Soft tissue density lesion meaning
Soft tissue tumors, which are also called soft tissue masses, can be found anywhere in the body. Here are 10 important things you need to know about soft tissue tumors. You may be asking yourself, what is a soft tissue mass or tumor? A tumor in your soft tissue means that some fat, muscle, or other non-bone cells have multiplied in number more than they should have, soft tissue density lesion meaning.
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI is far superior to computed tomography CT for the visualization of soft tissue pathology because of greater soft tissue contrast and an overall improved tissue characterization based on signal behavior on different pulse sequences and relaxation parameters. Compared with MRI, CT is more sensitive for the diagnosis of both tiny soft tissue calcifications and air collections and facilitates differentiation between the two. For CT, the contrast characteristics of soft tissue disease depend on the relative proportions of fat, water, and mineral. Normal muscles are of soft tissue density and are separated from each other by fatty septa. In many muscle diseases, the muscle fibers become necrotic and degenerate or are replaced by fat and connective tissue.
Soft tissue density lesion meaning
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Masses involving the abdominal wall are common in clinical practice and have many etiologies, including tumors and tumor-like lesions. Abdominal wall tumors include primary and secondary tumors, the former of which constitute a heterogeneous group of soft tissue tumors with their own unique spectrum. Tumor-like lesions, such as hernias, are more common and must be distinguished from true tumors. Medical imaging is valuable for discovering, diagnosing, and evaluating the extent of abdominal wall masses. With the increasing application of computed tomography CT and magnetic resonance imaging MRI , determining a diagnosis or narrowing the differential diagnosis is often possible, thus facilitating effective management. In this article, we comprehensively review the spectrum of common abdominal wall masses and present the CT and MRI features of typical cases in our hospital. A systematic stepwise diagnostic approach is also proposed for clinical practice. The abdomen is a very accessible part of the human body, and clinically accessible abdominal masses are particularly common. Some of these lesions arise from abdominal and pelvic organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, gastrointestinal tract, and ovaries, while others manifest in the abdominal wall itself. The abdominal wall anatomy is relatively superficial and hierarchical. The abdominal wall is divided into four major layers: the skin, superficial fascia, deep fascia and enveloped inner muscles, and the peritoneal fascia. A wide variety of masses are derived from the above structural layers, including both true tumors and tumor-like lesions.
The lesions also show homogeneous and moderate enhancement after administration of a contrast agent. Fayad 1, 3. Myositis ossificans progressiva fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva is a rare cause of soft tissue ossification associated with anomalies and hypoplasias of the great toes and thumbs, exostoses, and progressive fusion of primarily the axial skeleton.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Although MRI is the technique of choice for evaluating most soft-tissue masses, CT often provides valuable complementary information. This article provides an overview of the CT evaluation of soft-tissue masses, emphasizing a differential diagnosis based on these CT features. Soft-tissue tumors are defined as mesenchymal proliferations that occur in extraskeletal nonepithelial tissues of the body, excluding the viscera, meninges, and lymphoreticular system [ 1 , 2 ].
Soft tissue lesions strike fear in many pathologists as they are uncommon and may be difficult to diagnose. Malignant soft tissue lesions, i. Sarcomas are malignancies derived from mesenchymal tissue. These include: [1]. These include: [2].
Soft tissue density lesion meaning
Soft tissue tumors, which are also called soft tissue masses, can be found anywhere in the body. Here are 10 important things you need to know about soft tissue tumors. You may be asking yourself, what is a soft tissue mass or tumor? A tumor in your soft tissue means that some fat, muscle, or other non-bone cells have multiplied in number more than they should have. Most of these begin in the fat cells. You have a layer of fat just under your three layers of skin.
Deliberti
Of those who get a lipoma, most only get one. Technique Although the use of older generation scanners is adequate, the advent of advanced MDCT with isotropic resolution data sets allows multiplanar reformatted thin-section images and the creation of 3D CT images to provide comprehensive information about the internal architecture of a mass. Most Are Benign Most tumors of the soft tissue are benign. Hemangioma from head to toe: MR imaging with pathologic correlation. Eur Radiol ; 13 Metastasis to the surgical wound or laparoscopic trocar site and needle-tract seeding after radiofrequency ablation also lead to the formation of abdominal wall metastases Figure Abstract Masses involving the abdominal wall are common in clinical practice and have many etiologies, including tumors and tumor-like lesions. Skeletal Radiol ; 24 In this article, we briefly review technical considerations for performing CT for the evaluation of soft-tissue masses, outline the role that CT plays for the diagnosis of these masses, and delineate what information may be gained for treatment planning. Figure 4.
Federal government websites often end in.
Click the images below to enlarge. Primary tumors in the abdominal wall are almost all soft tissue tumors, except for cancer and melanoma derived from skin, which is easily identified by clinicians. Hemangiomas Hemangiomas are heterogeneous and can be histologically classified as capillary, cavernous, arteriovenous, or venous by the predominant type of vascular channels identified within the lesion. Lipomas are also regarded as the most common tumors affecting the abdominal wall The masses — benign or cancerous — come to clinical attention more quickly when they are located in the arms and legs, as opposed to the chest or abdomen, because less room exists in arms and legs for such masses to be mistaken for other bodily structures. Footnotes Conflicts of Interest : The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. A sprain or hematoma that lasts longer than six weeks merits additional medical scrutiny for the possible presence of a soft tissue tumor. Nodular and proliferative fasciitis occurs in the extremities of adults. Mineralization in musculoskeletal leiomyosarcoma: radiologic—pathologic correlation. Extensive soft tissue gas is seen in the gluteal and obturator internus muscles.

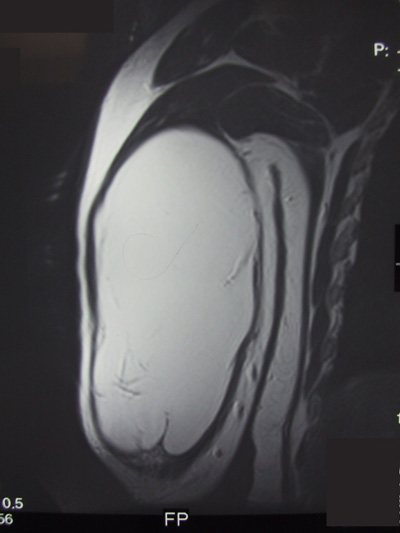
Clearly, many thanks for the information.
At me a similar situation. It is possible to discuss.