Strongest conjugate base is
Post by » Sun Jan 16, pm.
Please do not block ads on this website. So Cl - must be a weak base, it has very little tendency to accept a proton. For example, acetic acid ethanoic acid is a moderately weak acid in aqueous solution. Some of the acetic acid ethanoic acid molecules dissociate in water, producing acetate ions ethanoate ions and protons. Play the game now!
Strongest conjugate base is
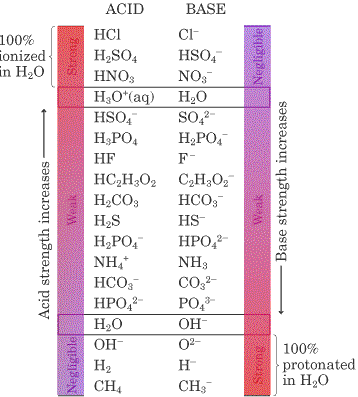
Through examples found in the sections on acids and bases proton-transfer processes are broken into two hypothetical steps: 1 donation of a proton by an acid, and 2 acceptance of a proton by a base. Water served as the base in the acid example and as the acid in the base example [ amphiprotic ]. The hypothetical steps are useful because they make it easy to see what species is left after an acid donated a proton and what species is formed when a base accepted a proton. We shall use hypothetical steps or half-equations in this section, but you should bear in mind that free protons never actually exist in aqueous solution. Suppose we first consider a weak acid , the ammonium ion. When it donates a proton to any other species, we can write the half-equation:. The submicroscopic representations below show the donation of the proton of ammonium. The removal of this proton results in NH 3 , which is easily seen at the submicroscopic level. But NH 3 is one of the compounds we know as a weak base. Another example, this time starting with a weak base, is provided by fluoride ion:.
Footnotes: 1.
.
Calculations and expressions involving K a and p K a were covered in detail in your first-year general chemistry course. Note that acidity constant is also known as the acid dissociation constant. You are no doubt aware that some acids are stronger than others. Sulfuric acid is strong enough to be used as a drain cleaner, as it will rapidly dissolve clogs of hair and other organic material. Acetic acid vinegar , will also burn your skin and eyes, but is not nearly strong enough to make an effective drain cleaner. Water, which we know can act as a proton donor, is obviously not a very strong acid. Even hydroxide ion could theoretically act as an acid — it has, after all, a proton to donate — but this is not a reaction that we would normally consider to be relevant in anything but the most extreme conditions. The relative acidity of different compounds or functional groups — in other words, their relative capacity to donate a proton to a common base under identical conditions — is quantified by a number called the acid dissociation constant , abbreviated K a. The common base chosen for comparison is water. We will consider acetic acid as our first example.
Strongest conjugate base is
The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for an ionization reaction can be used to determine the relative strengths of acids and bases. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is the base ionization constant K b , also called the base dissociation constant:. Once again, the activity of water has a value of 1, so water does not appear in the equilibrium constant expression.
Bang porn stars
I would look for the acid that ionizes the least strong acids ionize completely in water , then proceed from there. Through examples found in the sections on acids and bases proton-transfer processes are broken into two hypothetical steps: 1 donation of a proton by an acid, and 2 acceptance of a proton by a base. Consequently, Cl — is a very weak base. When this isotope of hydrogen loses its electron, what is left is just a proton. Water served as the base in the acid example and as the acid in the base example [ amphiprotic ]. See the tutorial on Acid and Base Definitions. The submicroscopic representations below show the donation of the proton of ammonium. When it donates a proton, a Cl — ion is produced, and so Cl — is the conjugate base. This table enables us to see how readily a given acid will react with a given base. The use of conjugate acid-base pairs allows us to make a very simple statement about relative strengths of acids and bases. CH 3 NH 2 is an amine and therefore a weak base.
See this Socratic answer.
The removal of this proton results in NH 3 , which is easily seen at the submicroscopic level. The reactions with most tendency to occur are between the strong acids in the top left-hand comer of the table and the strong bases in the bottom right-hand comer. Therefore, the weak acid with the "F" is a stronger acid than the one with the "H". When this hydrogen atom loses its electron, the result is a nucleus containing both a proton and a neutron. With CF3COO-, because fluorine is so electronegative, it attracts some of the negative charge on the O-, stabilizing the molecule. The hypothetical steps are useful because they make it easy to see what species is left after an acid donated a proton and what species is formed when a base accepted a proton. Suppose we first consider a weak acid , the ammonium ion. The stronger an acid, the weaker its conjugate base , and, conversely, the stronger a base, the weaker its conjugate acid. In basic salts, the anion is the conjugate base of a weak acid. Play the game now! Adding a proton to the strong base OH — gives H 2 O its conjugate acid. The difference between the other two weak acids is the "F" or "H".

0 thoughts on “Strongest conjugate base is”