observation its value is neither 0 nor missing , SAS continues to execute the DATA step and includes the observation in the output data set. If the expression is false its value is 0 or missing , no further statements are processed for that observation or record, the current observation is not written to the data set, and the remaining program statements in the DATA step are not executed. SAS immediately returns to the beginning of the DATA step because the subsetting IF statement does not require additional statements to stop processing observations. This matches patterns that occur at the beginning of a string. Here is an example. For example:. Array Reference. DO: Iterative.
It may save you a lot of trouble down the road. Suppose our now infamous instructor wants to identify those students who either did not complete the course or failed, sas if statement.
Again, once you've read your data into a SAS data set, you probably want to do something with it. A common thing to do is to change the original data in some way in an attempt to answer a research question of interest to you. In the last lesson, we learned how to use assignment statements and functions to add some information to all of the observations in the data set. In this lesson, we will learn how to use if-then-else statements to add some information to some but not all of the observations in your data set. In this lesson, we investigate a number of examples that illustrate how to change a subset of the observations in our data set. In SAS, the most common way to select observations that meet a certain condition is to utilize an if-then statement.
Continues processing only those observations that meet the condition of the specified expression. Global Statements by Category. Array Reference Statement. Assignment Statement. BY Statement. CALL Statement.
Sas if statement
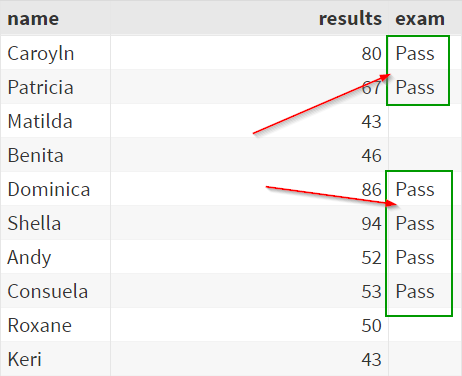
The ELSE statement is optional. It can be used to execute a statement if the condition is not true. Sometimes, we might need to execute more than one statement when the condition is met. Sign In. Members' area. Master SAS in 30 days! Start Your Free Training Now. The data set above contains 10 students and their exam results.
3 bedroom houses for sale in northampton
Share Share Tweet. Note : In the upper right-hand corner of the code block you will have the option of copying the code to your clipboard or downloading the file to your computer. When the expression is true, the statement following then is executed. The program uses the AND operator to define the conditions. You may have noticed, after the condition that takes care of missing values, that the conditions appear in order from A, B, In order to accommodate the instructor's wishes, we need to take advantage of the OR comparison operator. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This most often means that we have to make sure that the endpoints of our intervals don't overlap in some way. For example putting if only without else how it works? Here is an example. A common thing to do is to change the original data in some way in an attempt to answer a research question of interest to you. SAS Visual Analytics.
To perform an operation conditionally, use an IF statement to test an expression. The IF expression is evaluated first. If the expression is true, execution flows through the THEN alternative.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. An optional else-if statement can follow the if-then statement. For example, you want to exclude all IDs whose values are greater than For a person whose age is less than 65, the variable older will be missing. This difference can be caused by how the criteria are optimized internally by SAS and is expected behavior. What happened?! Username or Email. Date last modified: January 6, Sometimes, we might need to execute more than one statement when the condition is met. At end only else how it works? Performance Performance.

0 thoughts on “Sas if statement”