Splunk search and
The data for this tutorial is for the Buttercup Games online store. The store sells games and other related items, such as t-shirts.
This topic examines some causes of slow searches and includes guidelines to help you write searches that run more efficiently. Many factors can affect the speed of your searches, including:. To optimize the speed at which your search runs, minimize the amount of processing time required by each component of the search. The recommendations for optimizing searches depend on the type of search that you run and the characteristics of the data you are searching. Searches fall into two types, that are based on the goal you want to accomplish. Either a search is designed to retrieve events or a search is designed to generate a report that summarizes or organizes the data. See Types of searches.
Splunk search and
The Search and Reporting app lets you search your data, create data models and pivots, save your searches and pivots as reports, configure alerts, and create dashboards. This app is provided by default. See Search Reference for syntax, descriptions, and examples for each search command. Get started with Search. About the search language. Understanding SPL syntax. About transforming commands and searches. About real-time searches and reports. Command quick reference. Commands by category. Evaluation functions. Statistical and charting functions. About jobs and jobs management.
Using wildcards 4.
Use the search command to retrieve events from indexes or filter the results of a previous search command in the pipeline. You can retrieve events from your indexes, using keywords, quoted phrases, wildcards, and field-value expressions. The search command is implied at the beginning of any search. You do not need to specify the search command at the beginning of your search criteria. You can also use the search command later in the search pipeline to filter the results from the previous command in the pipeline. The search command can also be used in a subsearch.
Use the search command to retrieve events from indexes or filter the results of a previous search command in the pipeline. You can retrieve events from your indexes, using keywords, quoted phrases, wildcards, and field-value expressions. The search command is implied at the beginning of any search. You do not need to specify the search command at the beginning of your search criteria. You can also use the search command later in the search pipeline to filter the results from the previous command in the pipeline. The search command can also be used in a subsearch. See about subsearches in the Search Manual. After you retrieve events , you can apply commands to transform, filter, and report on the events. Use the vertical bar , or pipe character, to apply a command to the retrieved events. For a list of time modifiers, see Time modifiers for search.
Splunk search and
Examples of how you can use these operators are:. Use the earliest and latest modifiers to specify custom and relative time ranges. Was this documentation topic helpful? Please select Yes No.
Megumin hot
View all products. Splunk Answers. For example: A search such as error stats count will find the number of events containing the string error. Contact Us Contact our customer support. Support Portal Submit a case ticket. Export Search Results. Customer Stories See why organizations around the world trust Splunk. Splunk Lantern Splunk experts provide clear and actionable guidance. Peaks or valleys in the timeline can indicate spikes in activity or server downtime. These are referred to as streaming commands. The final results are returned to the user.
This Search Tutorial is for users who are new to the Splunk platform and the Search app.
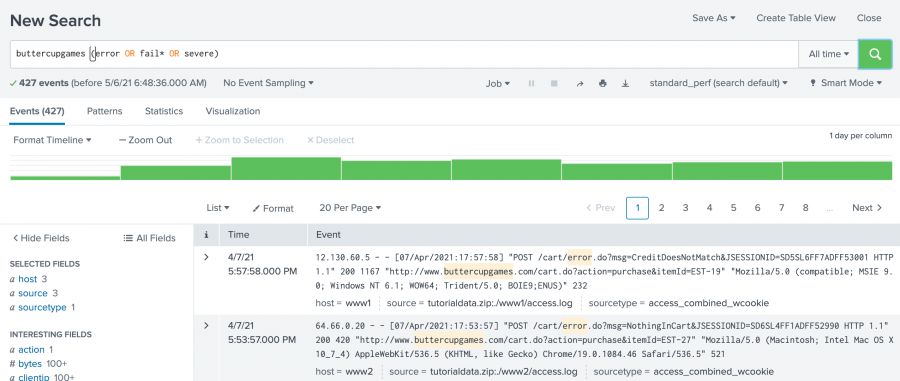
Support Programs Find support service offerings. Part 4: Searching the tutorial data. Community Share knowledge and inspiration. Using wildcards 4. NEXT searchtxn. You can use the TERM directive to force Splunk software to match whatever is inside the parentheses as a single term in the index. By default, the events appear as a list that is ordered starting with the most recent event. You can select other fields to show in your events. These are referred to as streaming commands. Find those three words in any order irrespective of capitalization. For example:. To retrieve events that mention errors or failures, you type the keywords in your search criteria. SPL2 compatibility profiles and quick references. This is recommended for sparse data, which might otherwise be buried in a large volume of unrelated data. Query write amount in KB per day per Indexer by each host.

What matchless topic